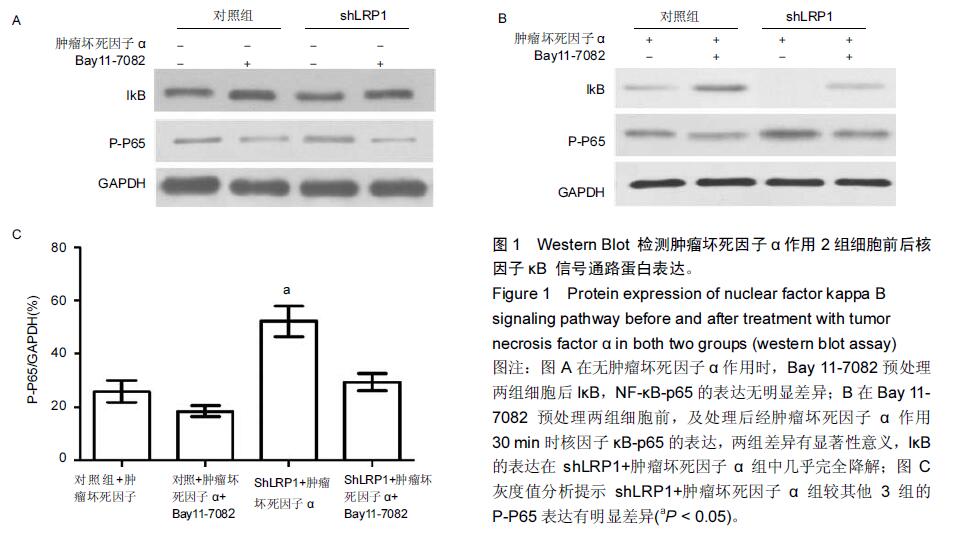
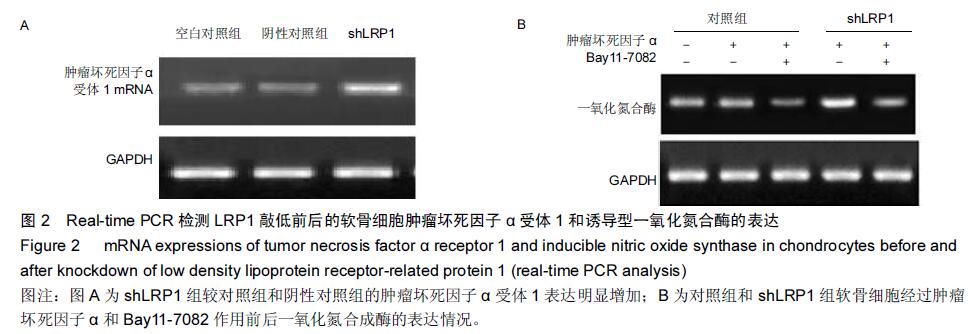
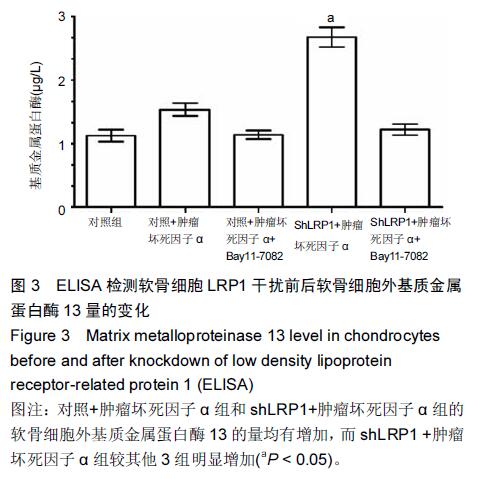
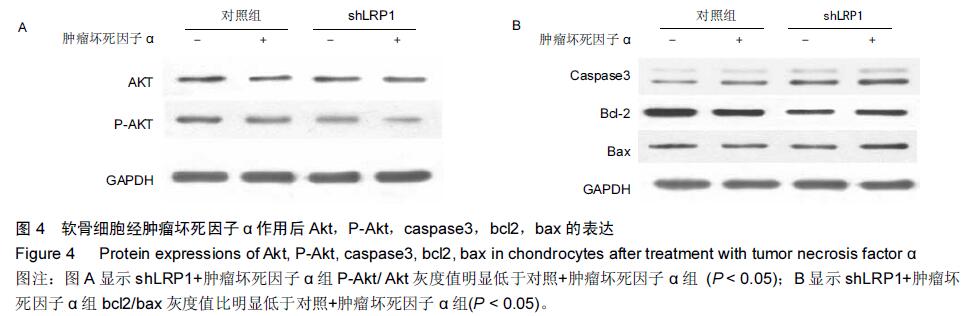
| [1] Goldring MB, Marcu KB.Cartilage homeostasis in health and rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11(3):224. [2] Mengshol JA,Vincenti MP, Coon CI, et al. Interleukin-1 induction of collagenase 3 (matrix metalloproteinase 13) gene expression in chondrocytes requires p38, c-Jun N-terminal kinase,and nuclear factor kappaB: differential regulation of collagenase 1 and collagenase 3. Arthritis Rheum.2000;43:801-811. [3] Zhong Y,Yu W,Feng J, et al. Curcumin suppresses tumor necrosis factor?α?induced matrix metalloproteinase?2 expression and activity in rat vascular smooth muscle cells via the NF?κB pathway.Exp Ther Med.2014;7:1653-1658. [4] Cawston TE, Young DA. Proteinases involved in matrix turnover during cartilage and bone breakdown.Cell Tissue Res.2010;339:221-235. [5] Troeberg L,Nagase H.Proteases involved in cartilage matrix degradation in osteoarthritis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta.2012;1824:133-145. [6] Herz J, Strickland DK. LRP: a multifunctional scavenger and signaling receptor.J Clin Invest. 2001; 108:779-784. [7] Gaultier A, Simon G, Niessen S, et al.LDL Receptor- related Protein 1 Regulates the Abundance of Diverse Cell-signaling Proteins in the Plasma Membrane Proteome.J Proteome Res.2010;9: 6689-6695. [8] Mantuano E,Lam MS,Gonias SL.LRP1 assembles unique co-receptor systems to initiate cell signaling in response to tissue-type plasminogen activator and myelin-associated glycoprotein.J Biol Chem.2013; 288(47):34009-34018. [9] Barmina OY, Walling HW, Fiacco GJ, et al. Collagenase-3 Binds to a Specific Receptor and Requires the Low Density Lipoprotein Receptor-related Protein for Internalization.J Biol Chem.1999;274:30087-30093. [10] Gonias SL,Campana WM.LDL receptor-related protein-1: a regulator of inflammation in atherosclerosis, cancer, and injury to the nervous system. Am J Pathol.2014;184(1):18-27. [11] Gaultier A, Arandjelovic S, Niessen S, et al.Regulation of tumor necrosis factor receptor-1 and the IKK-NF-κB pathway by LDL receptor- related protein explains the antiinflammatory activity of this receptor.Blood. 2008; 111: 5316-5325. [12] Wertz IE.TNFR1-activated NF-κB signal transduction: regulation by the ubiquitin / proteasome system. Curr Opin Chem Biol.2014;12(23):71-77. [13] Raggatt LJ, Jefcoat SC Jr, Choudhury I, et al.Matrix metalloproteinase-13 in?uences ERK signalling in articular rabbit chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage. 2006; 14: 680-689. [14] Manicourt DH, Poilvache P, Van Egeren A, et al. Synovial ?uid levels of tumor necrosis factor alpha and oncostatin M correlate with levels of markers of the degradation of crosslinked collagen and cartilage aggrecan in rheumatoid arthritis but not in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum.2000;43:281-288. [15] Henrotin Y, Kurz B. Antioxidant to treat osteoarthritis: dream or reality? .Curr Drug Targets.2007;8:347-357. [16] Suantawee T, Tantavisut S, Adisakwattana S, et al Upregulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase and nitrotyrosine expression in primary knee osteoarthritis. J Med Assoc Thai. 2015;98 Suppl 1:S91-97. [17] Henrotin Y, Kurz B, Aigner T. Oxygen and reactive oxygen species in cartilage degradation: friends or foes?. