中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (11): 1753-1758.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3076
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
胸腺素α1对酵母多糖诱导多器官功能衰竭模型大鼠肝损伤的保护
马明和,牛 毅
- 青海大学附属医院重症医学,青海省西宁市 810000
Thymosin alpha1 protects against liver injury in rats with zymosan-induced multiple organ failure
Ma Minghe, Niu Yi
- Department of Critical Care Medicine, Affiliated Hospital of Qinghai University, Xining 810000, Qinghai Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
多器官功能衰竭:又被称为多器官功能障碍综合征,主要表现为机体内2个或2个以上的器官发生急性功能障碍或衰竭,以全身性的产生和释放各种炎性递质为主要特点,多发生在病情急性进展期,是ICU患者死亡的重要原因。
胸腺素α1:是机体内胸腺肽中生物活性最强的组成成分之一,具有刺激淋巴细胞的增殖、分化,增强细胞免疫的作用,在炎症性病理过程中具有调节炎性介质分泌,细胞凋亡等作用,在临床上用于治疗慢性乙型肝炎。
背景:多器官功能衰竭模型中的肝损伤给临床医师的用药造成较大的困扰,胸腺素α1用于慢性肝炎的治疗,对肝损伤具有明显的保护作用。
目的:基于ADPN/Akt/NF-κB信号通路探讨胸腺素α1对多器官功能衰竭大鼠肝脏的保护机制。
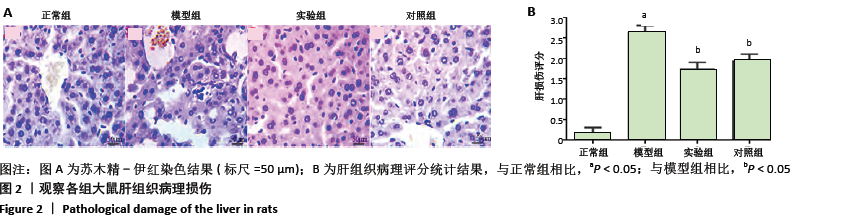
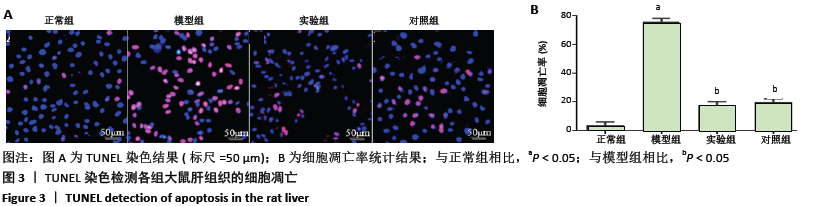
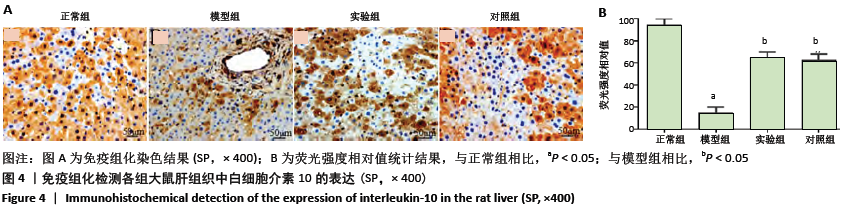
