| [1] Gilbert TW, Sellaro TL, Badylak SF. Decellularization of tissues and organs. Biomaterials 2006;27(19):3675-3683.[2] Rochkind S, Shahar A, Fliss D, et al. Development of a tissue-engineered composite implant for treating traumatic paraplegia in rats. Eur Spine J.2006;15(2):234-245.[3] Li Q, Geng YJ, Lu L, et al. Platelet-rich fibrin-induced bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell differentiation into osteoblast-like cells and neural cells. Neural Regen Res. 2011;6(31):2419-2423.[4] Mareschi K, Novara M, Rustichelli D, et al. Neural differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells: Evidence for expression of neural markers and eag K+ channel types. Exp Hematol. 2006;34(11):1563-1572.[5] Wang FW, Jia DY, Du ZH, et al. Roles of activated astrocytes in bone marrow stromal cell proliferation and differentiation. Neuroscience.2009;160(2):319-329.[6] Yin YQ, Chen B, Ke JL, et al. Xuefuzhuyu injection induces neuronal differentiation of rat bone morrow mesenchymal stem cells. Neural Regen Res. 2011;6(3):177-182.[7] Chen J, Li Y, Wang L, et al. Therapeutic benefit of intravenous administration of bone marrow stromal cells after cerebral ischemia in rats.Stroke.2001;32(4): 1005-1011.[8] Qu C, Mahmood A, Lu D, et al. Treatment of traumatic brain injury in mice with marrow stromal cells. Brain Res.2008; 1208:234-239.[9] Wang D, Zhang JJ. Electrophysiological functional recovery in a rat model of spinal cord hemisection injury following bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation under hypothermia. Neural Regen Res. 2012;7(10): 749-755.[10] Parr AM, Tator CH, Keating A. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells for the repair of central nervous system injury. Bone Marrow Transplant.2007; 40(7):609-619.[11] Badylak SF. Regenerative medicine and developmental biology:the role of the extracellular matrix. Anal Rec B New Anat.2005;287(1):36-41.[12] Badylak SF. The extracellular matrix as a biologic scaffold material. Biomaterials.2007;28(25):3587-3593.[13] Walsh S, Biernaskie J, Kemp SW, et al. Supplementation of acellular nerve grafts with skin derived precursor cells promotes peripheral nerve regeneration. Neuroscience.2009; 164(3):1097-1107.[14] Luo JC, Chen W, Chen XH, et al. A multi-step method for preparation of porcine small intestinal submucosa (SIS). Biomaterials.2011;32(3):706-713.[15] Ott HC, Matthiesen TC, Goh SK,et al. Perfusion-decellularized matrix using nature’s platform to engineer a bioartificial heart.Nat Med.2008;14(2):213-221.[16] Yang B, Zhang YF, Zhou LH, et al. Development of a porcine bladder acellular matrix with well-preserved extracellular bioactive factors for tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2010;16(5):1201-1211.[17] Ribatti D, Conconi MT, Nico B, et al. Angiogenic response induced by acellular brain scaffolds grafted onto the chick embryo chorioallantoic membrane. Brain Res.2003;989(1): 9-15.[18] Gong J, Wang H, Shi DJ, et al. Zhonghua Shengwu Yixue Gongcheng Zazhi. 2010;16(6):552-556.龚瑾,王辉,石德金,等.脱细胞脑组织支架初步制备及形态学观察[J].中华生物医学工程杂志,2010,16(6):552-556.[19] Sondell M, Lundborg G, Kanje M. Regeneration of the rat sciatic nerve into allografts made acellular through chemical extraction.Brain Res.1998;795(1-2):44-45.[20] Mekhail M, Wong KK, Padavan DT, et al. Genipin-Cross- linked electrospun collagen fibers.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2010;96(1):204-211.[21] Lien SM, Li WT, Huang TZ. Genipin-cross linked gelatin scaffolds for articular cartilage tissue engineering with a novel crosslinking method. Materials Science and Engineering C. 2008;28(1):36-43.[22] Engler AJ, Sen SH,Sweeney HL, et al. Matrix Elasticity Directs Stem Cell Lineage Speci?cation. Cell. 2006;126(4): 677-689. |
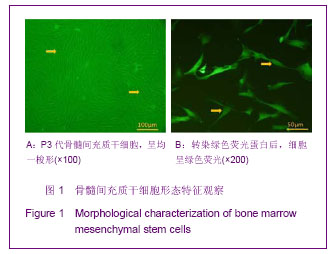
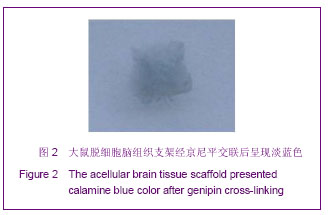
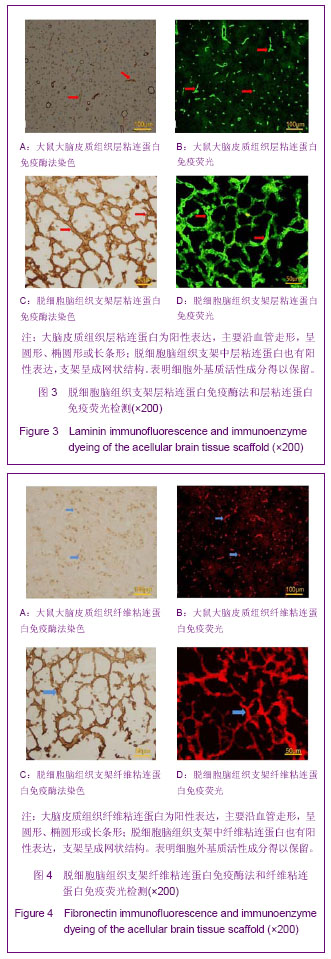
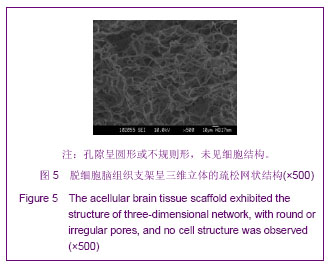
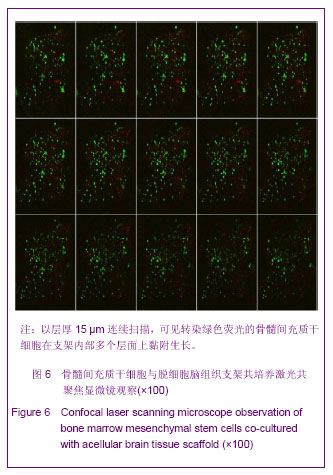
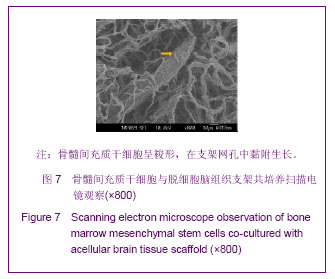
.jpg)