| [1] Sous M, Bareille R, Rouais F, et al. Cellular biocopatibility and resistance compression of macroporous beta-tricalcium phosphate ceramics. Biomaterials.1998;19(23): 2147- 2153.
[2] Ganeles J,Listgarten MA,Evian CI. Ultrastructure of durapatite-periodontal tissue interface in human intrabony defects. J Periodontal.1986;57: 133-134.
[3] Turnbull RS,Amler MH. Histological comparison of hydroxyapatite and betatricalcium phosphate implants in the rat parietal bone. J Dent Res.1985;64:218-219.
[4] Szpalski M,Gunzburg R. Application of calcium phosphate-based cancellous bone void fillers on trauma surgery.Orthopedics.2002;25(5 Suppl): 597-600.
[5] Wiltfang J,Merten HA,Schlegel KA,et al.Degradation characteristics of alpha and beta tri-calcium-phosphate (TCP) in minipigs.J Biomed Mater Res.2002;63(2):115-121.
[6] Kishimoto M,Kanemaru S,Yamashita M,et al.Cranial bone regeneration using a composite scaffold of Beta-tricalcium phosphate, collagen, and autologous bone fragments. Laryngoscope.2006;116(2): 212-216.
[7] Ogose A,Hotta T,Kawashima H,et al.Comparison ofhydroxy-apatite and beta tricalcium phosphate as bone substitutes after excision of bone tumors. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2005;72(1):94-101.
[8] Zerbo IR,Zijderveld SA,de Boer A,et al. Histomorphometry of human sinus floor augmentation using a porous beta-tricalcium phosphate: a prospective study. Clin Oral Implants Res.2004;15(6):724-732.
[9] Zerbo I,Bronckers A,de Lange G,et al.Localization of osteogenic and osteoclastic cells in porous beta-tricalcium phosphate particles used for human maxillary sinus floor elevation. Biomaterials.2005;26(12): 1445-1451.
[10] Suba Z,Takács D,Matusovits D,et al. Maxillary sinus floor grafting with beta-tricalcium phosphate in humans: density and microarchitecture of the newly formed bone. Clin Oral Implants Res.2006;17(1): 102-108.
[11] 王家葵,王一涛.续断功效与临床应用历史沿革考[J].中医杂志, 1992,33(6):49-50.
[12] 张万福.五鹤续断的地道历史考证[J].中国中药杂志,2003, 28(11): 1100-1101.
[13] 国家药典委员会.中华人民共和国药典(一部)[S].北京:中国医药科技出版社,2010.
[14] 谭洪根,林生,张启伟,等.高效液相色谱法测定续断药材中川续断皂苷Ⅵ的含量[J].中国中药杂志,2006,31(9): 726-727.
[15] 丁莉,武芸.五鹤续断部分生物学特征及栽培管理研究[J].湖北民族学院学报:自然科学版,2005,23(2):144-146.
[16] 李燕立,艾铁民,傅桂芳.中药续断显微鉴定研究[J].中国中药杂志,1993,18(5):265-268
[17] 武芸,丁莉,韩鸿,等.五鹤续断愈伤组织的诱导和增殖[J].安徽农业科学,2009,37(13):5877-5878.
[18] 武芸,武王莲,张泽,等.五鹤续断快繁体系的建立和优化[J].时珍国医国药,2010,21(4):988-989.
[19] Tian XY,Wang YW,Liu XK,et al. On the chemical constituents of Dipsacus asper. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2007;55(12): 1677-1681.
[20] Hung TM, Na M, Thuong PT,et al. Antioxidant activity of caffeoyl quinic acid derivatives from the roots of Dipsacus asper Wall. J Ethnopharmacol. 2006;108(2):188-192.
[21] 纪顺心,吴雪琴,李崇芳.中药续断对大鼠实验性骨损伤愈合作用的观察[J].中草药,1997,28(2):98-99.
[22] 张海亮,随丽娜.多孔羟基磷灰石生物活性玻璃修复兔颌骨缺损[J].医药论坛杂志,2007,28(8):26-27.
[23] Schlegel KA,Fichtner GF,Schultze-Mosgau S,et al.Histologic findings in sinus augment with autogenous bone chips versus a bovine bone substitute.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants.2003; 18:53-58.
[24] Lee JH,Kim MJ,Choi WS,et al.Concomitant reconstruction of mandibular basal and alveolar bone with a free fibular flaP.Int J Oral Maxillofac Sufg.2004;33:150-156.
[25] Monroe EA.New calcium phosphate ceramic material for Bone and tooth implants.J Dent Res.1971;12(6):50-51.
[26] Bragnces CR,Burke D,Lowenstein JD,et al. Differences in stiffness of the interface between a cementless porous implant and cancellous bone in vivo in dogs due to varying amounts of implant motion.Arthroplasty. 1996;11(10): 945-951.
[27] Franchi M,Bacchelli B,Martini D,et al.Early detachment of titanium particlesfrom various different surfaces of endosseous dental implants. Biomaterials. 2004; 25(6): 2239-2246.
[28] 程志安,吴燕峰,黄智清,等.续断对成骨细胞增值、分化、凋亡和细胞周期的影响[J].中医正骨,2004,16(12):705-707.
[29] Liu ZG,Zhang R,Li C,et al.The osteoprotective effect of Radix Dipsaci extract in ovariectomized rats.J Ethnophaimacol. 2009;123:74-81.
[30] 郭昭庆,党耕町,王志国.氟化钠及续断组分对成骨细胞增殖的影响[J].中华骨科杂志,1998,18(2):84.
[31] 龚小健,吴知行,陈真,等.川续断对离体子宫的作用[J].中国药科大学学报,1995,26(2):115.
[32] 王磊,张梅,王旭霞,等.中药川续断促进再生牙周对正畸力反应的研究[J].山东大学学报,2011,49(11):15-20.
[33] 郑志永.续断苷对人成骨细胞增殖和分化作用研究[J].山东中医药大学学报,2006,30(5):388-389. |
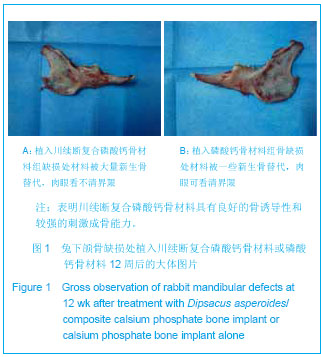
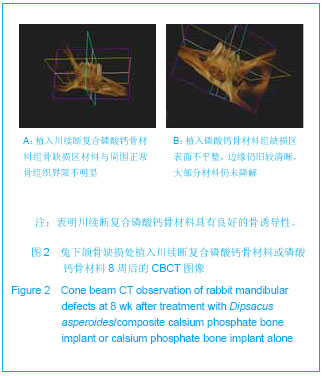

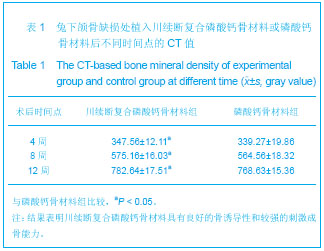
.jpg)