| [1]Pang ZP,Yang N,Vierbuchen T,et al.Induction of human neuronal cells by defined transcription factors. Nature.2011;476(7359):220-223.[2]Pfisterer U,Kirkeby A,Torper O,et al.Direct conversion of human fibroblasts to dopaminergic neurons.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(25):10343-10348.[3]Masip M,Veiga A,Izpisúa Belmonte JC,et al. Reprogramming with defined factors: from induced pluripotency to induced transdifferentiation.Mol Hum Reprod.2010;16(11): 856-868.[4]Campbell CE, von Recum AF.Microtopography and soft tissue response. J Invest Surg.1989;2(1): 51-74.[5]Mata A,Boehm C,Fleischman AJ,et al.Growth of connective tissue progenitor cells on microtextured polydimethylsiloxane surfaces.J Biomed Mater Res. 2002;62(4):499-506.[6]Wan Y,Wang Y,Liu Z,et al.Adhesion and proliferation of OCT-1 osteoblast-like cells on micro- and nano-scale topography structured poly(L-lactide).Biomaterials. 2005;26(21):4453-4459.[7]Charest JL,García AJ,King WP.Myoblast alignment and differentiation on cell culture substrates with microscale topography and model chemistries. Biomaterials.2007; 28(13):2202-2210.[8]Uttayarat P,Chen M,Li M,et al.Microtopography and flow modulate the direction of endothelial cell migration.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.2008; 294(2):H1027-1035 .[9]Bettinger CJ, Langer R, Borenstein JT. Engineering substrate topography at the micro‐and nanoscale to control cell function.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl.2009; 48(30):5406-5415.[10]Ghibaudo M,Trichet L,Le Digabel J,et al.Substrate topography induces a crossover from 2D to 3D behavior in fibroblast migration.Biophys J.2009; 97(1):357-368.[11]Kolind K,Dolatshahi-Pirouz A,Lovmand J,et al.A combinatorial screening of human fibroblast responses on micro-structured surfaces.Biomaterials.2010;31(35): 9182-9191.[12]Yim EK,Pang SW,Leong KW.Synthetic nanostructures inducing differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells into neuronal lineage.Exp Cell Res. 2007;313(9): 1820-1829.[13]Engler AJ,Sen S,Sweeney HL,et al. Matrix elasticity directs stem cell lineage specification. Cell. 2006;126 (4):677-689.