中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (53): 7925-7931.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.53.003
• 人工假体 artificial prosthesis • 上一篇 下一篇
围手术期血液管理与中药八珍汤对老年关节置换后血红蛋白及高凝状态的影响
宋玉成,邓迎杰,刘振锋,梁治权,廖 軍,洪汉刚,方 锐
- 新疆医科大学附属中医医院关节外科,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830000
Perioperative blood management combined with Bazhen Tang improves hemoglobin and hypercoagulability in senile patients after joint replacement
Song Yu-cheng, Deng Ying-jie, Liu Zhen-feng, Liang Zhi-quan, Liao Jun, Hong Han-gang, Fang Rui
- Department of Joint Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
八珍汤:中医方剂名,别名八珍散,为补益剂,具有益气补血之功效。主治气血两虚证。面色苍白或萎黄,头晕耳眩,四肢倦怠,气短懒言,心悸怔忡,饮食减少,舌淡苔薄白,脉细弱或虚大无力。临床常用于治疗病后虚弱、各种慢性病,以及妇女月经不调等属气血两虚者。
高凝状态:指肾病综合征患者由于血中促聚集的和促凝因子均增加,而抗聚集、抗凝和纤溶机制受损,以及静脉瘀血,高脂血症,低蛋白血症,血液浓缩,血液黏滞度增加,激素和利尿剂的使用等原因引起血浆纤维蛋白原水平的增高和纤维蛋白和纤维蛋白原降解产物含量的明显上升等现象,最终使得蛋白C和蛋白S水平多正常或增高,但是其活性降低,从而产生了高凝状态。临床上可使用抗凝药物来改善此状态。
摘要
背景:目前对于围手术期积极采用血液管理措施已是国际骨科领域的普遍方法,而中医药应用结合围手术期血液管理对骨科大手术后血液生化及高凝状态的影响和具体机制国内外报道不多。
目的:结合围术期血液管理措施,评价中药八珍汤对关节置换后老年患者血红蛋白及血液高凝状态的影响。
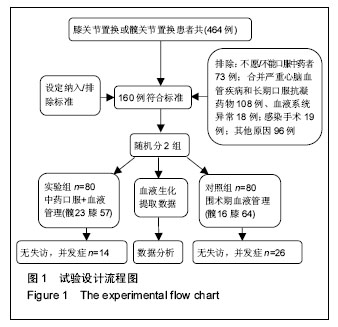
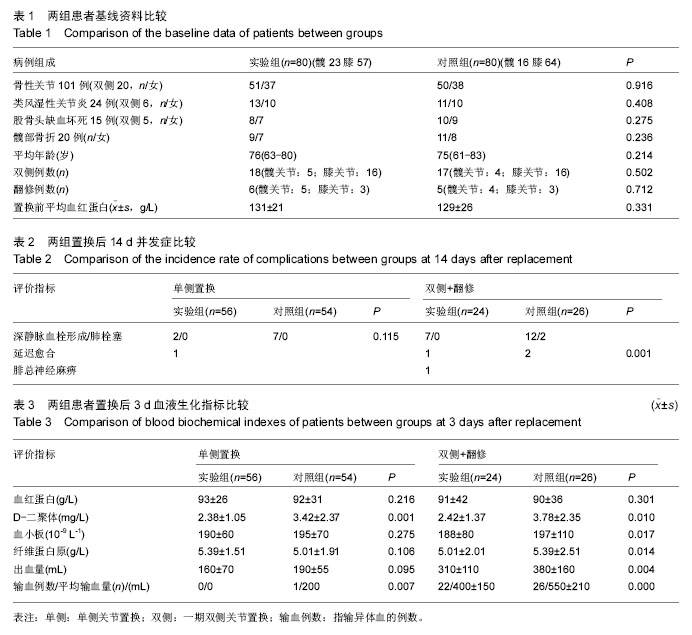
方法:选择接受髋、膝人工关节置换的患者160例,其中全髋关节置换59例;全膝关节置换91例。所有患者按性别、年龄、疾病等随机分为2组各80例,其中行单侧初次关节置换者实验组56例,对照组54例;行双侧一期置换及髋膝翻修者实验组24例,对照组26例。实验组置换前5 d开始加用中药八珍汤加减;对照组不服中药。2组所有病例置换后常规应用利伐沙班抗凝、氨甲环酸减少出血。记录置换后第3,7,14天患者外周血血红蛋白、D-二聚体、血小板、纤维蛋白原含量;记录置换后出血量;彩超观察置换后下肢深静脉血栓形成/肺栓塞发生率。
结果与结论:①单侧初次关节置换对照组有1例,应用异体血回输,双侧及翻修后实验组和对照组均需输异体血,但实验组输血量较少(P < 0.000);②双侧及翻修后7,14 d实验组血红蛋白回升较对照组快(P=0.012;0.003);③置换后3,7 d D-二聚体实验组下降较对照组快,且2组血小板、纤维蛋白原比较差异有显著性意义(P=0.010;0.017;0.014);④实验组置换后下肢深静脉血栓形成9例,无肺栓塞发生;对照组置换后下肢深静脉血栓形成19例,发生肺栓塞2例(转往呼吸ICU治愈),两组并发症比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.001);⑤结果说明,应用中药八珍汤结合围手术期血液管理可能对减少老年患者关节置换后出血,促进双侧或翻修术后血液血红蛋白回升有一定作用,并通过降低D-二聚体及纤维蛋白原含量,抑制血小板聚集,改善老年患者置换后血液高凝状态,从而减少深静脉血栓形成/肺栓塞的发生。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0001-5474-154X(宋玉成)
中图分类号:

.jpg)