中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (15): 2197-2205.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.15.010
• 组织构建综述 tissue construction review • 上一篇 下一篇
血管生长细胞因子与股骨头坏死
洪郭驹1,何 伟2,魏秋实2,陈雷雷2
- 1广州中医药大学,广东省广州市 510006;2广州中医药大学第一附属医院,广东省广州市 510407
-
收稿日期:2016-02-01出版日期:2016-04-08发布日期:2016-04-08 -
通讯作者:陈雷雷,博士,主治医师,广州中医药大学第一附属医院,广东省广州市 510407 -
作者简介:洪郭驹,男,1990年生,广东省汕头市人,汉族,广州中医药大学在读硕士,主要从事股骨头坏死基础与临床研究。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(81473697)
Angiogenic factors in osteonecrosis of the femoral head
Hong Guo-ju1, He Wei2, Wei Qiu-shi2, Chen Lei-lei2
- 1 Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China
2 First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510407, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2016-02-01Online:2016-04-08Published:2016-04-08 -
Contact:Chen Lei-lei, M.D., Attending physician, First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510407, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Hong Guo-ju, Studying for master’s degree, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Nature Science Foundation of China, No. 81473697
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程 ORCID: 0000-0003-3587-793X(Chen Lei-lei)
引用本文
洪郭驹,何 伟,魏秋实,陈雷雷. 血管生长细胞因子与股骨头坏死[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2016, 20(15): 2197-2205.
Hong Guo-ju, He Wei, Wei Qiu-shi, Chen Lei-lei. Angiogenic factors in osteonecrosis of the femoral head[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(15): 2197-2205.
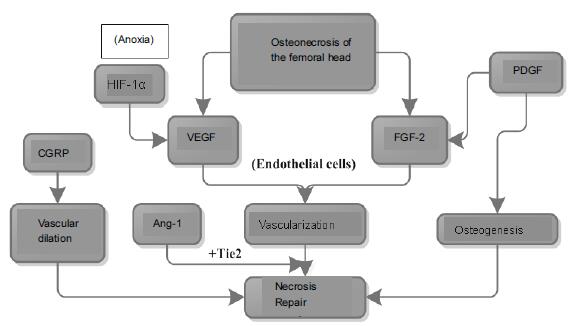
Hypoxia inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α): necrosis and hypoxia
| [1] Seamon J, Keller T, Saleh J, et al. The pathogenesis of nontraumatic osteonecrosis. Arthritis. 2012;2012:601763. [2] Riddle RC, Khatri R, Schipani E, et al. Role of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in angiogenic-osteogenic coupling. J Mol Med (Berl). 2009;87(6):583-590. [3] Semenza GL. HIF-1 and human disease: one highly involved factor. Genes Dev. 2000;14(16):1983-1991. [4] Wenger RH, Rolfs A, Spielmann P, et al. Mouse hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha is encoded by two different mRNA isoforms: expression from a tissue-specific and a housekeeping-type promoter. Blood. 1998;91(9):3471-3480. [5] Wan C, Shao J, Gilbert SR, et al. Role of HIF-1alpha in skeletal development. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1192:322-326. [6] Shomento SH, Wan C, Cao X, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factors 1alpha and 2alpha exert both distinct and overlapping functions in long bone development. J Cell Biochem. 2010;109(1):196-204. [7] Pouysségur J, Dayan F, Mazure NM. Hypoxia signalling in cancer and approaches to enforce tumour regression. Nature. 2006;441(7092):437-443. [8] Wiener CM, Booth G, Semenza GL. In vivo expression of mRNAs encoding hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1996;225(2): 485-488. [9] Li J, Fan L, Yu Z, et al. The effect of deferoxamine on angiogenesis and bone repair in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of rabbit femoral heads. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2015;240(2):273-280. [10] Radke S, Battmann A, Jatzke S, et al. Expression of the angiomatrix and angiogenic proteins CYR61, CTGF, and VEGF in osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Orthop Res. 2006;24(5):945-952. [11] Mazumdar J, Dondeti V, Simon MC. Hypoxia-inducible factors in stem cells and cancer. J Cell Mol Med. 2009;13(11-12):4319-4328. [12] Manalo DJ, Rowan A, Lavoie T, et al. Transcriptional regulation of vascular endothelial cell responses to hypoxia by HIF-1. Blood. 