中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (47): 7027-7033.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.47.005
• 组织工程骨及软骨材料 tissue-engineered bone and cartilage materials • 上一篇 下一篇
载三联抗痨药硫酸钙/聚氨基酸人工骨植入脊柱结核病灶内:植骨界面的组织学改变
张 卓1,孙宇航2,耿广起3,施建党3,王自立3,牛宁奎3,马文鑫3,刘海涛3,王 骞4
- 1宁夏自治区人民医院骨科,宁夏回族自治区银川市 750001;2宁夏医科大学,宁夏回族自治区银川市 750004;3宁夏医科大学总医院脊柱骨科,宁夏回族自治区银川市 750004;4美国南弗罗里达大学药学院,美国 33620
Histological changes of the bone-implant interface after calcium sulfate/ polyaminoacid artificial bone carrying triple-anti-tuberculosis drugs is implanted into the spinal tuberculosis focus
Zhang Zhuo1, Sun Yu-hang2, Geng Guang-qi3, Shi Jian-dang3, Wang Zi-li3, Niu Ning-kui3, Ma Wen-xin3, Liu Hai-tao3, Wang Qian4
- 1 Department of Orthopaedics, Ningxia People’s Hospital, Yinchuan 750001, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China; 2Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China; 3Department of Spine Surgery, General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China; 4College of Pharmacy of University of South Florida in U.S, St. Petersburg 33620, U.S
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
药物缓释系统:又称药物控释体系。以一定材料作载体,使药物按设计的剂量,在要求的时间范围内,以一定速度在体内缓慢释放,达到对疾病更有效治疗目的的给药制剂。
氨基酸聚合物:是由α-氨基酸为原料合成的具有强生物活性的聚合物,降解产物为氨基酸、H2O、和其他小分子,对机体无毒副反应,降解产物容易经代谢排出体外。聚氨基酸不同的活性基团不仅提升组织间粘附性,还能便于细胞识别并促进细胞生长。
背景:近年来国内外很多学者致力于脊柱结核病灶的局部药物缓释系统及骨缺损植骨材料的研究,但如何把两者有效结合成为具有药物缓释功能的植骨材料,并且切实观察该材料对疾病治疗效果的研究却较为少见。
目的:观察兔脊柱结核模型病灶清除部位植入载三联抗痨药异烟肼(H)、利福平(R)、吡嗪酰胺(Z)的硫酸钙/聚氨基酸人工骨后植骨界面骨愈合的组织学变化,评价此载药人工骨在兔脊柱结核模型病灶内的植骨融合能力。
方法:将新西兰大白兔36只,随机等分为3组,实验组、对照组为24只建立成功的兔脊柱结核模型,空白对照组为健康兔。实验组植入载三联抗痨药异烟肼、利福平、吡嗪酰胺的硫酸钙/聚氨基酸人工骨;对照组及空白对照组植入未载药硫酸钙/聚氨基酸人工骨。
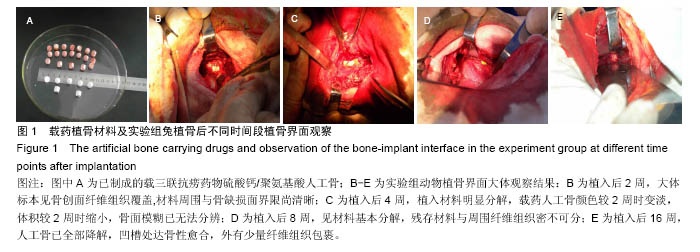
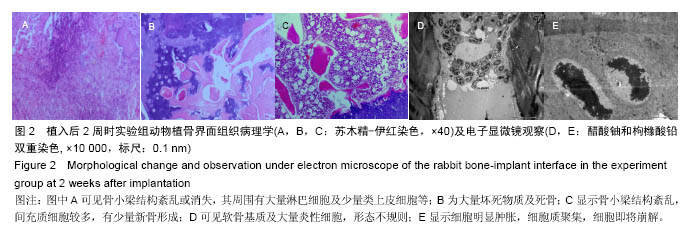
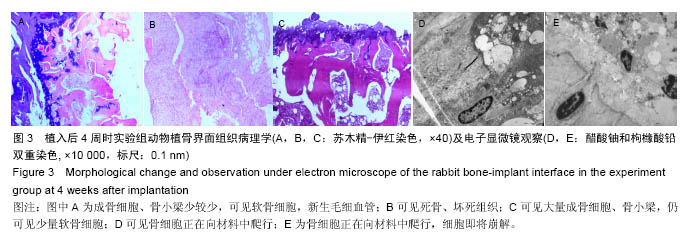
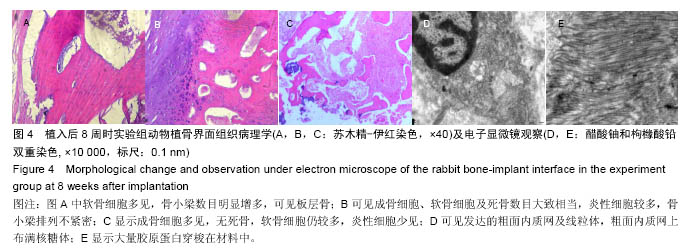
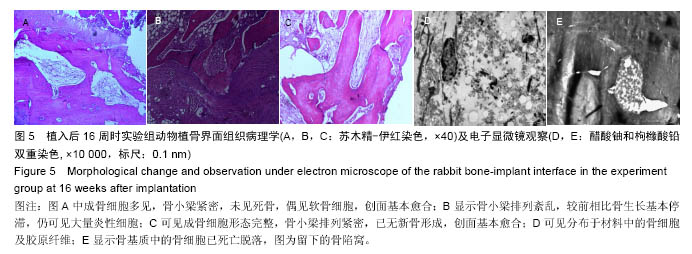
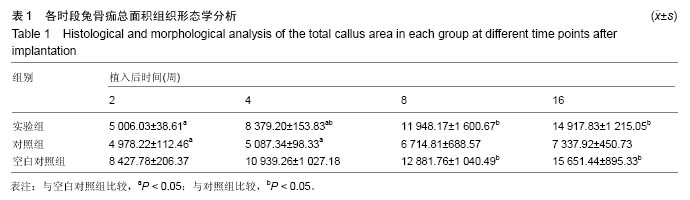
结果与结论:①植骨融合部位的脊柱段组织学变化:苏木精-伊红染色显示,人工骨材料植入后2周时,各组动物体内的载药与非载药硫酸钙/聚氨基酸人工骨均被纤维组织覆盖,并与创面紧密连接,植入后4周时植入材料均已明显分解,植入后8周时植入材料已大部分分解完毕,植入后16周后植骨材料已完全消失。实验组标本中,植入后4周已可见骨痂形成,但骨愈合程度在各阶段均晚于空白对照组。对照组骨愈合出现明显停滞。空白对照组4周可见骨痂形成,已初步连接,16周已基本愈合;②植骨融合部位的脊柱段组织超微结构:透射电镜及扫描电镜观察显示,植入后实验组成骨细胞可通过材料空隙爬行形成新骨;③结果说明:载抗痨药异烟肼、利福平、吡嗪酰胺的硫酸钙/聚氨基酸人工骨植入兔脊柱结核模型病灶清除后的骨缺损部位,载药人工骨在局部有支架作用,在骨缺损区骨细胞能够爬行替代并实现骨界面融合。
中图分类号:
.jpg)