| [1] Fan H, Liu H, Toh SL, et al. Enhanced differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells co-cultured with ligament fibroblasts on gelatin/silk fibroin hybrid scaffold. Biomaterials.2008;29(8): 1017-1027.[2] Pittenger MF, Mosca JD, McIntosh KR. Human mesenchymal stem cells: progenitor cells for cartilage, bone, fat and stroma. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2000;25(1):3-11.[3] Chun-mao H, Su-yi W, Ping-ping L,et al. Human bone marrow- derived mesenc- hymal stem cells differentiate into epidermal- like cells in vitro. Differentiation.2007;75(4):292-298.[4] Orlic D, Kajstura J, Chimenti S, et al. Bone marrow cells regenerate infarcted myocardium. Nature.2001; 410(6829): 701-705.[5] Woodbury D, Schwarz EJ, Prockop DJ.Adult rat and human bone marrow stromal cells differentiate into neurons. J Neurosci Res.2000;61(4):364-370. [6] Mah J. Histochemistry of the foetal human temporo- mandibular joint articular disc. Eur J Orthod.2004;26(4): 359-365.[7] Leonardi R, Lo Muzio L, Bernasconi G, et al. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in human dysfunctional temporomandibular joint discs. Arch Oral Biol.2003;48(3): 185-192.[8] Detamore MS, Hegde JN, Wagle RR, et al.Cell type and distribution in the porcine temporomandibular joint disc. J Oral Maxillofac Surg.2006; 64(2):243-248.[9] 张晓强,李旭,吴涛,等.山羊骨髓间充质干细胞分离培养及向软骨细胞诱导分化[J].南方医科大学学报,2009;29(3):419-422,427.[10] 苏雪莲,包广洁,康宏.碱性成纤维细胞生长因子对骨髓间充质干细胞向颞下颌关节盘细胞分化的影响[J].生物医学工程学杂志, 2012,29(4):732-736.[11] Landesberg R, Takeuchi E, Puzas JE. Cellular, biochemical and molecular characterization of the bovine temporomandibular joint disc. Arch Oral Biol. 1996;41(8-9): 761-767.[12] Detamore MS, Hegde JN, Wagle RR, et al. Cell type and distribution in the porcine temporomandibular joint disc. J Oral Maxillofac Surg.2006;64(2):243-248.[13] Minarelli AM, Liberti EA. A microscopic survey of the human temporomandibular joint disc. J Oral Rehabil.1997; 24(11): 835-840.[14] Mills DK, Fiandaca DJ, Scapino RP. Morphologic, microscopic, and Immunohistochemical investigations into the function of the primate TMJ disc. J Orofac Pain.1994;8(2):136-154.[15] Chin LP, Aker FD, Zarrinnia K. The viscoelastic properties of the human temporomandibular joint disc. J Oral Maxillofac Surg.1996;54(3):315-319.