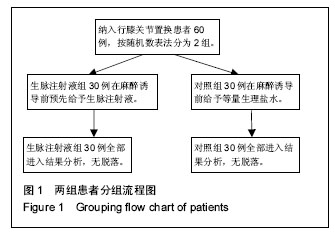
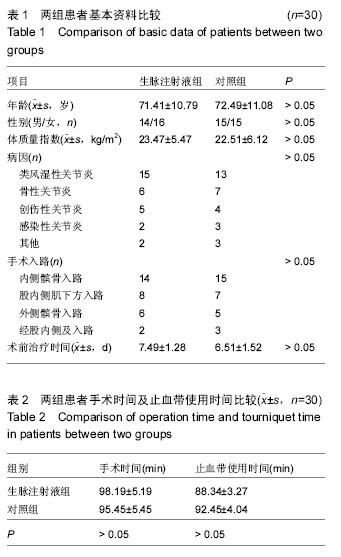
| [1] Brinkman JM, Bubra PS, Walker P, et al.Midterm results using a medial pivot total knee replacement compared with the Australian National Joint Replacement Registry data.ANZ J Surg. 2014;84(3): 172-176.[2] 孙国荣,景克荣,权亚喜,等.生脉注射液对慢性心衰患者心功能及其心率变异性的影响[J].西部中医药,2013,26(4):68-70.[3] Abo-Alhol TR, Fitzpatrick CK, Clary CW, et al.Patellar mechanics during simulated kneeling in the natural and implanted knee.J Biomech. 2014;47(5): 1045- 1051.[4] 鲍航行,王金法,蔡运火,等.全膝关节置换术后止血带性缺血再灌注损伤的临床研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2011, 13(3): 242-246.[5] 张东,李洪祥,陈颖,等.生脉注射液对家兔心肺复苏后多器官功能障碍防治的研究[J].中华急诊医学杂志, 2013, 22(9): 989-993.[6] Beard DJ, Harris K, Dawson J, et al.Meaningful changes for the Oxford hip and knee scores after joint replacement surgery.J Clin Epidemiol. 2015;68(1): 73-79.[7] 刘璇,李正,华声瑜,等.生脉注射液抗大鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤的药理学研究[J].中成药,2015,37(2):251-255[8] 周明武,李琛琪,杨瑞甫,等.兔肢体缺血再灌注损伤骨骼肌细胞Caveolin-3的变化[J].中华显微外科杂志,2014, 37(4): 368-372.[9] 裴强,赵习德,桑文凤,等.参附注射液与生脉注射液治疗慢性心力衰竭的对比研究[J].中成药,2013,35(3):471-475.[10] 宋莹莹.生脉注射液对慢性心力衰竭患者血清IL-1、IL-8、IL-12和IL-18水平的影响[J].中国老年学杂志, 2013, 33(8):1877-1878.[11] Podsiadlo P, Cicuttini FM, Wolski M, et al.Trabecular bone texture detected by plain radiography is associated with an increased risk of knee replacement in patients with osteoarthritis: A 6 year prospective follow up study. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014;22(1): 71-75.[12] Fitzpatrick CK, Rullkoetter PJ. Estimating total knee replacement joint load ratios from kinematics.J Biomech. 2014;,47(12):3003-3011.[13] 胡蓉.中医药防治心肌缺血再灌注损伤的研究概况[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2009,18(10):1184-1187.[14] 唐帅,徐仲煌,杨宏,等.乌司他丁对双侧全膝关节置换术后患者炎性反应和急慢性疼痛的影响[J].基础医学与临床, 2014,34(4):514-518.[15] Olive DJ,Barrington MJ,Said SA, et al. A randomised controlled trial comparing three analgesia regimens following total knee joint replacement: continuous femoral nerve block, intrathecal morphine or both. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2015;43(4):454-460.[16] Guerra ML, Singh PJ, Taylor NF. Early mobilization of patients who have had a hip or knee joint replacement reduces length of stay in hospital: a systematic review. Clin Rehabil. 2015;29(9):844-854.[17] 詹淑玉,邵青,李正,等.生脉注射液中人参皂苷Rg1,Rb1在心肌缺血大鼠体内的药动学-药效学结合研究[J].中国中药杂志,2014,39(7):1300-1305.[18] 范阜东,陈成,钱军岭,等.生脉注射液在体外循环心肌保护中的作用[J].山东医药,2013,53(4):85-88.[19] 杜景柏,李俊江,徐莺,等.持续生脉注射液静脉注射治疗急性冠脉综合征合并心源性休克的疗效观察[J].中国中西医结合急救杂志,2013,20(5):283-285.[20] 岳燕军,董存元,陈素娟,等.生脉注射液对慢阻肺发作期患者血清BNP、肺功能及氧代谢的影响[J].海南医学,2013, 24(2):225-227.[21] Liu L, Ishijima M, Kaneko H, et al. Disability for daily living is a predictor for joint replacement in patients with end-stage knee osteoarthritis. J Bone Miner Metab. 2014;32(2):192-199.[22] 尹兰英,郝玉苓,王岑,等.生脉注射液对心脏瓣膜置换术丙泊酚全麻患者的心肌保护作用[J].中医杂志,2016,57(8): 686-689.[23] Al-Hadithy N,Patel R, Navadgi B, et al.Mid-term results of the FPV patellofemoral joint replacement.Knee. 2014;21(1):138-141.[24] Engh GA,Sheridan MJ, Ammeen DJ, et al. The Functional Assessment Test: A Method of Evaluating Improvement in Function After Knee Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(4):712-718.