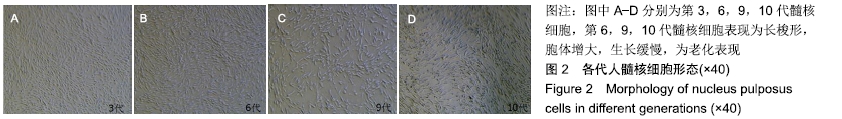
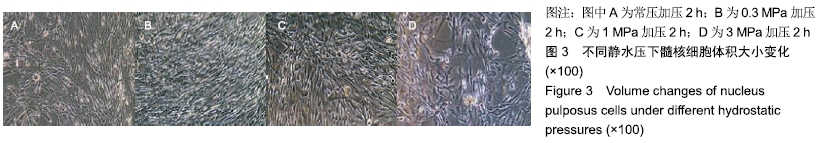
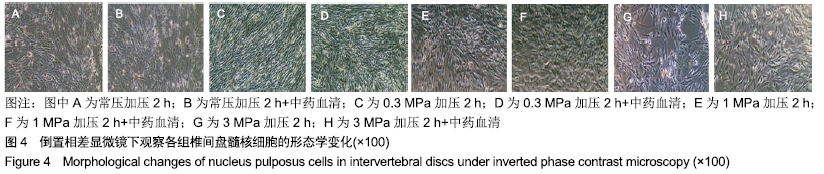
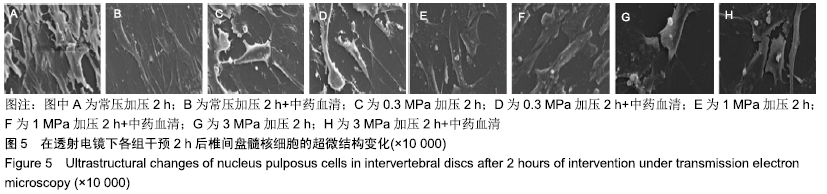
中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (8): 1200-1206.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2499
• 脊柱组织构建 spinal tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
人椎间盘髓核细胞增殖活性与益肾活血通络方的干预调控
陈 江1,肖辉灯2,孙 旗1,张 帆1,祝永刚2,刘志超2,郭菲宇2,柳根哲2
- 1北京中医药大学东直门医院,北京市 100700;2首都医科大学附属北京中医医院,北京市 100010
Proliferative activity of nucleus pulposus cells in human intervertebral disc and intervention with Yishen Huoxue Tongluo Recipe
Chen Jiang1, Xiao Huideng2, Sun Qi1, Zhang Fan1, Zhu Yonggang2, Liu Zhichao2, Guo Feiyu2, Liu Genzhe2
- 1Dongzhimen Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China; 2Beijing Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100010, China
摘要:
文题释义:
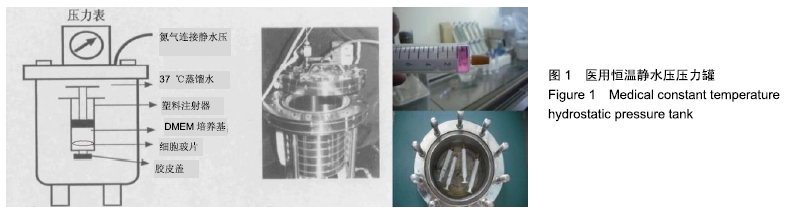
静水压:是椎间盘承受压力负荷的主要力学形式。静水压压力随体位和活动量的不同而发生改变:平卧休息位时最低约0.3 MPa,坐位时接近1 MPa,弯腰搬重物可达3 MPa。在该实验中压力值的选择上,也参考以上数据,分别为0.3 MPa、1 MPa和3 MPa,以模拟人体不同体位下椎间压力环境,另设对照组为常压(1 atm≈0.1 MPa)。
NF-κB信号通路:最新研究发现,NF-κB信号通路与椎间盘退变过程联系紧密。在细胞受压力、氧化应激、毒素、细胞因子、应力、炎症递质等刺激时,NF-κB活性得以恢复,与κB序列相结合后发挥基因转录、调节下游蛋白表达的作用。该实验基于益肾活血通络方的确切疗效,从与椎间盘退变过程密切相关的NF-κB信号通路入手,研究其发挥临床疗效的可能机制。
