| [1] Kobayashi H, Kikyo N. Epigenetic regulation of open chromatin in pluripotent stem cells. Transl Res.2015;165(1): 18-27.[2] Mueller-Planitz F, Klinker H, Becker PB. Nucleosome sliding mechanisms: new twists in a looped history. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2013;20(9):1026-1032.[3] Schaukowitch K, Kim TK. Emerging epigenetic mechanisms of long non-coding RNAs. Neuroscience. 2014;264:25-38.[4] Rothbart SB, Strahl BD. Interpreting the language of histone and DNA modifications. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1839(8): 627-643.[5] Law JA, Jacobsen SE. Establishing, maintaining and modifying DNA methylation patterns in plants and animals. Nat Rev Genet.2010;11(3):204-220.[6] Lister R, Mukamel EA, Nery JR, et al. Global epigenomic reconfiguration during mammalian brain development. 2013;341(6146):1237905.[7] Shirane K, Toh H, Kobayashi H, et al. Mouse oocyte methylomes at base resolution reveal genome-wide accumulation of non-CpG methylation and role of DNA methyltransferases. PLoS Genet. 2013 ;9(4):e1003439.[8] Deaton AM, Bird A. CpG islands and the regulation of transcription. Genes Dev. 2011;25(10):1010-1022.[9] Smith ZD, Meissner A. DNA methylation: roles in mammalian development. Nat Rev Genet.2013;14(3):204-220.[10] Long HK, Blackledge NP, Klose RJ. ZF-CxxC domain-containing proteins, CpG islands and the chromatin connection. Biochem Soc Trans. 2013;41(3):727-740.[11] Wu H, Zhang Y. Reversing DNA methylation: mechanisms, genomics, and biological functions. Cell .2014;156(1-2): 45-68.[12] Hashimoto K, Otero M, Imagawa K, et al. Regulated transcription of human matrix metalloproteinase 13 (MMP13) and interleukin-1beta (IL1B) genes in chondrocytes depends onmethylation of specific proximal promoter CpG sites. J Biol Chem.2013;288(14):10061-10072.[13] Dansranjavin T, Krehl S, Mueller T, et al. The role of promoter CpG methylation in the epigenetic control of stem cell related genes during differentiation. Cell Cycle 2009;8(6):916-924.[14] Hsiao SH, Lee KD, Hsu CC, et al. DNA methylation of the Trip10 promoter accelerates mesenchymal stem cell lineage determination. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;400(3): 305-312.[15] Thaler R, Agsten M, Spitzer S, et al. Homocysteine suppresses the expression of the collagen cross-linker lysyl oxidase involving IL-6, Fli1, and epigenetic DNA methylation. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(7):5578-5588.[16] Huang H, Sabari BR, Garcia BA, et al. SnapShot: histone modifications. Cell. 2014;159(2):458-458.e1.[17] Lee JS, Smith E, Shilatifard A. The language of histone crosstalk. Cell.2010;142(5):682-685.[18] Greer EL, Shi Y. Histone methylation: a dynamic mark in health, disease and inheritance. Nat Rev Genet.2012;13(5): 343-357.[19] Schuettengruber B, Martinez AM, Iovino N, et al. Trithorax group proteins: switching genes on and keeping them active. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011;12(12):799-814.[20] Voigt P, Tee WW, Reinberg D. A double take on bivalent promoters. Genes Dev. 2013;27(12):1318-1338.