[25] van der Veen HC, van Raay JJ. Fracture of an Oxford femoral component: A case report. Knee. 2014;21(1): 325-327.[26] Bosco JA, Alvarado CM, Slover JD, et al. Decreasing Total Joint Implant Costs and Physician Specific Cost Variation Through Negotiation. J Arthroplasty.2014; 29(4):678-680.[27] Singh JA, Lewallen DG. Underlying diagnosis predicts patient-reported outcomes after revision total knee arthroplasty. Rheumatology. 2014;53(2):361-366.[28] Hussain SM, Wang Y, Muller DC, et al. Association between index-to-ring finger length ratio and risk of severe knee and hip osteoarthritis requiring total joint replacement.Rheumatology. 2014;53(7):1200-1207.[29] Amiri S, Masri BA, Anglin C, et al. A method for assessing joint line shift post knee arthroplasty considering the preoperative joint space. Knee. 2014; 21(2):359-363.[30] Singh JA, Lewallen DG. Patient-level improvements in pain and activities of daily living after total knee arthroplasty.Rheumatology. 2014;53(2):313-320.[31] 林丽娜,张圣恭,王万铁,等.生脉注射液对兔肺缺血/再灌注损伤时细胞凋亡的影响[J].中国中西医结合急救杂志, 2007,14(6):361-363.[32] 张海龙,赵丽琴,李民,等.七氟醚预处理对全膝关节置换术患者早期康复的影响[J].临床麻醉学杂志,2015,31(9): 862-865.[33] 杨波,康小琴,赵运,等.生脉注射液对不停跳冠脉搭桥术患者氧代谢的影响[J].陕西中医,2013,34(10):1294-1295.[34] 樊旺哲,宋震坤,吴建民.丹参对骨骼肌缺血再灌注损伤影响机制的研究进展[J].医学综述,2009,14(19): 2994-2996.[35] 孙晓莉,郑雪冰,王蕊,等.生脉注射液对心肺复苏中心肌再灌注损伤的保护作用[J].中国实验诊断学,2015,19(8): 1334-1336.[36] 孙晓莉,郑雪冰,周小煊,等.生脉注射液对心肌缺血再灌注损伤家兔肿瘤坏死因子-α及白细胞介素-8的影响[J].中药药理与临床,2008,24(6):8-10.[37] 刘璇,李正,华声瑜,等.生脉注射液抗大鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤的药理学研究[J].中成药,2015,37(2):251-255.[38] 张晓明.生脉注射液的药理作用机制及临床应用[J].医学综述,2013,19(15):2813-2816.[39] 刘燕君,桂丹,周代伟,等.生脉注射液对失血性休克兔促炎因子肿瘤坏死因子α和IL-6的影响[J].广东医学,2011, 32(1):43-45.[40] 范阜东,陈成,钱军岭,等.生脉注射液在体外循环心肌保护中的作用[J].山东医药,2013,53(4):85-88.[41] Oral E, Neils A, Yabannavar P, et al.The effect of an additional phosphite stabilizer on the properties of radiation cross-linked vitamin e blends of UHMWPE.J Orthop Res. 2014;32(6):757-761.[42] Yang H, Li L, Zhou K, et al. Shengmai injection attenuates the cerebral ischemia/reperfusion induced autophagy via modulation of the AMPK, mTOR and JNK pathways. Pharm Biol. 2016;54(10):2288-2297.[43] Li F, Cheng TF, Dong X, et al. Global analysis of chemical constituents in Shengmai injection using high performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2016;117:61-72. [44] Chen Y, Tang Y, Zhang YC, et al. A metabolomic study of rats with doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy and Shengmai injection treatment. PLoS One. 2015;10(5): e0125209. [45] Jiang LP, Zhao J, Cao YF, et al. The Inhibition of the Components from Shengmai Injection towards UDP-Glucuronosyltransferase. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014;2014:594354. [46] Zhao XP, Kang LY, Tang RM, et al. Strategies and key technologies for risk control and management in quality of Chinese medicine injections based on integrated pharmacology. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2014;39(24):4689-4692. [47] Zhan S, Fan X, Zhang F, et al. A proteomic study of Shengmai injection's mechanism on preventing cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury via energy metabolism modulation. Mol Biosyst. 2015;11(2): 540-548. |
.jpg)
.jpg)