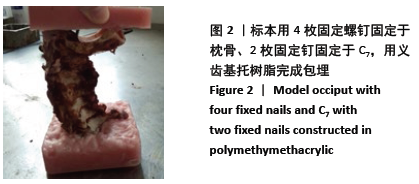
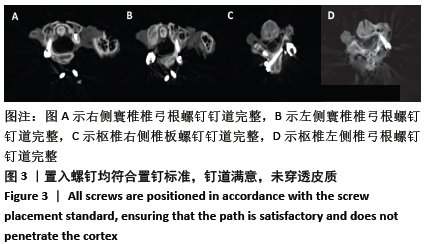
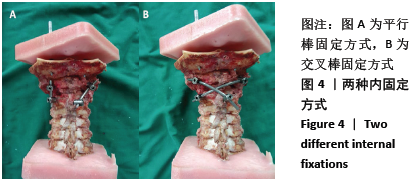
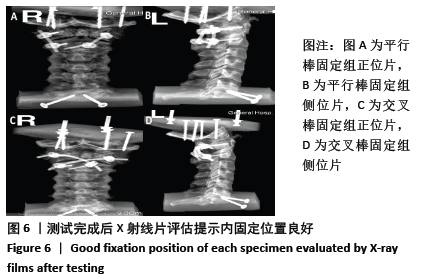
[1] 屈巍,闫亮,宋宗让,等.寰枢椎弓根螺钉置入单节段固定治疗Jefferson骨折合并不稳定齿状突骨折[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2017, 21(31):4957-4962.
[2] 王正雷,王海斌,刘建辉,等.采用椎弓根螺钉内固定治疗寰枢椎骨折脱位[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2020,28(10):933-935.
[3] SHAO J, GAO YZ, GAO K, et al. Posterior screw-rod fixation and selective axial loosening for the treatment of atlantoaxial instability or dislocation caused by os odontoideum: a case series for a single posterior approach. World Neurosurg. 2019;132:e193-e201.
[4] 吴继彬,吴东迎,孙玛骥,等. 经后路寰枢椎椎弓根钉内固定治疗寰枢椎失稳[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2017,25(21):2002-2005.
[5] 王诗军,李钰婷,李淳德.后路内固定系统修复寰枢椎不稳的生物力学特征[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2015,19(48):7819-7824.
[6] GABRIEL JP, MUZUMDAR AM, KHALIL S, et al. A novel crossed rod configuration incorporating translaminar screws for occipitocervical internal fixation: an in vitro biomechanical study. Spine. 2011;11:30-35.
[7] 马向阳,杨进城,邱锋,等. 枕颈交叉棒临床固定技术的建立与临床应用[J].中国骨与关节损杂志,2015,30(11):1121-1123.
[8] MARCUS R, RENE S, LUTZ C, et al. Posterior Atlantoaxial Fixation: Biomechanieal in vitro comparison of six different techniques.niques. Spine. 2002;27(16):1724-1732.
[9] ZHU Q, OUYANG J, LU W, et al. Traumatic instabilities of the cervical spine caused by high-speed axial compression in a human model:An in vitro biomechanical study.Spine. 1999;24(5):440-444.
[10] Chun DH, Yoon DH, Kim KN, et al. Biomechanical comparison of four different atlantoaxial posterior fixation constructs in adults: a finite element study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2018;43(15):E891-E897.
[11] 廖穗祥,郑勇强,张东升,等.新型蝶形枕颈内固定系统固定的生物力学稳定性研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2018,28(6):535-540.
[12] 蔡璇,王杰,李浩鹏,等.寰枢椎前路可动固定系统的研制及生物力学研究[J].山西医科大学学报,2018,49(4):422-425.
[13] LIU S, SONG Z, LIU L, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of C1 lateral mass and C2 translaminar bicortical screws in atlantoaxial fixation: an in vitro human cadaveric study. Spine J. 2018;18(4):674-681.
[14] 魏文智,李全义,王秋莲.Magerl技术结合单椎板夹固定术治疗对寰枢椎脱位患者并发症和生活质量的影响[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2017,16(21):2148-2152.
[15] 赵文龙,倪斌,郭群峰,等.后路寰枢椎经关节螺钉结合寰椎椎板钩与寰枢椎椎弓根螺钉固定融合治疗寰枢椎脱位的疗效比较[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2017,27(1):10-16.
[16] 谭泽赳,张宏其,刘少华,等.颅环牵引结合Magerl技术治疗儿童寰枢椎前脱位[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2019,27(11):966-970.
[17] CHUN DH, YOON DH, KIM KN, et al. Biomechanical comparison of four different atlantoaxial posterior fixation constructs in adults: a finite element study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2018;43(15):E891-E897.
[18] DU JY, AICHMAIR A, KUEPER J, et al. Biomechanical analysis of screw constructs for atlantoaxial fixation in cadavers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neurosurg Spine. 2015;22(2):151-161.
[19] HUANG DG, WANG T, HAO DJ, et al. Posterior C1-C2 screw-rod fixation and autograft fusion for the treatment of os odontoideum with C1-C2 instability. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2017;163:71-75.
[20] 郑建章,吴宏,胡世平,等.寰枢椎椎弓根钉内固定术治疗寰枢椎不稳疗效分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2020,35(3):252-254.
[21] 李小峰,赵朵,李炜峰,等.后路椎弓根螺钉单节段内固定治疗寰椎骨折[J].脊柱外科杂志,2019,17(6):379-382.
[22] DOBRAN M, NASI D, ESPOSITO DP, et al. Posterior fixation with c1 lateral mass screws and c2 pars screws for type ii odontoid fracture in the elderly: long-term follow-up. World Neurosurg. 2016;96:152-158.
[23] 马向阳,尹庆水,刘景发,等.寰椎侧块螺钉与寰椎椎弓根螺钉的解剖与生物力学对比研究[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2005,20(6):361-363.
[24] 周田华,汤逊,苏涌跃,等.寰枢椎椎弓根钉内固定治疗齿状突骨折的疗效观察[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2015,30(5):508-509.
[25] 朱昌荣,王建华,马向阳,等.枢椎椎板螺钉在儿童颅颈交界区手术中使用的临床疗效[J].实用骨科杂志,2019,25(7):577-580+587.
[26] PUNYARAT P, BUCHOWSKI JM, KLAWSON BT, et al. Freehand technique for C2 pedicle and pars screw placement: is it safe? Spine J. 2018;18(7): 1197-1203.
[27] 马向阳,尹庆水,吴增晖,等.枢椎椎板螺钉与椎弓根螺钉抗拔出强度的比较[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2007,17(2):137-139.
[28] 马向阳,尹庆水,吴增晖,等.寰枢椎后路四种钉棒固定技术的三维稳定性评价[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2008,18(6):464-468.
[29] PARK J, SCHEER JK, LIM TJ, et al. Biomechanical analysis of Goel technique for C1-2 fusion. J Neurosurg Spine. 2011;14(5):639-646.
[30] DIMITRIEV AE,LEHMAN RA,HELGESON MD, et al. Acute and long-term stability of atlantoaxial fixation methods. Spine. 2009;34(4):365-370.
[31] LEHMAN RA JR, DMITRIEV AE, WILSON KW. Biomechanical analysis of the C2 intralaminar fixation technique using a crossed-link and offset connector for an unstable atlantoaxial joint. Spine. 2012;12:151-156.
|