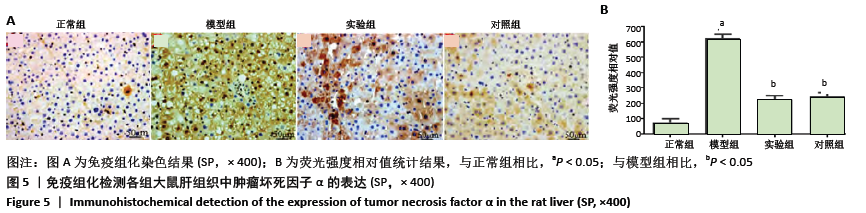
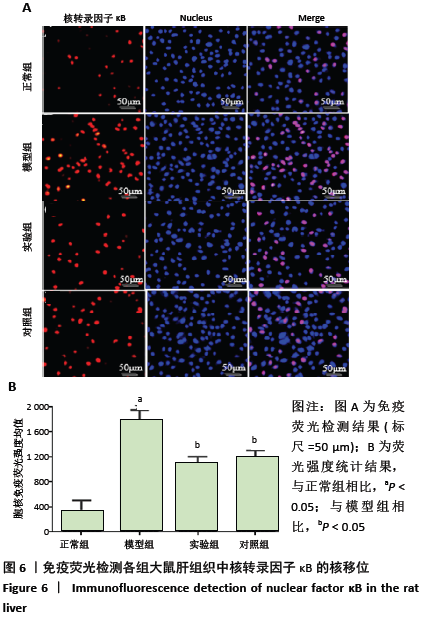
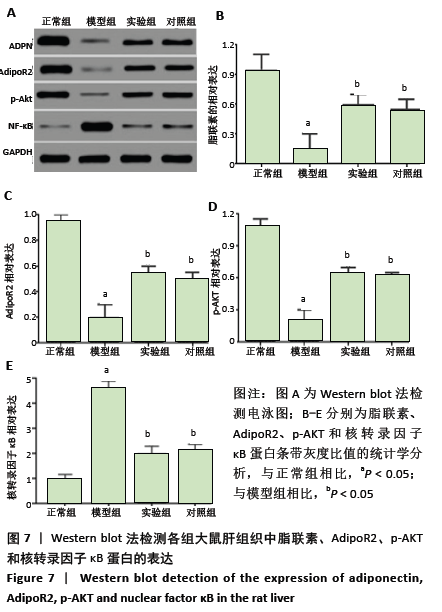
方法:SPF级SD雄性大鼠随机分为4组:正常组、模型组、实验组、对照组。除正常组外其余大鼠参照文献采用腹腔注射500 mg/kg酵母多糖(50 g/L)构建大鼠多器官功能衰竭模型;正常组大鼠腹腔注射等剂量生理盐水。注射30 min后,实验组、对照组大鼠每日定点分别腹腔注射2 mL的 0.5 mg/kg胸腺素α1和甘草酸二铵注射液,正常组和模型组腹腔注射等剂量生理盐水。在连续给药7 d后,进行肝功能检测;采用苏木精-伊红染色、TUNEL染色检测大鼠肝组织病理学改变及细胞凋亡率;采用免疫组化、Western blot检测大鼠肝组织白细胞介素10、肿瘤坏死因子α的水平及脂联素、AdipoR2、p-AKT和核转录因子κB的蛋白表达。
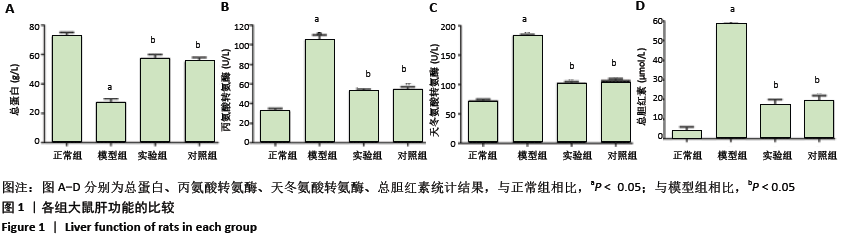
结果与结论:①与正常组相比,模型组大鼠血清中丙氨酸转氨酶、天冬氨酸转氨酶、总胆红素、肝损伤病理评分、细胞凋亡率、肿瘤坏死因子α水平及核转录因子κB的蛋白表达明显升高,总蛋白、白细胞介素10水平及脂联素、AdipoR2、p-AKT的蛋白表达明显降低(均P < 0.05);与模型组相比,实验组和对照组大鼠血清中丙氨酸转氨酶、天冬氨酸转氨酶、总胆红素、肝损伤病理评分、细胞凋亡率、肿瘤坏死因子α水平及核转录因子κB的蛋白表达明显降低,总蛋白、白细胞介素10水平及脂联素、AdipoR2、p-AKT的蛋白表达明显升高(均P < 0.05);②结果说明,胸腺素α1对酵母多糖诱导的多器官衰竭大鼠的肝脏有保护作用,其机制与ADPN/Akt/NF-κB信号通路信号通路有关,ADPN/Akt被激活,抑制核转录因子κB的活化,从而减轻炎症反应。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6049-1268 (马明和)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: