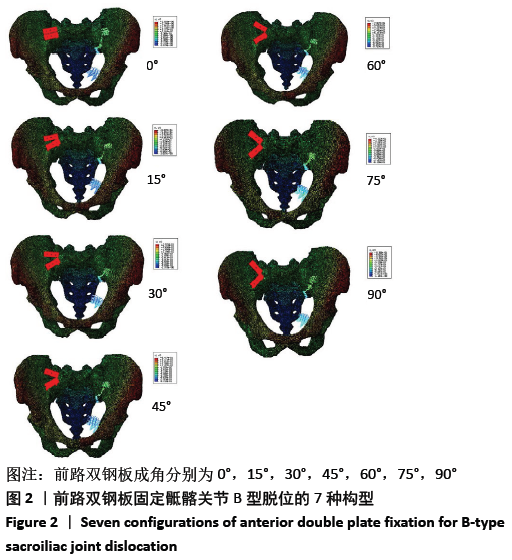
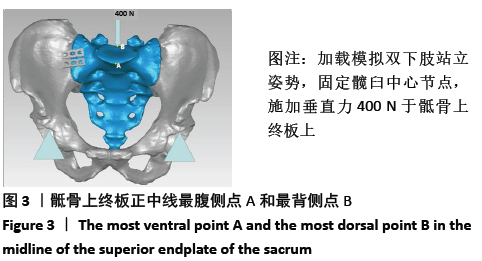
[1] 赵英伟,靳宝成,闫冰,等.前路钢板螺钉内固定治疗髋臼骨折伴骶髂关节脱位的疗效分析[J].中外医疗,2019,38(12):31-33.
[2] 吴涛,程晓东,崔蕴威, 等.不同内固定方式固定骶髂关节脱位的三维有限元分析[J].河北医科大学学报,2018,39(9):1026-1030.
[3] 孟欢,林光湖,冯小仍, 等.经第二骶椎髂骨翼螺钉和骶髂关节螺钉治疗C型骶髂关节脱位的有限元对比研究[J].中华创伤杂志, 2018,34(6):505-512.
[4] 黄沛彦,安智全,王明海, 等.前路钢板螺钉内固定治疗髋臼骨折伴骶髂关节脱位的疗效分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2017, 32(3): 236-239.
[5] CHOY WS, KIM KS, LEE SK, et al. Anterior pelvic plating and sacroiliac joint fixation in unstable pelvic ring injuries. Yonsei Med J. 2012;53:422-426.
[6] MATTA JM, SAUCEDO T. Internal fixation of pelvic ring fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989;242:83.
[7] BEAULE PE, ANTONIADES J, MATTA JM. Trans-sacral fixation for failed posterior fixation of the pelvic ring. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2006; 126:49-52.
[8] 谭振,王光林.骨盆骨折后环损伤的诊断及治疗研究进展[J].四川大学学报(医学版),2017,48(5):655-660.
[9] 阮世捷,王俊美,李海岩,等.密质骨厚度对儿童骨盆碰撞损伤影响分析[J].天津科技大学学报,2019,34(1):64-69.
[10] 郭鹏年,张占阅,高耀东.骨盆定制假体的设计及有限元分析[J].中国骨伤,2019,32(6):564-568.
[11] 向春玲,黄华军,张雁儒.快速高仿真人骨有限元几何建模——基于Mimics、Geomagic及Ansys软件的应用[J].宁波大学学报(理工版),2019,32(6):16-22.
[12] 李宁,杨涵,黄秋悦, 等.3D打印钛合金个性化骨盆假体静态和步态有限元分析[J].医用生物力学,2017,32(6):487-493.
[13] ZHAO Y, LI JM, WANG D, et al. Comparison of stability of two kinds of sacro-iliac screws in the fixation of bilateral sacral fractures in a finite element model. Injury. 2012;43:490-494.
[14] WEISL H. The ligaments of the sacroiliac joint examined with particular reference to their function. Acta Anat(Basel). 1954;20:201-213.
[15] EICHENSEER PH, SYBERT DR, COTTON JR. A finite element analysis of sacroiliac joint ligaments in response to different loading conditions. Spine. 2011;36:E1446-1452.
[16] 周恩昌,唐萍,殷浩,等.膝内翻对骨盆—腰椎矢状位序列影响的有限元分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2017,32(12):1233-1236.
[17] 刘敏,周晓赛,王俊诚, 等.不同方法治疗不稳定骨盆骨折中前环损伤的有限元分析[J].中国骨伤,2019,32(2):156-160.
[18] 李海岩,崔振宇,崔世海,等.6岁儿童骨盆有限元模型的构建和验证[J].汽车工程学报,2017,7(2):100-105.
[19] SHI DF, WANG F, WANG DM, et al. 3-D finite element analysis of the influence of synovial condition in sacroiliac joint on the load transmission in human pelvic system. Med Eng Phys. 2014;36:745-753.
[20] MILLER JA, SCHULTZ AB, ANDERSSON GB. Load-displacement behavior of sacroiliac joints. J Orthop Res. 1987;5:92-101.
[21] DALSTRA M, HUISKES R, VAN ERNING L. Development and validation of a three-dimensional finite element model of the pelvic bone. J Biomech Eng. 1995;117:272-278.
[22] PHILLIPS AT, PANKAJ P, HOWIE CR, et al. Finite element modeling of the pelvis: inclusion of muscular and ligmentous boundary conditions. Med Eng Phys. 2007;29:739-748.
[23] ZHAO Y, ZHANG S, SUN T, et al. Mechanical comparison between lengthened and short sacroiliac screws in sacral fracture fixation: A finite element analysis. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2013;99:601-606.
[24] FUNG YC. Biomechanics: mechanical properties of living tissues. Springer; 1983.
[25] 罗军,王虎,吴任涛, 等.前路钢板螺钉内固定治疗髋臼骨折伴骶髂关节脱位的临床观察[J].甘肃医药,2019,38(2):145-146.
[26] 熊元,陈明,郑琼,等.直视复位结合经皮骶髂关节螺钉固定治疗难复性骶髂关节脱位[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2018,20(3):193-198.
[27] KIM KT, LEE SH, SUK KS, et al. Biomechanical changes of the lumbar segment after total disc replacement: Charite Prodisc and Maverick using finite element model study. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2010;47:446-453.
[28] YINGER K, SCALISE J, OLSON SA, et al. Biomechanical comparison of posterior pelvic ring fixation. J Orthop Trauma.2003; 17:481-487.
[29] LI L. The nature and determinal theorem of parallelogram (Chin). The Shan Xi Province Educates, 2004.
[30] PEL JJ, SPOOR CW, GOOSSENS RH, et al. Biomechanical model study of pelvic belt influence on muscle and ligament forces. J Biomech. 2008; 41:1878-1884.
|