中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (47): 7014-7020.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.47.003
• 组织工程骨及软骨材料 tissue-engineered bone and cartilage materials • 上一篇 下一篇
新型复合壳聚糖季铵盐纳米粒子抗感染骨水泥的生物学特性
贺 强,马建兵,孙相祥,赵光辉
- 西安市红会医院关节外科,陕西省西安市 710054
Biological property of a novel bone cement composited by quaternary ammonium salt chitosan nanoparticles
He Qiang, Ma Jian-bing, Sun Xiang-xiang, Zhao Guang-hui
- Department of Joint Surgery, Xi’an Honghui Hospital, Xi’an 710054, Shaanxi Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
骨水泥:是指是一种用于填充骨与植入物间隙或骨腔并具有自凝特性的生物材料。骨水泥固定可保证置换后假体的即时稳定,在骨组织-骨水泥-假体界面上无任何微动,允许置换后早期负重,疗效肯定。
壳聚糖:是甲壳素脱乙酰基后得到的一种天然碱性多糖,该多糖具有良好的生物活性、生物相容性、生物可降解性以及抗菌防腐等特殊功能,同时不具有肾毒性,不会产生细菌耐药性。
背景:全膝关节置换后假体周围感染一直是关节外科领域很难攻克的问题。对于肾功能不全的患者和抗生素的细菌耐药性问题,现有的抗生素骨水泥不能有效的解决。
目的:研制由壳聚糖季铵盐纳米粒子复合制成,无肾脏毒性和无细菌耐药性的新型抗感染骨水泥。
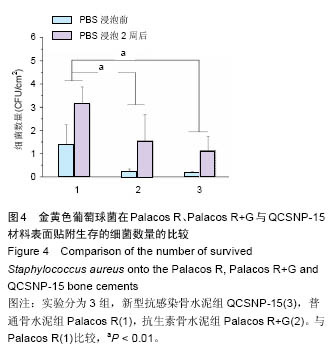
方法:实验分为3组,新型抗感染骨水泥组QCSNP-15,普通骨水泥组Palacos R,抗生素骨水泥组Palacos R+G。分别对各组骨水泥进行扫描电镜观察、骨水泥固化时间测定以及体外抗压强度试验;还进行了细胞毒性实验及体外抗菌实验。
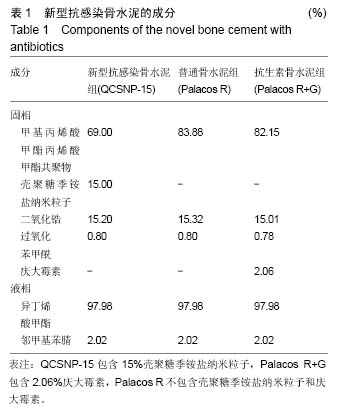
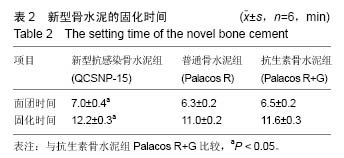
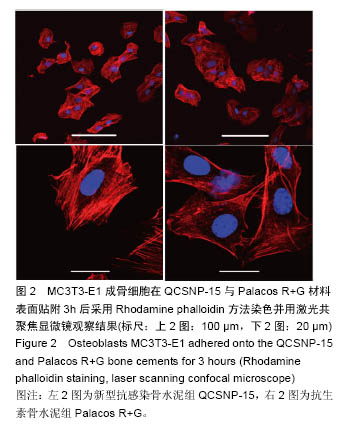
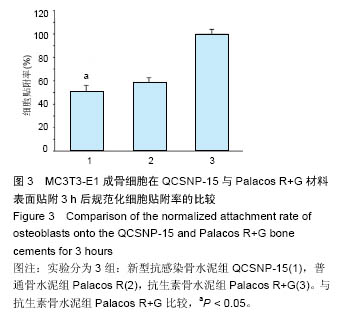
结果与结论:①扫描电镜结果:QCSNP-15材料表面有壳聚糖季铵盐纳米粒子分布;②固化时间: QCSNP-15长于抗生素骨水泥Palacos R+G;③抗压强度:QCSNP-15的抗压强度低于普通Palacos R 骨水泥(P < 0.05),但仍然大于ISO 5833所规定的70 MPa的标准;④材料表面细胞贴附性:MC3T3-E1成骨细胞在新型骨水泥QCSNP-15材料表面贴附良好,与抗生素骨水泥Palacos R+G细胞贴附结果类似,细胞伪足完全展开;⑤细胞毒性:3 h QCSNP-15成骨细胞贴附率低于抗生素骨水泥Palacos R+G(P < 0.05);⑥材料的体外抗菌性:QCSNP-15具有与抗生素骨水泥Palacos R+G相近的抗菌活性,在PBS中浸泡2周后仍然具有一定的抗菌活性;⑦结果说明QCSNP-15具有与抗生素骨水泥相当的固化时间和优良的体外生物力学强度,无明显的细胞毒性,和有优良的体外抗菌活性。
中图分类号:

.jpg)