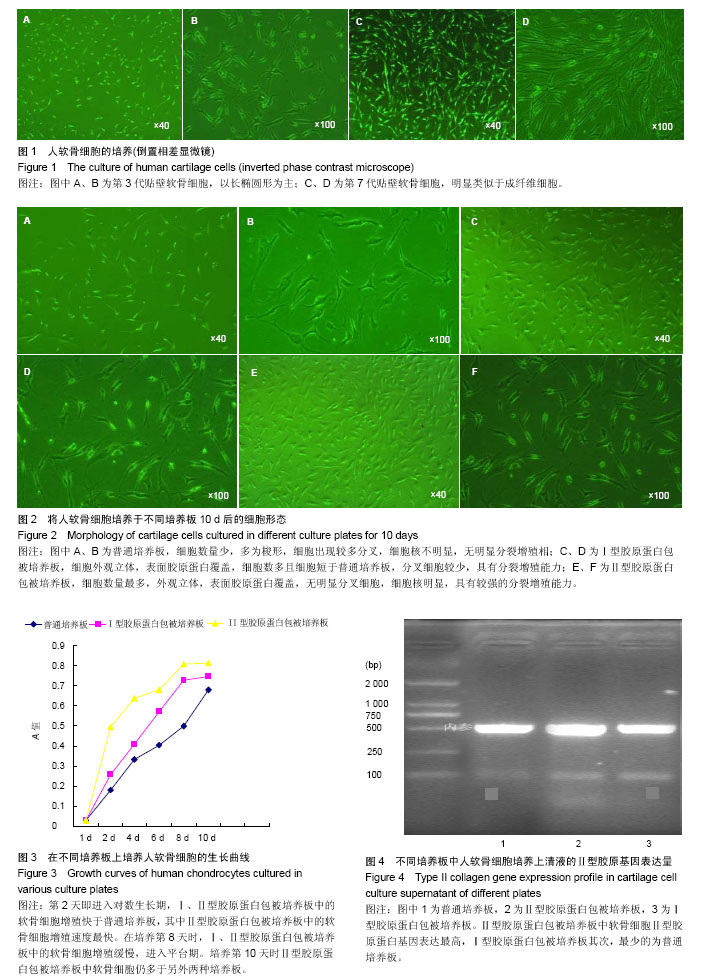
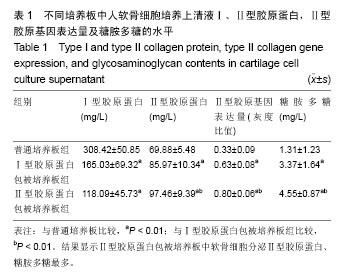
| [1] Brittberg M,Lindahl A,Nilsson A,et al.Treatment of deep cartilage defects in the Knee with autologous chondrocytes transplantation.N Engl J Med. 1994;331(14):889-895.
[2] Kosher RA, Church RL. Stimulation of in vitro somite chondrogenesis by procollagen and collagen. Nature. 1975;258(5533):327-330.
[3] Shouldes MD,Raines RT.Collagen structure and stability.Annu Rev Biochem.2009;78:929-958.
[4] 顾其胜.胶原蛋白的临床应用[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2006, 20(10):1052-1057.
[5] Award H, Butler DL,Boivin GP,et al.Autologous mesenchymal stem cell-mediated repair of tendon.Tissue Eng. 1999;5(3): 267-277.
[6] Wakitani S,Goto T,Young RG,et al.Repair of large fullthickness ar-ticular cartilage defects with all graft articular chondrocytes embedded in a collagen gel.Tissue Eng.1998;4(4):429-444.
[7] Hunter W.Of the structure and diseases of articulating cartilages. Clin orthop Relat Res.1995;(317):3-6.
[8] Schulz RM,Bader A.Cartilage tissue engineering and bioreactor systems for the cultivation and stimulaion of chondrocytes.Eur Biophys J.2007;36(4-5):539-568.
[9] Buckwalter JA,Mankin HJ.Articular cartilage: tissue design and chondrocyte matrix interactions.AAOS Inst Course Lect. 1998;47(3):477-486.
[10] Tew SR,Murdoch AD,Rauchenberg RP,et al.Cellular methods in cartilage research: primary human chondrocytes in culture and chondrogenesis in human bone marrow stem cells. Methods.2008;45(1):2-9.
[11] Outerbridge HK,Outerbridge RE,Smith DE.Osteochondral defects in the knee, A treatment using lateral patella autografts.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2000;37(7):145-151.
[12] Shapiro F,Koide S,Glimcher MJ.Cell origin and differentiation in the repair of full-thickness detects of articular cartilage.J Bone Joint Surg Am .1993;75(4):532-553.
[13] Schulze-Tanzil G,de Souza P,Villegas Castrejon H,et al.Redifferentiation of dedifferentiated human chondrocytes in high-density cultures.Cell Tissue Res. 2002;308(3):371-379.