[16] Hirschmann PN, Shuttleworth CA. The collagen composition of the mandibular joint of the foetal calf. Arch Oral Biol, 1976; 21(12):771-773.[17] Willard VP, Kalpakci KN, Reimer AJ, et al. The regional contribution of glycosaminoglycans to temporomandibular joint disc compressive properties. J Biomech Eng. 2012; 134(1): 011011.[18] 柯一凡.动态和静态压力作用对山羊颞下颌关节盘细胞凝胶组织的影响[D].兰州:兰州大学,2010.[19] 王志顺,王江泳,王保芝,等.骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞诱导分化的超微结构改变[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009, 13(1):11-16.[20] 路艳蒙,傅文玉,朴英杰,等,人骨髓间充质干细胞的超微结构[J].电子显微学报,2002, 21(4):373-376.[21] 孙芳菲,张春礼,李小建,等.联合应用生长因子促骨髓间充质干细胞向韧带样细胞分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(10): 1711-1718.[22] 胡杨,马莹,何惠宇,等.骨髓间充质干细胞成骨方向诱导过程中的基因表达[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(49): 9131-9137. [23] 赵基栋,苗宗宁,钱寒光,等.转化生长因子β3诱导骨髓间充质干细胞分化为软骨细胞[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010, 14(40):7497-7500.[24] 牛玉明,胡媛媛,冷卫东,等.碱性成纤维细胞生长因子和地塞米松联合诱导骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖和成骨分化[J].郧阳医学院学报,2010,29(1): 9-11,15,封4. [25] 张云鹏,白希壮,孙羽. BMP-14与bFGF联合诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向软骨分化的实验研究[J].中国医科大学学报,2009,38(12): 898-899,903. [26] 田力,范妮娜,田晓晔,等.骨髓间充质干细胞定向诱导移植修复关节软骨(英文)[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(46): 9041-9044. [27] 蒋柳宏,郑有华,张志光,等. bFGF基因转染对兔骨髓间充质干细胞生物学特性的影响[J].中山大学学报(医学科学版),2009, 30(S2): 41-46.[28] 史德刚,栗国梁,张积仁,等. 重组碱性成纤维细胞生长因子基因转染对于骨髓源性成骨细胞的生物学特性及对血管生成的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(33):6411-6417. [29] 臧业峰,刘亚,邱玉金.兔腰椎融合术中BMP和bFGF对骨髓间充质干细胞的作用[J].潍坊医学院学报,2008,30(6):530-532. [30] 田力,梁晓鹏,田晓晔,等.骨髓间充质干细胞在诱导液条件下向软骨细胞的定向诱导分化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008, 12(38):7495-7498.[31] 张德强,汤欣,张卫国.可吸收性珊瑚羟基磷灰石与人骨髓间充质干细胞诱导成骨细胞复合培养及碱性成纤维细胞生长因子的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(18):3512-3516.[32] 缪黄泰,吴星欣,辛毅,等. 碱性成纤维细胞生长因子体外诱导犬骨髓间充质干细胞向心肌样细胞分化[J].新乡医学院学报,2013, 30(10):777-782.[33] 买霞,陈小义,杨丽颖,等. bFGF通过上调ERK表达诱导BMSCs向神经胶质样细胞分化[J]. 解剖科学进展,2012,18(6):541- 544,548.[34] Khan M,Yamauchi M,Srisawasdi S, et al.Homocysteine decreases chondrocyte- mediated matix mineralizationin differentiating chick limb-bud mensenchymal cell micro-mass cultures. Bone.2001;28(4):387-398. [35] 舒维娜,康宏.山羊颞下颌关节盘细胞透射电镜观察[J].现代口腔医学杂志,2008, 22(6): 612-614. |
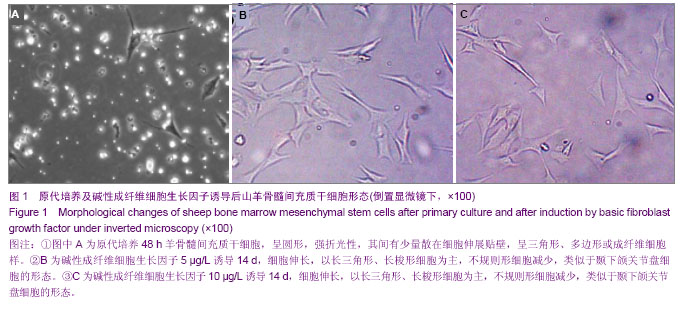
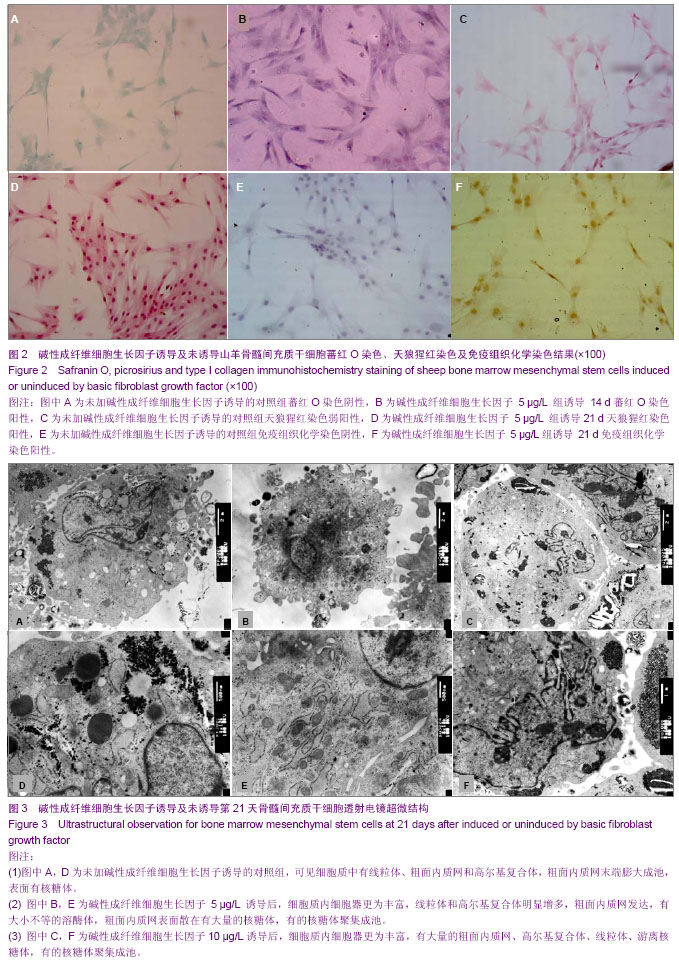
.jpg)