[14]Nikkhah M,Edalat F,Manoucheri S,et al.Engineering microscale topographies to control the cell-substrate interface.Biomaterials.2012;33(21):5230-5246.[15]Ankam S,Suryana M,Chan LY,et al.Substrate topography and size determine the fate of human embryonic stem cells to neuronal or glial lineage.Acta Biomaterialia.2013;9(1):4535-4545.[16]Chew SY,Low WC.Scaffold‐based approach to direct stem cell neural and cardiovascular differentiation: An analysis of physical and biochemical effects. J Biomed Mater Res A.2011;97(3):355-374.[17]Yang Y,Leong KW.Nanoscale surfacing for regenerative medicine.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol.2010;2(5):478-495.[18]Moe AA,Suryana M,Marcy G,et al.Microarray with micro- and nano-topographies enables identification of the optimal topography for directing the differentiation of primary murine neural progenitor cells.Small.2012; 8(19):3050-3061.[19]Lee MR, Kwon KW, Jung Het al.Direct differentiation of human embryonic stem cells into selective neurons on nanoscale ridge/groove pattern arrays. Biomaterials. 2010;31(15):4360-4366.[20]Xiong Y, Zeng YS, Zeng CG, et al.Synaptic transmission of neural stem cells seeded in 3-dimensional PLGA scaffolds.Biomaterials.2009;30(22):3711-3722.[21]Gao X, Chau YY, Xie J,et al.Regulating cell behaviors on micropillar topographies affected by interfacial energy.RSC Adv.2015;5(29):22916-22922.[22]Li X,Katsanevakis E,Liu X,et al.Engineering neural stem cell fates with hydrogel design for central nervous system regeneration.Prog Polym Sci. 2012;37(8): 1105-1129.[23]Chai C, Leong KW.Biomaterials approach to expand and direct differentiation of stem cells.Molecular Therapy. 2007;15(3):467-480.[24]Christopherson GT, Song H, Mao HQ.The influence of fiber diameter of electrospun substrates on neural stem cell differentiation and proliferation. Biomaterials. 2009;30(4):556-564. |
.jpg)

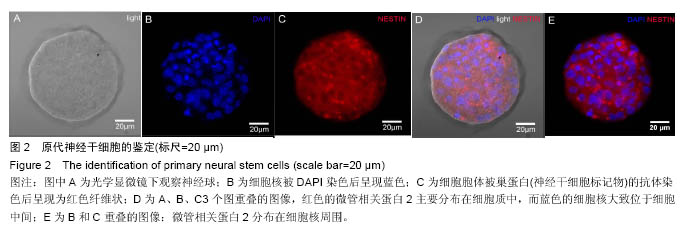
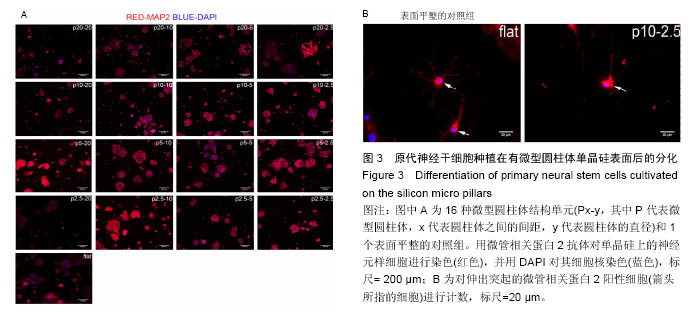
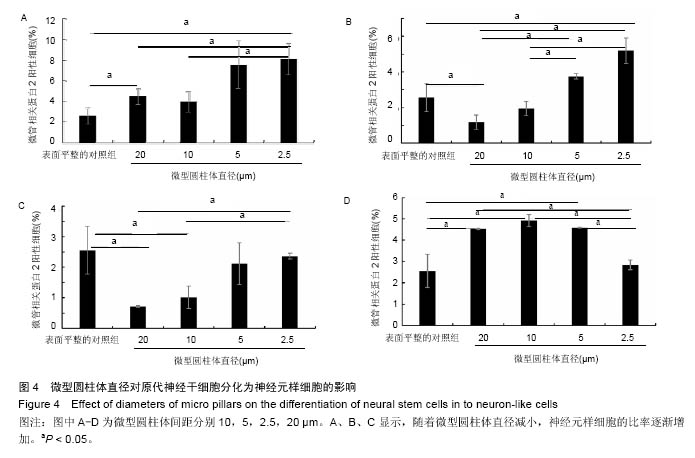
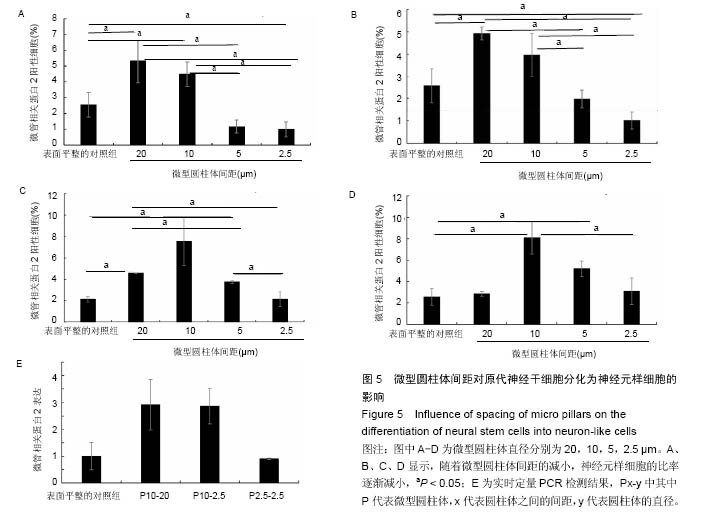
.jpg)
.jpg)