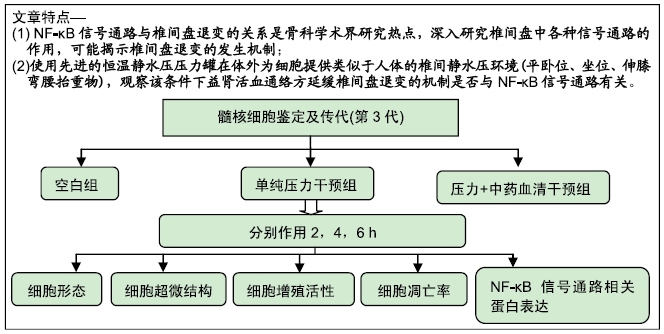
背景:NF-κB信号通路与椎间盘退变的关系是骨科学术界研究热点,深入研究椎间盘中各种信号通路的作用,有助于了解椎间盘退变的发生机制。
目的:通过研究不同静水压压力下益肾活血通络方含药血清对人椎间盘髓核细胞NF-κB信号通路的调控作用,以期能从分子生物学角度探讨益肾活血通络方治疗椎间盘退变性疾病的可能机制及作用靶点。
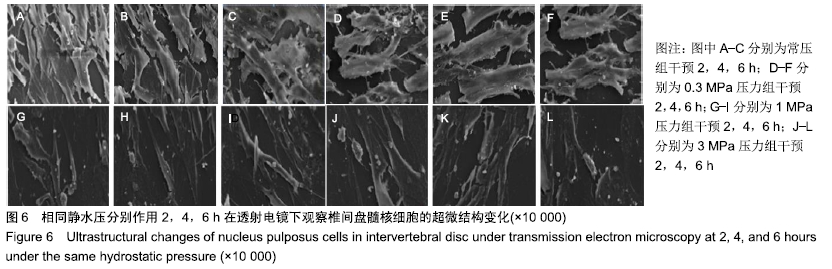
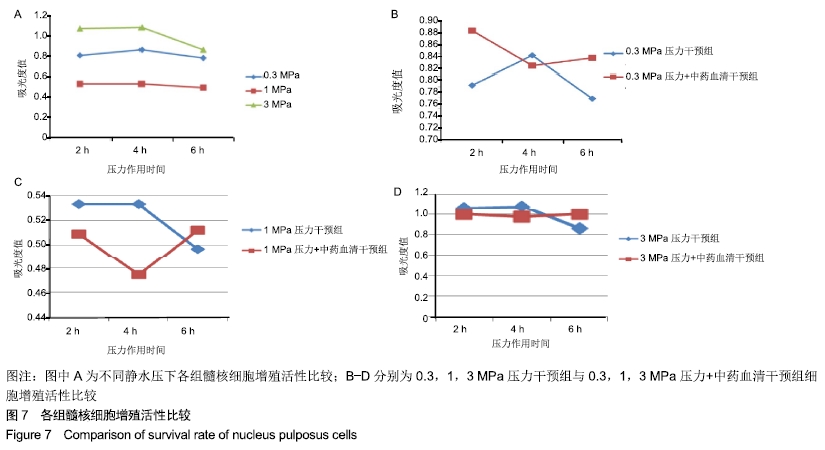
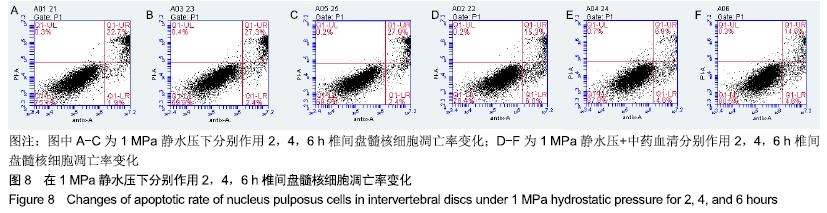
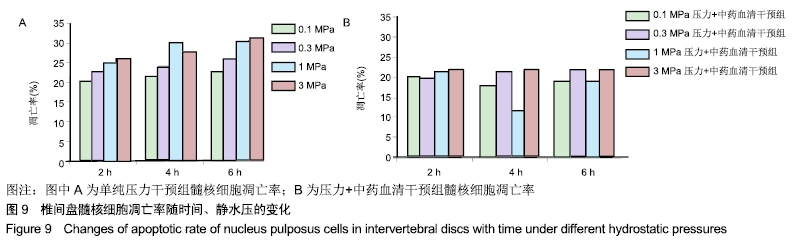
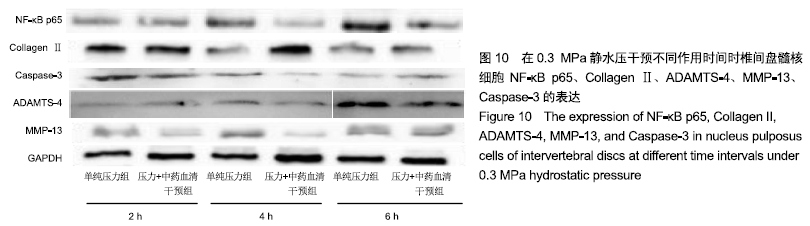
方法:将第3代人椎间盘髓核细胞分为8组,分别加入益肾活血通络方含药血清,在体外不同静水压加载条件(0.3,1,3 MPa)下作用2,4,6 h后,使用倒置相差显微镜观察椎间盘髓核细胞的形态及生长状况;使用透射电镜观察椎间盘髓核细胞的超微结构;采用CCK-8法检测各组髓核细胞的增殖活性;采用Annexin V-FITC/Propidium Iodide凋亡试剂盒检测髓核细胞的凋亡率;采用Western blot法检测髓核细胞内NF-κB p65、Collagen Ⅱ、ADAMTS-4、MMP-13、Caspase-3的表达。
结果与结论:①在同一压力及作用时间下压力+中药血清组髓核细胞形态较常压组、单纯压力组更完整,生长状况更好,其中0.3,1 MPa压力+中药血清组优于3 MPa压力+中药血清组;②压力+中药血清组髓核细胞增殖活性更高,其中0.3 MPa压力+中药血清组与0.3 MPa单纯压力组比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);③压力+中药血清组椎间盘髓核细胞的凋亡率较常压组、单纯压力干预组低(P < 0.05);④与单纯压力组比较,压力+中药血清组Collagen Ⅱ、Caspase-3表达增加,NF-κB p65、ADAMTS-4、MMP-13表达减少(P < 0.05);⑤结果表明,益肾活血通络方能增加细胞活性,减少细胞凋亡,有效延缓髓核细胞的退变,其机制可能与椎间盘髓核细胞NF-κB信号通路促进Collagen Ⅱ、Caspase-3表达,抑制NF-κB p65、ADAMTS-4、MMP-13表达有关。
ORCID: 0000-0002-7355-6179(柳根哲)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: