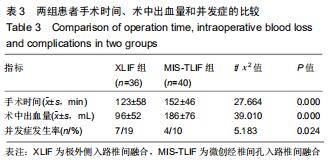
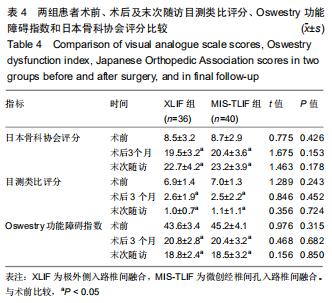
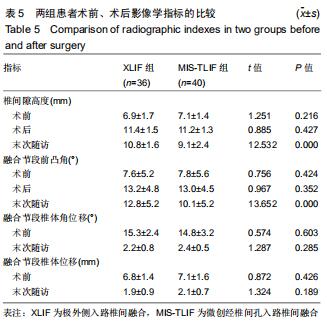
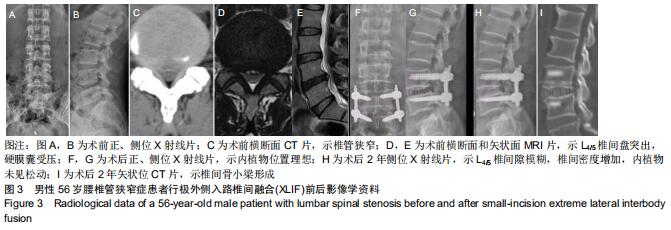
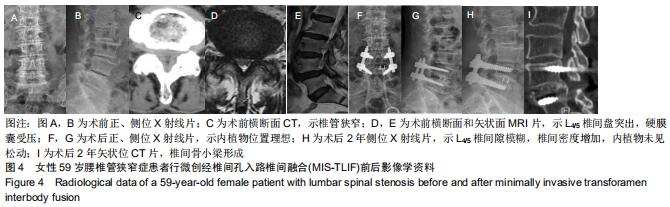
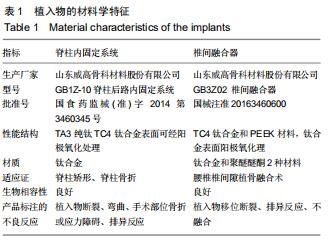
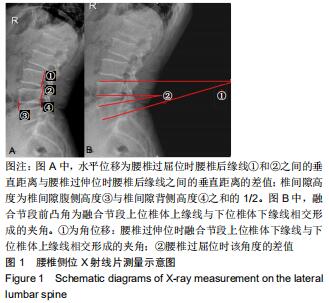
|
[1] GU G, ZHANG H, FAN G, et al. Comparison of minimally invasive versus open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in two-level degenerative lumbar disease. Int Orthop. 2014;38(4):817-824.
[2] YOSHIHARA H, YONEOKA D. National trends in the surgical reatment for lumbar degenerative disc disease: United States 2000 to 2009. Spine J. 2015;15(2): 265-271.
[3] 张永峰,张世磊,袁斌,等. 显微镜辅助下经椎间孔椎间融合微创治疗腰椎退变性疾病的临床疗效比较[J].中华解剖与临床杂志,2018,23(3):198-202.
[4] 郑召民,章健,刘辉,等.微创小切口侧前方腰椎间融合术治疗腰椎退变性疾病的近期疗效和围手术期并发症[J] .中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2018,28(5):410-417.
[5] 易红蕾,许俊杰,段明阳,等.极外侧入路腰椎间融合术对腰椎矢状面序列的影响[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2019,27(19):1754-1758.
[6] KEOROCHANA G, SETRKRAISING K, WORATANARAT P, et al. Clinical outcomes after minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion and lateral lumbar interbody fusion for treatment of degenerative lumbar disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosurg Rev. 2018;41(3):755-770.
[7] CHEN YC, ZHANG L, LI EN,et al. An updated meta-analysis of clinical outcomes comparing minimally invasive with open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in patients with degenerative lumbar diseases. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(43):e17420.
[8] LU T, LU Y. Comparison of biomechanical performance among posterolateral fusion and transforaminal, extreme, and oblique lumbar interbody fusion: a finite element analysis. World Neurosurg. 2019; 129(9):e890-e899.
[9] 杨舟,朱青安.侧方入路腰椎内固定的生物力学研究进展[J].医用生物力学, 2019,34(6):656-661.
[10] 轩安武,谢雁春,张猛,等.微创经椎间孔入路与极外侧入路腰椎椎间融合术治疗短节段腰椎退行性疾病的近期疗效比较[J].脊柱外科杂志,2019, 17(2):84-89.
[11] 王诗成,潘磊,刘青华,等.小切口XLIF联合侧路椎弓根钉固定治疗腰椎不稳[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2018,36(6):697-704.
[12] ROBERT EI, JONATHAN NS, ANTOINE GT. Two-Year Comparative Outcomes of MIS Lateral and MIS Transforaminal Interbody Fusion in the Treatment of Degenerative Spondylolisthesis: Part II: Radiographic Findings. Spine. 2016;41(Suppl 8):S133-S144.
[13] JONATHAN NS,ANTOINE T, ROBERT I. Two-year Comparative Outcomes of MIS Lateral and MIS Transforaminal Interbody Fusion in the Treatment of Degenerative Spondylolisthesis: Part I: Clinical Findings. Spine. 2016;41(Suppl 8): S123-S132.
[14] SHENG SR, GENG YB, ZHOU KL,et al. Minimally invasive surgery for degenerative spondylolisthesis: transforaminal or oblique lumbar interbody fusion. J Comp Eff Res. 2020;9(1):45-51.
[15] EPSTEIN NE. Review of Risks and Complications of Extreme Lateral Interbody Fusion (XLIF). Surg Neurol Int. 2019;10:237.
[16] 蓝思彬,吴增晖,许俊杰,等.极外侧入路腰椎间融合术联合双侧椎弓根螺钉固定治疗腰椎滑脱症[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2018,28(5):405-409.
[17] HAYAMA S, NAKANO A, NAKAYA Y, et al. The evaluation of indirect neural decompression after lateral lumbar interbody fusion using intraoperative computed tomography myelogram. World Neurosurg. 2018;120(10):e710-e718.
[18] PEREIRA EA,FARWANA M,LAM KS. Extreme lateral interbody fusion relieves symptoms of spinal stenosis and low-grade spondylolisthesis by indirect decompression in complex patients. J Clin Neurosci.2017; 35(1):56-61.
[19] 秦世强,孙宇庆,倪文卓,等.OLIF与TLIF治疗退变性腰椎滑脱合并腰椎管狭窄症的疗效对比[J].实用骨科杂志, 2018,24(7):628-632.
[20] BRODANO GB,MARTIKOS K,LOLLI F,et al. Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in degenerative disk disease and spondylolisthesis grade I:minimally invasive versus open surgery. J Spinal Disord Tech.2015;28(10):E559-E64.
[21] 陈意磊,朱志海,王玉康,等.斜侧方椎间融合术与经椎间孔椎间融合术在腰椎退变性疾病中前凸矫正效果的对比研究[J].中华医学杂志,2018,98(25): 1990-1995.
[22] LI H,ZHANG R,SHEN C. Differences in radiographic and clinical outcomes of oblique lateral interbody fusion and lateral lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar disease: a meta-analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord.2019;20(1):582.
[23] CHEN E, XU J, YANG S, et al.Cage Subsidence and Fusion Rate in Extreme Lateral Interbody Fusion with and without Fixation. World Neurosurg. 2019;122(2):e969-e977.
|