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2005;13:643-654. [18] Zhou Y, Liu SQ, Yu L,et al.Berberine prevents nitric oxide-induced rat chondrocyte apoptosis and cartilage degeneration in a rat osteoarthritis model via AMPK and p38 MAPK signaling. Apoptosis.2015;20(9):1187-1199. [19] Mak P, Li J, Samanta S, et al.ERβ regulation of NF-kB activation in prostate cancer is mediated by HIF-1. 2015; 6(37):40247-40254. [20] Chtourou Y, Aouey B, Kebieche M, et al.Protective role of naringin against Cisplatin induced oxidative stress, inflammatory response and apoptosis in rat striatum via suppressing ROS-mediated NF-κB and P53 signaling pathways. Chem Biol Interact.2015;239:76-86. [21] Figueroa F,Motta A,Acosta M,et al.Role of macrophage secretions on rat polycystic ovary: its effect on apoptosis. Reproduction. 2015;150(5):437-448. [22] Hasan SK,Sultana S.Geraniol attenuates 2-acetylaminofluorene induced oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in the liver of wistar rats. Toxicol Mech Methods.2015;25(7):559-573. [23] Chen C,Ma C,Zhang Y,et al.Pioglitazone inhibits advanced glycation end product-induced TNF-α and MMP-13 expression via the antagonism of NF-κB activation in chondrocytes. Pharmacology.2014; 94(5):265-272. [24] Xu L, Sun C, Zhang S, et al. Sam68 Promotes NF-κB Activation and Apoptosis Signaling in Articular Chondrocytes during Osteoarthritis. Inflamm Res. 2015;64(11): 895-902. [25] Graham B,Gibson SB.The two faces of NF-kappaB in cell survival responses. Cell Cycle.2005;4:1342–1345. [26] Karin M,Lin A.NF-kappaB at the crossroads of life and death . Nat Immunol.2002;3:221-227. [27] Luo JJ,Li CY,Liu S, et al. Overexpression of Helicobacter pylori VacA N-terminal fragment induces proinflammatory cytokine expression and apoptosis in human monocytic cell line through activation of NF-κB. Can J Microbiol.2013;59:523-533. [28] Liu X, Xiao Q, Zhao K,et al. Ghrelin inhibits high glucose-induced PC12 cell apoptosis by regulating TLR4/NF-κB pathway. Inflammation.2013;36:1286-1294. [29] Swaminathan JK, Khan M, Mohan IK,et al. Cardioprotective properties of Crataegus oxycantha extract against ischemia–reperfusion injury. Phytomedicine.2010;17:744-752. [30] Cui N,Li S,Zhao X,et al.Expression of Bcl-2, bax and caspase-3 in nerve tissues of rats chronically exposed to 2,5-hexanedione.Neurochem Res.2007;32:1566-1572. [31] Postolow F, Fediuk J, Nolette N,et al.Hypoxia and Nitric Oxide Exposure Promote Apoptotic Signaling in Contractile Pulmonary Arterial Smooth Muscle But Not in Pulmonary Epithelium. Pediatric Pulmonology. 2011; 46:1194-1208. [32] Rath PC,Aggarwal BB.TNF-induced signaling in apoptosis. J Clin Immunol.1999;19: 350 -364. |
.jpg)
.jpg)