2005;105(2):659-669. [13] Ding H, Gao YS, Hu C, et al. HIF-1α transgenic bone marrow cells can promote tissue repair in cases of corticosteroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head in rabbits. PLoS One. 2013;8(5):e63628. [14] Hong JM, Kim TH, Chae SC, et al. Association study of hypoxia inducible factor 1alpha (HIF1alpha) with osteonecrosis of femoral head in a Korean population. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2007;15(6):688-694. [15] Chachami G, Kalousi A, Papatheodorou L, et al. An association study between hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha (HIF-1α) polymorphisms and osteonecrosis. PLoS One. 2013;8(11):e79647. [16] Hoeben A, Landuyt B, Highley MS, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor and angiogenesis. Pharmacol Rev. 2004;56(4):549-580. [17] Whitlock PR, Hackett NR, Leopold PL, et al. Adenovirus-mediated transfer of a minigene expressing multiple isoforms of VEGF is more effective at inducing angiogenesis than comparable vectors expressing individual VEGF cDNAs. Mol Ther. 2004;9(1):67-75. [18] Varoga D, Drescher W, Pufe M, et al. Differential expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in glucocorticoid-related osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467(12):3273-3282. [19] Suzuki O, Bishop AT, Sunagawa T, et al. VEGF-promoted surgical angiogenesis in necrotic bone. Microsurgery. 2004;24(1):85-91. [20] Bouletreau PJ, Warren SM, Spector JA, et al. Hypoxia and VEGF up-regulate BMP-2 mRNA and protein expression in microvascular endothelial cells: implications for fracture healing. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002;109(7):2384-2397. [21] Wang W, Li S, Niu D. Study on relationship between osteoporosis and mRNA expressions of vascular endothelial growth factor and bone morphogenetic protein 2 in nontraumatic avascular necrosis of femoral head. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2010;24(9):1072-1077. [22] Yang C, Yang SH, Du JY, et al. Basic fibroblast growth factor gene transfection to enhance the repair of avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Chin Med Sci J. 2004;19(2):111-115. [23] Jia Y, Chu TW, Zhou Y, Luo G, et al. Enhancing blood flow of necrotic femoral head by adenovirus hu-VEGF121 transfection in rabbits. Disan Junyi Daxue Xuebao. 2005;27(9):885-887. [24] Kim T, Hong JM, Lee J, et al. Promoter polymorphisms of the vascular endothelial growth factor gene is associated with an osteonecrosis of the femoral head in the Korean population. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2008; 16(3):287-291. [25] Lee YJ, Lee JS, Kang EH, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor polymorphisms in patients with steroid-induced femoral head osteonecrosis. J Orthop Res. 2012;30(1):21-27. [26] Liu B, Cao Y, Wang D, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor -634G/C polymorphism associated with osteonecrosis of the femoral head in a Chinese population. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2012;16(7):739-743. [27] Hong JM, Kim TH, Kim HJ, et al. Genetic association of angiogenesis- and hypoxia-related gene polymorphisms with osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Exp Mol Med. 2010;42(5):376-385. [28] Egger M, Schgoer W, Beer AG, et al. Hypoxia up-regulates the angiogenic cytokine secretoneurin via an HIF-1alpha- and basic FGF-dependent pathway in muscle cells. FASEB J. 2007;21(11):2906-2917. [29] Wang W, Li S, Niu D, et al. Relationship between the bone mass and the expressions of vascular endothelial growth factor, basic fibroblast growth factor, and bone morphogenetic protein 2 mRNA in avascular necrosis of femoral head. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2011;25(8):984-991. [30] Li W, Sakai T, Nishii T, et al. Distribution of TRAP-positive cells and expression of HIF-1alpha, VEGF, and FGF-2 in the reparative reaction in patients with osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Orthop Res. 2009;27(5):694-700. [31] Ingber D. Extracellular matrix and cell shape: potential control points for inhibition of angiogenesis. J Cell Biochem. 1991;47(3):236-241. [32] Moscatelli D, Presta M, Rifkin DB. Purification of a factor from human placenta that stimulates capillary endothelial cell protease production, DNA synthesis, and migration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1986;83(7): 2091-2095. [33] Nakamae A, Sunagawa T, Ishida O, et al. Acceleration of surgical angiogenesis in necrotic bone with a single injection of fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF-2). J Orthop Res. 2004;22(3):509-513. [34] Eppley BL, Connolly DT, Winkelmann T, et al. Free bone graft reconstruction of irradiated facial tissue: experimental effects of basic fibroblast growth factor stimulation. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1991;88(1):1-11. [35] Globus RK, Patterson-Buckendahl P, Gospodarowicz D. Regulation of bovine bone cell proliferation by fibroblast growth factor and transforming growth factor beta. Endocrinology. 1988;123(1):98-105. [36] Li X, Gong Y, Song Y, et al. Study on the effect of composite of basic fibroblast growth factor and partially deproteinized bone on the repair of femoral head defects. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2005;19(3):183-186. [37] Kuroda Y, Akiyama H, Kawanabe K, et al. Treatment of experimental osteonecrosis of the hip in adult rabbits with a single local injection of recombinant human FGF-2 microspheres. J Bone Miner Metab. 2010;28(6): 608-616. [38] Yang C, Yang SH, Du JY, et al. Basic fibroblast growth factor gene transfection to enhance the repair of avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Chin Med Sci J. 2004;19(2):111-115. [39] Shah P, Keppler L, Rutkowski J. A review of platelet derived growth factor playing pivotal role in bone regeneration. J Oral Implantol. 2014;40(3):330-340. [40] Alvarez RH, Kantarjian HM, Cortes JE. Biology of platelet-derived growth factor and its involvement in disease. Mayo Clin Proc. 2006;81(9):1241-1257. [41] Chung R, Foster BK, Zannettino AC, et al. Potential roles of growth factor PDGF-BB in the bony repair of injured growth plate. Bone. 2009;44(5):878-885. [42] Grotendorst GR, Pencev D, Martin GR, et al. Molecular mediators of tissue repair. In: Hunt TK, Heppenstall RB, Pines E, Rovee D, eds. Soft and Hard Tissue Repair. New York: Praeger, 1984:20-40. [43] Grotendorst GR, Martin GR, Pencev D, et al. Stimulation of granulation tissue formation by platelet-derived growth factor in normal and diabetic rats. J Clin Invest. 1985;76(6):2323-2329. [44] Lindahl P, Johansson BR, Levéen P, et al. Pericyte loss and microaneurysm formation in PDGF-B-deficient mice. Science. 1997;277(5323): 242-245. [45] Cao R, Bråkenhielm E, Pawliuk R, et al. Angiogenic synergism, vascular stability and improvement of hind-limb ischemia by a combination of PDGF-BB and FGF-2. Nat Med. 2003;9(5):604-613. [46] Yang M, Khachigian LM, Hicks C, et al. Identification of PDGF receptors on human megakaryocytes and megakaryocytic cell lines. Thromb Haemost. 1997; 78(2):892-896. [47] Pósán E, Szepesi K, Gáspár L, et al. Thrombotic and fibrinolytic alterations in the aseptic necrosis of femoral head. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2003;14(3): 243-248. [48] Cenni E, Fotia C, Rustemi E, et al. Idiopathic and secondary osteonecrosis of the femoral head show different thrombophilic changes and normal or higher levels of platelet growth factors. Acta Orthop. 