| [1]Rogers C.AAOS Supports Research on many Fronts.Am Acad Orthop Sur Bull.2007.[2]Long T,Yang J,Shi SS,et al.Fabrication of three-dimensional porous scaffold based on collagen fiber and bioglass for bone tissue engineering.J Biomed Mater Res Part B Appl Biomater. 2015;103 (7):1455-1464.[3]Wei J,Smith AA,Liu B,et al.Reengineering autologous bone grafts with the stem cell activator WNT3A. Biomaterials. 2015; 47:29-40.[4]Zhou X,Sahai N,Qi L,et al.Biomimetic and nanostructured hybrid bioactive glass. Biomaterials. 2015;50:1-9.[5]Brian Alan F,Nikita K,Anusuya D,et al.Current concepts of bone tissue engineering for craniofacial bone defect repair.Craniom Trau Reconstr.2014;8(1):23-30.[6]Lo H,Kadiyala S,Guggino SE,et al.Poly(L-lactic acid) foams with cell seeding and controlled-release capacity.J Biomed Mater Res Part A.2015;30(4):475-484.[7]Park SM,Kim DS.Electrolyte-assisted electrospinning for a self-assembled, free-standing nanofiber membrane on a curved surface.Adv Mater.2015;7:1682-1687.[8]Harris LD,Kim BS,Mooney DJ.Open pore biodegradable matrices formed with gas foaming. J Biomed Mater Res. 2015;42(3):396-402.[9]Zeltinger J,Sherwood J,Graham D,et al.Effect of pore size and void fraction on cellular adhesion, proliferation, and matrix deposition.Tissue Eng Part A.2001;7(5):557-572.[10]Logeartavramoglou D,Anagnostou F,Bizios R,et al. Engineering bone: challenges and obstacles. J Cell Molecul Med.2010;9(5):72-84.[11]Ji W,Sun Y,Yang F,et al. Bioactive Electrospun Scaffolds Delivering Growth Factors and Genes for Tissue Engineering Applications.Pharma Rese.2011;28(6):1259-1272.[12]Pham QP,Sharma U,Mikos AG.Electrospun poly(epsilon-caprolactone) microfiber and multilayer nanofiber/microfiber scaffolds: characterization of scaffolds and measurement of cellular infiltration.Biomacromolecules. 2006;7(10):2796-2805.[13]Tuzlakoglu K,Bolgen N,Salgado AJ,et al.Nano-and micro-fiber combined scaffolds: A new architecture for bone tissue engineering.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2005;16(12):1099-1104.[14]Cotí KK,Belowich ME,Monty L,et al.Mechanised nanoparticles for drug delivery.Nanoscale. 2009;1(1):16-39.[15]Guo G,Fu S,Zhou L,et al.Preparation of curcumin loaded poly(ε-caprolactone)-poly(ethylene glycol)-poly (ε-caprolactone) nanofibers and their in vitro antitumor activity against Glioma 9L cells.Nanoscale. 2011;3(9):3825-3832.[16]Zhou S,Deng X,Yang H.Biodegradable poly(-caprolactone)-poly(ethylene glycol) block copolymers: characterization and their use as drug carriers for a controlled delivery system.Biomaterials. 2003;24:3563-3570.[17]Xie J,MacEwan MR,Schwartz AG,et al.Electrospun nanofibers for neural tissue engineering. Nanoscale. 2010; 2(1):35-44.[18]Zhang D,Tong A,Zhou L,et al.Osteogenic differentiation of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells (PMSCs) on electrospun nanofiber meshes.Cytotechnology. 2012; 64(6):701-710.[19]Fu N,Liao J,Lin S,et al.PCL-PEG-PCL film promotes cartilage regeneration in vivo.Cell Prolif.2016;49(6):729-739.[20]Lutolf MP,Hubbell JA.Synthetic biomaterials as instructive extracellular microenvironments for morphogenesis in tissue engineering. Nat Biotechnol.2005;23(1):47.[21]Kim SS,Sun Park M,Jeon O,et al. Poly(lactide-co-glycolide)/ hydroxyapatite composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering.Biomaterials.2006;27(8):1399-1409.[22]Pittenger MF,Mackay AM,Beck SC,et al.Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999;284 (5411):143-147.[23]Mackenzie TC,Flake AW.Multilineage differentiation of human MSC after in utero transplantation. Cytotherapy. 2001;3(5): 403-405.[24]Kim J,Jeong SY,Ju YM,et al.In vitro osteogenic differentiation of human amniotic fluid-derived stem cells on a poly(lactide- co-glycolide) (PLGA)-bladder submucosa matrix (BSM) composite scaffold for bone tissue engineering. Biomed Mater. 2013;8:014107.[25]Takashi F,Yasutaka A,Ryo F,et al.Runx2 induces osteoblast and chondrocyte differentiation and enhances their migration by coupling with PI3K-Akt signaling.J Cell Biol. 2004;166(1): 85-95.[26]Doherty MJ,Ashton BA,Walsh S,et al.Vascular pericytes express osteogenic potential in vitro and in vivo.J Bone Miner Res.2010;13(5):828-838.[27]Viereck V,Siggelkow H,Tauber S,et al.Differential regulation of Cbfa1/Runx2 and osteocalcin gene expression by vitamin-D3, dexamethasone, and local growth factors in primary human osteoblasts. J Cell Biochem.2002;86(2):348-356. |
.jpg)
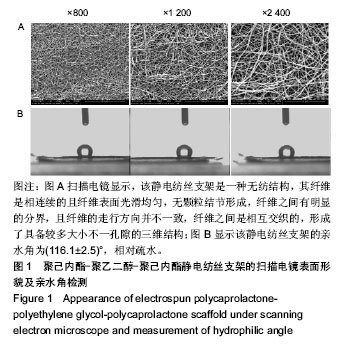
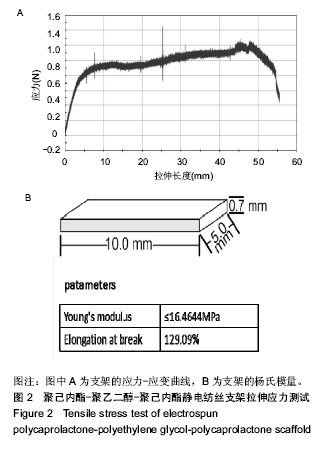
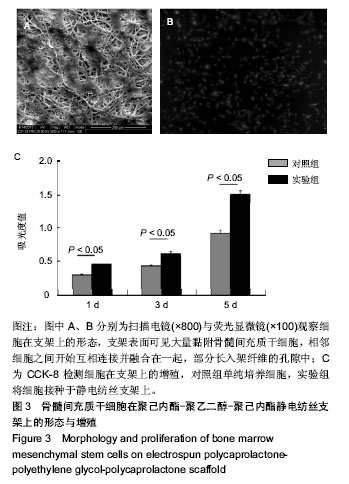
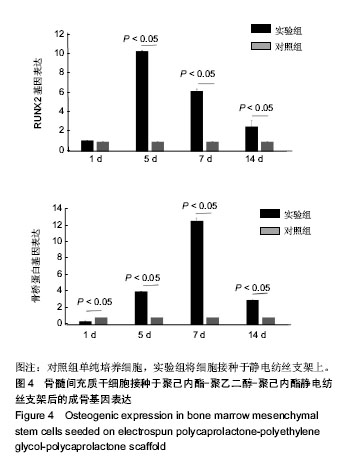
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)