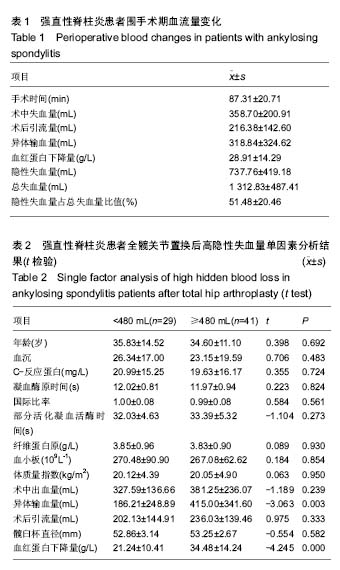
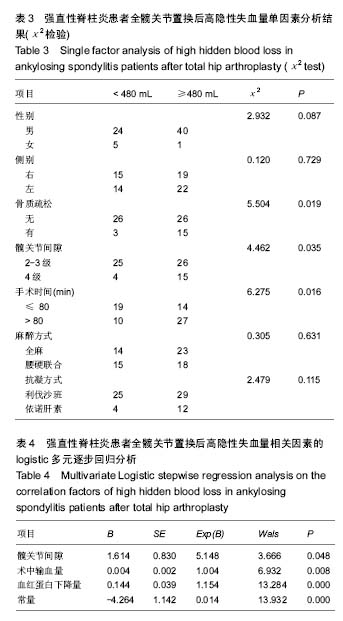
| [1] Soehart DH,Porter ML.Long-term results of total hip replacement in young patients who had ankylosing spondytitis. Eighteen to thirty-year results with survivorship analysis.J Bone Joint Surg (Am).1997;79(8): 1181-1189.[2] Ibn Yacoub Y, Amine B, Laatiris A, et al.Gender and disease features in Moroccan patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Rheumatol. 2012;31(2):293-297.[3] Bangjian H, Peijian T, Ju L.Bilateral synchronous total hip arthroplasty for ankylosed hips. Int Orthop.2012;36(4):697-701.[4] Bhan S, Eachempati KK, Malhotra R.Primary cementless total hip arthroplasty for bony ankylosis in patients with ankylosing spondylitis.J Arthroplasty. 2008;23(6):859-866.[5] Sehat KR,Evans RL,Newman J.HHidden blood loss following hip and knee arthroplasty. Correct management of blood loss should take hidden loss into account. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004;86(4):561-565.[6] Gao F, Sun W, Guo W, et al.Topical Application of Tranexamic Acid Plus Diluted Epinephrine Reduces Postoperative Hidden Blood Loss in Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty.2015;30(12): 2196-200.[7] Liu X, Zhang X, Chen Y, et al.Hidden blood loss after total hip arthroplasty.J Arthroplasty.2011;26(7):1100-1105.e1.[8] Miao K, Ni S, Zhou X, et al.Hidden blood loss and its influential factors after total hip arthroplasty.J Orthop Surg Res.2015;10:36.[9] Tan M, Wu T, Guo J, et al.[HEMOSTASIS EFFECT OF COMPRESSION DRESSING THERAPY AFTER TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi.2016;30(4):416-420.[10] Li J, Zhou Y, Jing J, et al.Comparison of effects of two anticoagulants on hidden blood loss after total hip arthroplasty.Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2013;27(4):432-435.[11] 郑杰,高迪,贾斌,等.老年全髋置换患者术后隐性出血与生存质量关系的对照研究[J].中国中医急症, 2013,07:1135-1136+ 1182.[12] Bell TH, Berta D, Ralley F, et al.Factors affecting perioperative blood loss and transfusion rates in primary total joint arthroplasty: a prospective analysis of 1642 patients. Can J Surg. 2009;52(4):295-301.[13] Zhao J, Li J, Zheng W, et al.Low body mass index and blood loss in primary total hip arthroplasty: results from 236 consecutive ankylosing spondylitis patients.Biomed Res Int.2014;2014:742393.[14] Bowditch MG, Villar RN.Do obese patients bleed more? A prospective study of blood loss at total hip replacement.Ann R Coll Surg Engl.1999;81(3):198-200.[15] 李军,荆珏华,史占军,等. 利伐沙班对全髋关节置换术隐性出血影响的病例对照研究[J].中国骨伤,2014,27(1):34-37.[16] Gao F, Sun W, Guo W,et al.Topical Application of Tranexamic Acid Plus Diluted Epinephrine Reduces Postoperative Hidden Blood Loss in Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty.2015;30 (12): 2196-200. [17] 徐海永,张明,方怀玺,等. 初次全髋关节置换后的隐性失血:影响因素分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(13):1974-1978. [18] Gross JB.Estimating allowable blood loss: corrected for dilution. Anesthesiology.1983;58(3):277-80.[19] Nadler SB, Hidalgo JH, Bloch T. Prediction of blood volume in normal human adults.Surgery. 1962;51(2):224-232.[20] Cherian JJ, Kapadia BH, Issa K,et al Preoperative Blood Management Strategies for Total Hip Arthroplasty.Surg Technol Int.2013;9(30):23-37.[21] Li J, Zhao J, He C, et al.Comparison of Blood Loss After Total Hip Arthroplasty Between Ankylosing Spondylitis and Osteoarthritis.J Arthroplasty.2016;31(7):1504-1509.[22] Meiser A, Casagranda O, Skipka G, et al.[Quantification of blood loss. How precise is visual estimation and what does its accuracy depend on?]. Anaesthesist. 2001;50(1): 13-20. [23] Bao N, Zhou L, Cong Y, et al.Free fatty acids are responsible for the hidden blood loss in total hip and knee arthroplasty.Med Hypotheses.2013;81(1):104-107.[24] Erskine JG, Fraser C, Simpson R, et al. Blood loss with knee joint replacement. J R Coll Surg Edinb.1981;26(5):295-297. [25] McManus KT, Velchik MG, Alavi A, et al.Non invasive assessment of postoperative bleeding in TKA patients wTc 99m RNCs.J Nuclear Med.1987:28(1): 565-567.[26] Kropfl A,Davies J,Berger U,et al.Intramedullary pressure and bone marrow fat extravasation in reamed and unreamed femoral nailing. J Orthop Res.1999;17(2): 261-268.[27] Lakshmanan P,Purushothaman B,Sharma A.Impact of reinfusion drains on hemoglobin level in total knee arthroplasty.Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ).2010;39(2):70-74.[28] Francois RJ,Gardner DL,Degrave EJ,et al.Histopathologic evidence that sacroiliitis in ankylosing spondylitis is not merely enthesitis.Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43(9):2011-2024.[29] 龚科,张琦,董纪元.双侧全膝关节置换术后输血的危险因素分析[J].解放军医学院学报,2016,1:43-46+55.[30] Lawrence VA,Silverstein JH,Cornell JE,et al.Higher Hb level is associated with better early functional recovery after hip fracture repair. Transfusion.2003;43(12):1717-1722. [31] Green D,Lawler M,Rosen M,et al.Recombinant human erythropoietin:Effect on the functional performance of anemic orthopedic patient.Arch Phy Med Rehabil.1996;77(3) : 242-346.[32] Prasad N, Padmanabhan V, Mullaji A. Blood loss in total knee arthroplasty: an analysis of risk factors.Int Orthop. 2007;31(1): 39-44. |
.jpg)
.jpg)