中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (49): 7964-7968.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.49.016
• 脑及脊髓损伤动物模型 Animal models of brain and spinal cord injuries • 上一篇 下一篇
X染色体上脆性X智力低下基因1敲除模型小鼠针刺长强穴学习记忆及海马CA1区γ-氨基丁酸A型受体α1亚基表达的影响
吴 强1,陈丽云2,张学君1
- 1福建中医药大学针灸学院,福建省福州市 350122;2福州市中医院,福建省福州市 350001
Effects of acupuncturing Changqiang acupoint on the learning and memory function and gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor alpha1 subunit expression in the hippocampal CA1 region of the fragile X mental retardation 1 located on X chromosome knockout mice
Wu Qiang1, Chen Li-yun2, Zhang Xue-jun1
- 1College of Acupuncture and Massage, Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fuzhou 350122, Fujian Province, China; 2Chinese Medicine Hospital of Fuzhou, Fuzhou 350001, Fujian Province, China
摘要:
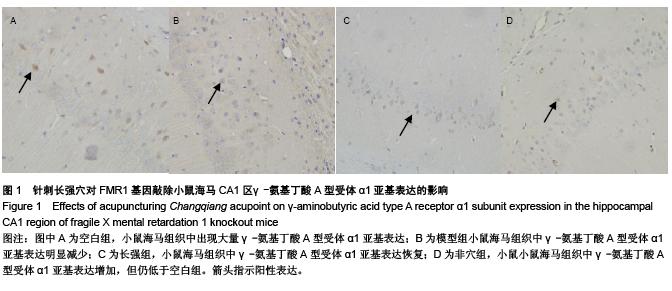
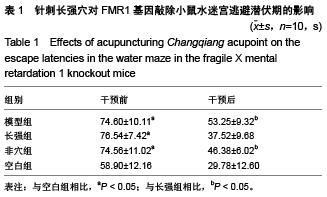
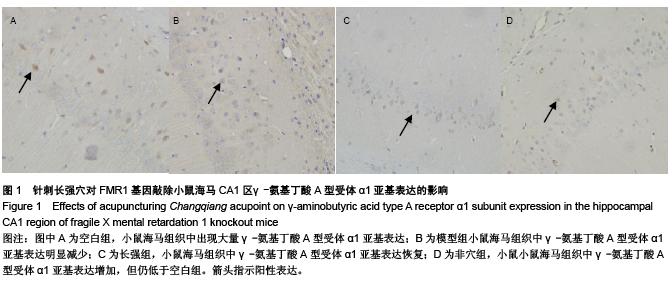
背景:X染色体上脆性X智力低下基因1敲除小鼠海马区γ-氨基丁酸A型受体α1亚基表达低于野生型小鼠。 目的:观察针刺长强穴对X染色体上脆性X智力低下基因1敲除小鼠学习记忆及海马CA1区γ-氨基丁酸A型受体α1亚基表达的影响。 方法:采用X染色体上脆性X智力低下基因1敲除纯合子小鼠雌雄各5只,一雌一雄合笼饲养。所繁殖幼鼠经基因型鉴定为X染色体上脆性X智力低下基因1敲除纯合子小鼠者,随机分为模型组、长强组、非穴组,各10只,另取野生型小鼠10只作为空白组。长强组小鼠采用平补平泻,行提插手法针刺长强穴1 min,频率160-200次/min,1次/d,连续治疗10 d;非穴组刺激小鼠右肋弓最低点上1 cm处;模型组及空白组每日只进行模拟抓取。 结果与结论:与空白组相比,模型组小鼠水迷宫逃避潜伏期明显延长(P < 0.05);而与模型组相比,长强组小鼠水迷宫逃避潜伏期明显缩短(P < 0.05),海马CA1区γ-氨基丁酸A型受体α1亚基表达率增加(P < 0.05);而非穴组小鼠水迷宫逃避潜伏期及海马CA1区γ-氨基丁酸A型受体α1亚基表达率与模型组接近(P > 0.05)。且针刺X染色体上脆性X智力低下基因1敲除小鼠长强穴后其海马CA1区γ-氨基丁酸A型受体α1亚基阳性细胞率与逃避潜伏期呈负相关(r=-0.554,P=0.001)。提示针刺长强穴可改善X染色体上脆性X智力低下基因1敲除小鼠的学习记忆能力,上调γ-氨基丁酸A型受体α1亚基在海马CA1区的表达。
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)