中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (3): 478-484.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.03.027
• 骨与关节循证医学 evidence-based medicine of the bone and joint • 上一篇 下一篇
髓内钉与锁定接骨板治疗肱骨近端两部分骨折的Meta分析
王 磊1,王凤凤2,马延辉1,张 杰1,呼 芳1,马改平1,刘梅梅1,马张稳1
- 延安大学附属医院,1骨科四病区,2血液免疫科,陕西省延安市 716000
Meta analysis of clinical outcome of intramedullary nails versus locking plates for two-part proximal humerus fracture
Wang Lei1, Wang Feng-feng2, Ma Yan-hui1, Zhang Jie1, Hu Fang1, Ma Gai-ping1, Liu Mei-mei1, Ma Zhang-wen1
- 1Forth Ward, Department of Orthopedics, 2Department of Hematogenic Immunity, Affiliated Hospital of Yan’an University, Yan’an 716000, Shaanxi Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
髓内钉的生物学特性:可控制骨折部位的轴向力线、带锁髓内钉可以防止骨折旋转畸形、降低了内置物断裂的风险;采用闭合及微创技术,减少了手术感染率;减少对骨膜血运的破坏、保留血肿内的有成骨作用的生长因子、扩髓碎屑具有自体植骨效应、肌肉收缩产生微动提供力学刺激等因素促进骨折愈合;中心固定、弹性固定、应力分散避免应力遮挡作用,再骨折发生率低;固定牢固可以早期功能锻炼和负重;内固定取出通过小切口,微创。
锁定钢板:是一种带有螺纹孔的骨折固定装置,这些孔在带有螺纹头的螺钉拧入后,钢板就成为一种(螺钉)角度固定装置。可同时具有锁定和非锁定孔,以供不同螺钉拧入。任何能够拧入角度固定(稳定)的螺钉、栓的钢板实质上都是锁定钢板。
摘要
背景:切开复位钢板内固定及闭合复位髓内钉内固定技术是治疗肱骨近端两部分骨折的常用方法,但对于哪种内固定更好仍然有很大争议。
目的:应用Meta方法分析髓内钉与锁定接骨板治疗肱骨近端2部分骨折的疗效。
方法:通过计算机检索PubMed、SCI、Embase、Cochrane图书馆及中国生物医学数据库、维普信息数据库、万方数据库、中国期刊全文数据库,有关髓内钉与锁定接骨板治疗肱骨近端两部分骨折的随机对照和半随机对照试验,应用RevMan 5.2统计学软件对两种治疗方式的手术时间、术中出血量、骨折愈合时间、术后并发症(异位骨化、内固定疼痛、螺钉切出、肱骨头坏死)、术后肩关节Constant评分等进行Meta分析。
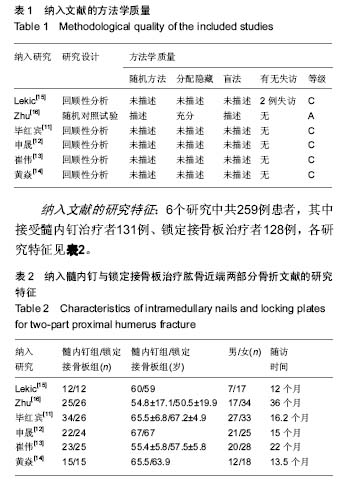
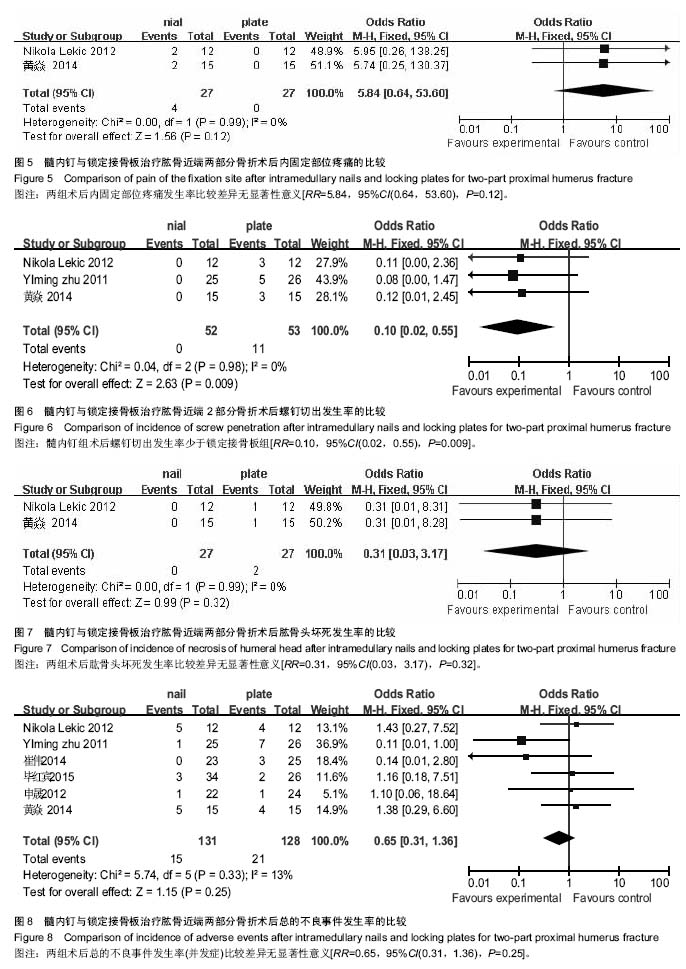
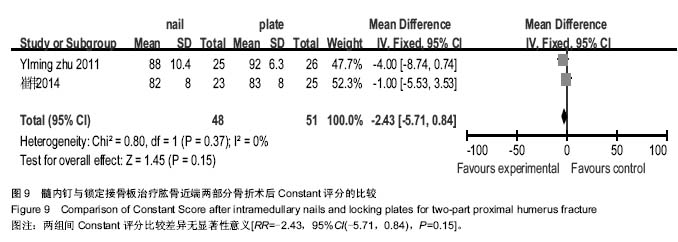
结果与结论:共纳入临床对照试验6个,共259例患者,其中接受髓内钉治疗131例,锁定接骨板治疗128例。Meta分析显示:髓内钉与锁定接骨板治疗肱骨近端两部分骨折的骨折愈合时间、异位骨化并发症发生率、术后内固定部位疼痛发生率、肱骨头坏死发生率、术后总体并发症发生率及术后肩关节Constant评分比较差异无显著性意义,但髓内钉治疗肱骨近端两部分骨折的手术时间、术中出血量、术后螺钉切出率明显少于锁定接骨板治疗(P < 0.05)。结果表明对比锁定接骨板,髓内钉治疗肱骨近端两部分骨折可降低术后螺钉切出率。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-3279-6504(马张稳)
中图分类号:

.jpg)