[14] Watt F. Effect of seeding density on stability of the dedifferentiated phenotype of pig articular chondrocytes in culture.J Cell Sci.1988;89:373-378.
[15] Temenoff JS,Mikos AG.Review: tissue engineering for regeneration of articular cartilage. Biomaterials. 2000;21(3):431-440.
[16] Nerem RM,Sambanis A.Tissue engineering : from biology to biological substitutes.Tissue Eng.1995;1(1):3-13.
[17] Benya PD,Shaffer JD.Dedifferentiated chondrocytes reexpress the differentiated collagen phenotype when cultured in agarose gels.Cell. 1982;30(1):215-224.
[18] Kuriwaka M,Ochi M,Uchio Y,et al.Optimum combination of monolayer and three-dimensional cultures for cartilage-like tissue engineering.Tissue Eng.2003;9(1):41-49.
[19] Pieper JS,Vander Kraan PM,Hafmans T,et al.Crosslinked type II collagen matrices:preparation,characterization,and potential for cartilage ngineering.Biomaterials.2002;23(15):3183-3192.
[20] Van Beuningen HM,Stoop R,Buma P,et al.Phenotypic differences in murine chondrocyte cell lines derived from mature articular cartilage.Osteoarthritis Cartiage. 2002; 10(12): 977-986.
[21] Ushida T,Furukawa K,Toita K,et al.Three-dimensional seeding of chondrocytes encapsulated in collagen gel into PLLA scaffolds.Cell Transplant.2002;11:489-494.
[22] Ma,HL,Hung,SC,Lin SY,Chen YL,et al.Chonderogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells encapsulated in alginate beads.J Biomed Mater Res.2003;64(2):273-281.
[23] Kimura T,Yasui N,Ohsawa S,et al.Chondrocytes embedded in collagen gels maintain cartilage phenotype dur ing long term cultures.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1984;(186):231-239.
[24] Speer DP,Chvapil M,Volz R,et al.Enhancement of healing in osteochondral defects by collagen sponge implants.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1979;(144):326-335.
[25] Ito Y,Ochi M,Adachi N,et al.Repair of osteochondral defect with tissue-engineered chondral plug in a rabbit model. Arthroscopy.2005;21(10):1155-1163.
[26] Darting EM,Athanasiou KA.Retaining zonal chondrocyte phenotype by means of novel growth environments.Tissue Eng.2005;11(3-4):395-403.
[27] Qi WN,Scully SP.Extracelluar collagen regulates expression of transforming growth factorth factor-betal gene.J Orthop Res.2000;18:928-932.
[28] Qi WN,Scully SP.Effect of type II collagen in chondrocyte response to TGF-beta1 regulation.Exp Cell Res. 1998;241(1): 142-150.
[29] Qui W,Scully S.Extracellular collagens demonstrate a type specific influence on cytokine regulation of articular chondrocytes.Proc of the ORS, Atlanta, GA; 1996:308.
[30] Tew SR,Murdoch AD,Rauchenberg RP,et al.Cellular methods in cartilage research: primary human chondrocytes in culture and chondrogenesis in human bone marrow stem cells. Methods.2008;45(1):2-9.
[31] 周强,李起鸿,戴刚.骺板软骨细胞复合三维支架体外构建组织工程软骨的研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2004,18(2):92-95.
[32] 林建华,陈晓东,邓凌霄,等.大鼠软骨细胞复制性老化的体外观察[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2007,21(11):1228-1232.
[33] 周强,李起鸿,戴刚.三步酶消化法高效分离兔原代关节软骨细胞及体外培养观察[J].中华外科杂志,2005,43(8):522-526.
[34] Sandell LJ,Sugai JV,Trippel SB.Expression of collagens Ⅰ, Ⅱ, Ⅹ,and Ⅺ and aggrecan mRNAs by bovine growth plate chondrocytes insitu.J Orthop Res.1994;12(1):1-14.
[35] Miot S,Woodfield T,Daniels AU,et al. Effects of scaffold composition and architecture on human nasal chondrocyte redifferentiation and cartilaginous matrix deposition. Biomaterials.2005;26(15):2479-2489.
[36] 张艳,柴岗,刘伟,等.体外培养过程中去分化的人软骨细胞基因表达谱的变化[J].中华整形外科杂志,2007,23(4):331-334.
[37] Karlsen TA,Shahdadfar A,Brinchmann JE.Human primary articular chondrocytes, chondroblasts-like cells, and dedifferentiated chondrocytes: differences in gene, microRNA,and protein expression and phenotype.Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2011;17(2):219-227.
[38] Binette F,McQuaid DP,Haudenschild,DR,et al.Expression of a stable articular cartilage phenotype without evidence of hypertrophy by adult human articular chondrocytes in vitro.J Orthop Res.1998;16:207-216.
[39] Liu H, Lee YW, Dean,MF. Re-expression of differentiated proteoglycan phenotype by dedifferentiated human chondrocytes during culture in alginate beads.Biochim Biophys Acta.1998;1425:505-515. |