2011; 82(1):42-49. [49] Lerner UH. Deletions of genes encoding calcitonin/alpha-CGRP, amylin and calcitonin receptor have given new and unexpected insights into the function of calcitonin receptors and calcitonin receptor-like receptors in bone. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2006;6(1):87-95. [50] Fernandez S, Knopf MA, Bjork SK, et al. Bone marrow-derived macrophages express functional CGRP receptors and respond to CGRP by increasing transcription of c-fos and IL-6 mRNA. Cell Immunol. 2001;209(2):140-148. [51] Hoff AO, Catala-Lehnen P, Thomas PM, et al. Increased bone mass is an unexpected phenotype associated with deletion of the calcitonin gene. J Clin Invest. 2002;110(12):1849-1857. [52] Owan I, Ibaraki K. The role of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) in macrophages: the presence of functional receptors and effects on proliferation and differentiation into osteoclast-like cells. Bone Miner. 1994;24(2):151-164. [53] Gibbins IL, Furness JB, Costa M, et al. Co-localization of calcitonin gene-related peptide-like immunoreactivity with substance P in cutaneous, vascular and visceral sensory neurons of guinea pigs. Neurosci Lett. 1985;57(2):125-130. [54] Cao T, Pintér E, Al-Rashed S, et al. Neurokinin-1 receptor agonists are involved in mediating neutrophil accumulation in the inflamed, but not normal, cutaneous microvasculature: an in vivo study using neurokinin-1 receptor knockout mice. J Immunol. 2000;164(10): 5424-5429. [55] Wang L, Wang K, Zhang L, et al. Study on effect of sensory neuropeptide in steroid-induced avascular necrosis of femoral head. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2010;24(9):1078-1081. [56] Wang L, Wang N, Li M, et al. To investigate the role of the nervous system of bone in steroid-induced osteonecrosis in rabbits. Osteoporos Int. 2010;21(12): 2057-2066. [57] Li J, Wang Y, Li Y, et al. The effect of combined regulation of the expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ and calcitonin gene-related peptide on alcohol-induced adipogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014;392(1-2):39-48. [58] Wang YS, Wang YH, Zhao GQ, et al. Osteogenic potential of human calcitonin gene-related peptide alpha gene-modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Chin Med J (Engl). 2011;124(23):3976-3981. [59] Toda M, Suzuki T, Hosono K, et al. Roles of calcitonin gene-related peptide in facilitation of wound healing and angiogenesis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2008;62(6):352-359. [60] Mishima T, Ito Y, Hosono K, et al. Calcitonin gene-related peptide facilitates revascularization during hindlimb ischemia in mice. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011; 300(2):H431-439. [61] Davis S, Aldrich TH, Jones PF, et al. Isolation of angiopoietin-1, a ligand for the TIE2 receptor, by secretion-trap expression cloning. Cell. 1996;87(7): 1161-1169. [62] Schnürch H, Risau W. Expression of tie-2, a member of a novel family of receptor tyrosine kinases, in the endothelial cell lineage. Development. 1993;119(3):957-968. [63] Augustin HG, Koh GY, Thurston G, et al. Control of vascular morphogenesis and homeostasis through the angiopoietin-Tie system. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009; 10(3): 165-177. [64] Jeansson M, Gawlik A, Anderson G, et al. Angiopoietin-1 is essential in mouse vasculature during development and in response to injury. J Clin Invest. 