[21] Lalonde ME, Cheng X, Cote J. Histone target selection within chromatin: an exemplary case of teamwork. Genes Dev. 2014;28(10):1029-1041.[22] Bannister AJ, Kouzarides T. Regulation of chromatin by histone modifications. Cell Res. 2011;21(3):381-395.[23] Choudhary C,Weinert BT, Nishida Y, et al. The growing landscape of lysine acetylation links metabolism and cell signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol .2014;15(8):536-550.[24] Meyer MB, Benkusky NA, Pike JW. The RUNX2 cistrome in osteoblasts: characterization, down-regulation following differentiation, and relationship to gene expression. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(23):16016-16031.[25] Ito T, Yadav N, Lee J, et al. Arginine methyltransferase CARM1/PRMT4 regulates endochondral ossification. BMC Dev Biol. 2009;9:47.[26] Nimura K, Ura K, Shiratori H, et al. A histone H3 lysine 36 trimethyltransferase links Nkx2-5 to Wolf–Hirschhorn syndrome. Nature.2009;460(7252):287-291.[27] Wei Y, Chen YH, Li LY, et al. CDK1-dependent phosphorylation of EZH2 suppresses methylation of H3K27 and promotes osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2011;13(1):87-94.[28] Hemming S, Cakouros D, Isenmann S, et al.EZH2 and KDM6A act as an epigenetic switch to regulate mesenchymal stem cell lineage specification. Stem Cells .2014;32(3): 802-815.[29] Yang D, Okamura H, Nakashima Y, et al. Histone demethylase Jmjd3 regulates osteoblast differentiation via transcription factors Runx2 and osterix. J Biol Chem.2013; 288(47):33530-33541.[30] Sinha KM, Yasuda H, Zhou X, et al. Osterix and NO66 histone demethylase control the chromatin of Osterix target genes during osteoblast differentiation. J Bone Miner Res .2014; 29(4): 855-865.[31] Takada I, Mihara M, Suzawa M, et al. A histone lysine methyltransferase activated by non-canonical Wnt signalling suppresses PPAR-gamma transactivation. Nat Cell Biol . 2007;9(11):1273-1285.[32] Park E, Kim Y, Ryu H, et al. Epigenetic mechanisms of Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome. Neuromolecular Med. 2014;16(1): 16-24.[33] Rodriguez-Carballo E, Ulsamer A, Susperregui AR, et al. Conserved regulatory motifs in osteogenic gene promoters integrate cooperative effects of canonical Wnt and BMP pathways. J Bone Miner Res.2011;26(4):718-729.[34] Wang CY, Yang SF, Wang Z, et al. PCAF acetylates Runx2 and promotes osteoblast differentiation. J Bone Miner Metab. 2013;31(4):381-389.[35] Campeau PM, Kim JC, Lu JT, et al. Mutations in KAT6B, encoding a histone acetyltransferase, cause Genitopatellar syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 2012;90(2):282-289[36] Bradley EW, Carpio LR, Olson EN, et al. Histone deacetylase 7 (Hdac7) suppresses chondrocyte proliferation and β-catenin activity during endochondral ossification. J Biol Chem.2015; 290(1):118-126.[37] Dudakovic A, Camilleri ET, Lewallen EA, et al. Histone deacetylase inhibition destabilizes the multi-potent state of uncommitted adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells. J Cell Physiol .2015;230(1):52-62.[38] Pham L, Kaiser B, Romsa A, et al. HDAC3 and HDAC7 have opposite effects on osteoclast differentiation. J Biol Chem. 2011; 286(14):12056-12065.[39] Hesse E, Saito H, Kiviranta R, et al. Zfp521 controls bone mass by HDAC3-dependent attenuation of Runx2 activity. J Cell Biol .2010;191(7): 1271-1283.[40] Chen WP, Bao JP, Hu PF, et al. Alleviation of osteoarthritis by Trichostatin A, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, in experimental osteoarthritis. Mol Biol Rep. 2010;37(8):3967-3972.[41] Culley KL, Hui W, Barter MJ, et al. Class I histone deacetylase inhibition modulates metalloproteinase expression and blocks cytokine-induced cartilage degradation. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65(7):1822-1830.[42] Zhang YX, Sun HL, Liang H, et al. Dynamic and distinct histone modifications of osteogenic genes during osteogenic differentiation. J Biochem. 2015;158(6):445-457. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
染色质修饰:染色质化学修饰是指对染色质的组成成分,如DNA、RNA、组蛋白、非组蛋白进行化学基团的添加或去除的反应过程。常见的染色质化学修饰方式有甲基化-去甲基化、乙酰化-去乙酰化、磷酸化-去磷酸化。除此之外,还包括泛素化、ADP-核糖基化和二硫键形成等修饰方式。
组蛋白修饰:真核生物约146 bp的DNA缠绕核心组蛋白八聚体(各两分子的H2A,H2B,H3,H4)构成染色体的基本单位核小体,核小体再通过DNA和组蛋白H1连接构成染色质纤维。组蛋白不仅在染色体组装方面有着重要作用,而且组蛋白翻译后修饰在调控基因动态表达方面也有着重要的作用。组蛋白翻译后修饰多发生在组蛋白的N-端尾部,包括甲基化、乙酰化、磷酸化等修饰,这些修饰有助于其他蛋白质与DNA结合,从而产生协同或者拮抗作用来调控基因转录。
文题释义:
染色质修饰:染色质化学修饰是指对染色质的组成成分,如DNA、RNA、组蛋白、非组蛋白进行化学基团的添加或去除的反应过程。常见的染色质化学修饰方式有甲基化-去甲基化、乙酰化-去乙酰化、磷酸化-去磷酸化。除此之外,还包括泛素化、ADP-核糖基化和二硫键形成等修饰方式。
组蛋白修饰:真核生物约146 bp的DNA缠绕核心组蛋白八聚体(各两分子的H2A,H2B,H3,H4)构成染色体的基本单位核小体,核小体再通过DNA和组蛋白H1连接构成染色质纤维。组蛋白不仅在染色体组装方面有着重要作用,而且组蛋白翻译后修饰在调控基因动态表达方面也有着重要的作用。组蛋白翻译后修饰多发生在组蛋白的N-端尾部,包括甲基化、乙酰化、磷酸化等修饰,这些修饰有助于其他蛋白质与DNA结合,从而产生协同或者拮抗作用来调控基因转录。.jpg) 文题释义:
染色质修饰:染色质化学修饰是指对染色质的组成成分,如DNA、RNA、组蛋白、非组蛋白进行化学基团的添加或去除的反应过程。常见的染色质化学修饰方式有甲基化-去甲基化、乙酰化-去乙酰化、磷酸化-去磷酸化。除此之外,还包括泛素化、ADP-核糖基化和二硫键形成等修饰方式。
组蛋白修饰:真核生物约146 bp的DNA缠绕核心组蛋白八聚体(各两分子的H2A,H2B,H3,H4)构成染色体的基本单位核小体,核小体再通过DNA和组蛋白H1连接构成染色质纤维。组蛋白不仅在染色体组装方面有着重要作用,而且组蛋白翻译后修饰在调控基因动态表达方面也有着重要的作用。组蛋白翻译后修饰多发生在组蛋白的N-端尾部,包括甲基化、乙酰化、磷酸化等修饰,这些修饰有助于其他蛋白质与DNA结合,从而产生协同或者拮抗作用来调控基因转录。
文题释义:
染色质修饰:染色质化学修饰是指对染色质的组成成分,如DNA、RNA、组蛋白、非组蛋白进行化学基团的添加或去除的反应过程。常见的染色质化学修饰方式有甲基化-去甲基化、乙酰化-去乙酰化、磷酸化-去磷酸化。除此之外,还包括泛素化、ADP-核糖基化和二硫键形成等修饰方式。
组蛋白修饰:真核生物约146 bp的DNA缠绕核心组蛋白八聚体(各两分子的H2A,H2B,H3,H4)构成染色体的基本单位核小体,核小体再通过DNA和组蛋白H1连接构成染色质纤维。组蛋白不仅在染色体组装方面有着重要作用,而且组蛋白翻译后修饰在调控基因动态表达方面也有着重要的作用。组蛋白翻译后修饰多发生在组蛋白的N-端尾部,包括甲基化、乙酰化、磷酸化等修饰,这些修饰有助于其他蛋白质与DNA结合,从而产生协同或者拮抗作用来调控基因转录。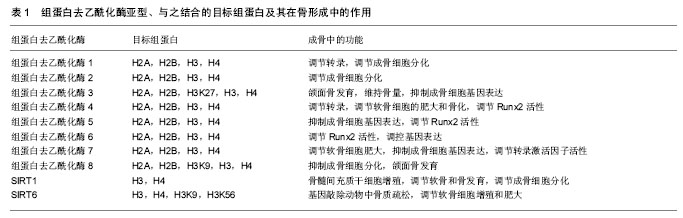
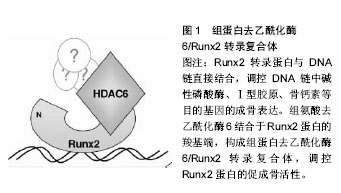
.jpg) 文题释义:
染色质修饰:染色质化学修饰是指对染色质的组成成分,如DNA、RNA、组蛋白、非组蛋白进行化学基团的添加或去除的反应过程。常见的染色质化学修饰方式有甲基化-去甲基化、乙酰化-去乙酰化、磷酸化-去磷酸化。除此之外,还包括泛素化、ADP-核糖基化和二硫键形成等修饰方式。
组蛋白修饰:真核生物约146 bp的DNA缠绕核心组蛋白八聚体(各两分子的H2A,H2B,H3,H4)构成染色体的基本单位核小体,核小体再通过DNA和组蛋白H1连接构成染色质纤维。组蛋白不仅在染色体组装方面有着重要作用,而且组蛋白翻译后修饰在调控基因动态表达方面也有着重要的作用。组蛋白翻译后修饰多发生在组蛋白的N-端尾部,包括甲基化、乙酰化、磷酸化等修饰,这些修饰有助于其他蛋白质与DNA结合,从而产生协同或者拮抗作用来调控基因转录。
文题释义:
染色质修饰:染色质化学修饰是指对染色质的组成成分,如DNA、RNA、组蛋白、非组蛋白进行化学基团的添加或去除的反应过程。常见的染色质化学修饰方式有甲基化-去甲基化、乙酰化-去乙酰化、磷酸化-去磷酸化。除此之外,还包括泛素化、ADP-核糖基化和二硫键形成等修饰方式。
组蛋白修饰:真核生物约146 bp的DNA缠绕核心组蛋白八聚体(各两分子的H2A,H2B,H3,H4)构成染色体的基本单位核小体,核小体再通过DNA和组蛋白H1连接构成染色质纤维。组蛋白不仅在染色体组装方面有着重要作用,而且组蛋白翻译后修饰在调控基因动态表达方面也有着重要的作用。组蛋白翻译后修饰多发生在组蛋白的N-端尾部,包括甲基化、乙酰化、磷酸化等修饰,这些修饰有助于其他蛋白质与DNA结合,从而产生协同或者拮抗作用来调控基因转录。