2011;121(6):2278-2289. [65] Homer JJ, Greenman J, Drevs J, et al. Soluble Tie-2 receptor levels independently predict locoregional recurrence in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck. 2002;24(8):773-778. [66] Makinde T, Agrawal DK. Intra and extravascular transmembrane signalling of angiopoietin-1-Tie2 receptor in health and disease. J Cell Mol Med. 2008;12(3):810-828. [67] Thurston G. Complementary actions of VEGF and angiopoietin-1 on blood vessel growth and leakage. J Anat. 2002;200(6):575-580. Park BH, Jang KY, Kim KH, et al. COMP-Angiopoietin-1 ameliorates surgery-induced ischemic necrosis of the femoral head in rats. Bone. 2009;44(5):886-892. |
| [1] | 李中峰, 陈明海, 凡一诺, 魏秋实, 何 伟, 陈镇秋. 右归饮治疗激素性股骨头坏死作用机制的网络药理学分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(8): 1256-1263. |
| [2] | 侯婧瑛, 于萌蕾, 郭天柱, 龙会宝, 吴 浩. 缺氧预处理激活HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA通路促进骨髓间充质干细胞生存和血管再生[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [3] | 耿 瑶, 尹志良, 李兴平, 肖东琴, 侯伟光. hsa-miRNA-223-3p调控人骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [4] | 刘立华, 孙 伟, 王云亭, 高福强, 程立明, 李子荣, 王江宁. 头颈部开窗减压治疗L1型激素性股骨头坏死:单中心前瞻性临床研究[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(6): 906-911. |
| [5] | 刘 钊, 徐西林, 申意伟, 张晓峰, 吕 航, 赵 军, 王政春, 刘旭卓, 王海涛. 塌陷预测方法联合分期分型对股骨头坏死治疗的指导作用与前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(6): 929-934. |
| [6] | 李时斌, 赖 渝, 周 毅, 廖建钊, 章晓云, 张 璇. 激素性股骨头坏死发病机制及相关信号通路的靶点效应[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(6): 935-941. |
| [7] | 刘 波, 陈祥和, 杨 康, 余慧琳, 陆鹏程. DNA甲基化在运动干预骨质疏松中的作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(5): 791-797. |
| [8] | 郑小龙, 何晓铭, 龚水帝, 庞凤祥, 杨 帆, 何 伟, 刘少军, 魏秋实. 酒精性股骨头坏死患者的骨转换特点[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(5): 657-661. |
| [9] | 陈俊毅, 王 宁, 彭称飞, 朱伦井, 段江涛, 王 烨, 贝朝涌. 脱钙骨基质与慢病毒介导沉默P75神经营养因子受体转染骨髓间充质干细胞构建组织工程骨[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(4): 510-515. |
| [10] | 马志杰, 李京育, 曹 放, 刘 蓉, 赵德伟. 多孔碳化硅涂覆生物活性钽新型生物医用材料的影响因素及生物学性能[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(4): 558-563. |
| [11] | 吴子健, 胡昭端, 谢有琼, 王 峰, 李 佳, 李柏村, 蔡国伟, 彭 锐. 3D打印技术与骨组织工程研究文献计量及研究热点可视化分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [12] | 石晓岫, 毛世龙, 刘 洋, 马幸双, 罗彦凤. 钽与钛(合金)骨科材料的差异比较:理化指标及抗菌和成骨能力[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(4): 593-599. |
| [13] | 叶海民, 丁凌华, 孔维豪, 黄祖泰, 熊 龙. 多级微管结构骨支架载体促进成骨成血管作用及机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(4): 621-625. |
| [14] | 李晓壮, 段 浩, 王伟舟, 唐志宏, 王旸昊, 何 飞. 骨组织工程材料治疗骨缺损疾病在体内实验中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [15] | 曾祥洪, 梁博伟. 股骨头坏死保髋治疗的新策略[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(3): 431-437. |
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
Therefore, further explorations are needed in distinguishing angiogenic factors because of their possible functions and other factors which are not included in this review. Large amount of basic studies, including animal experiments and gene research, are required. Moreover, factor-factor and gene-factor interactions should be considered in the future focus, and development in clinical therapeutic techniques will also be an issue of concern. It will provide a new insight into the future studies by establishing the primary mechanisms of angiogenic factors through the inter-pathway regulation.
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
1 此问题的已知信息:股骨头坏死发生率高的原因。这主要由生物力学和解剖学方面的特点来决定的。①负重大:髋关节是人体最大的关节,支撑着整个上半身的重量,而且负重区只占股骨头的1/4,头与臼之间压力较大,长期保持着这种较大的压力,不但容易造成骨结构上的损伤,而且影响局部的血液循环。②剪力大。髋关节不同于其它负重关节那样两骨端关节力线垂直,股骨干与股骨头颈之间形成132°的角,躯干的重力是由髋臼通过股骨头和股骨颈移行至股骨干,力线不垂直,就形成了剪力。因此,头颈所承受的生理压力要比其他关节大得多。③活动范围大。髋关节的活动范围仅次于肩关节,屈曲、后伸、外展、内收、旋转等。活动范围大,损伤的机会也较多。④血供少。股骨头的血供主要依靠囊外动脉环发出的外侧支持带和内侧支持带动脉,血管的吻合支量少且薄弱,当一支血管被阻断而另一支不能及时代偿时,就会造成股骨头的供血障碍,股骨头骨组织失去血液的供养,就形成了缺血性坏死。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||