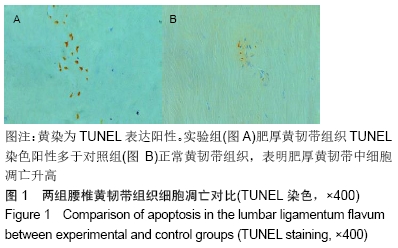
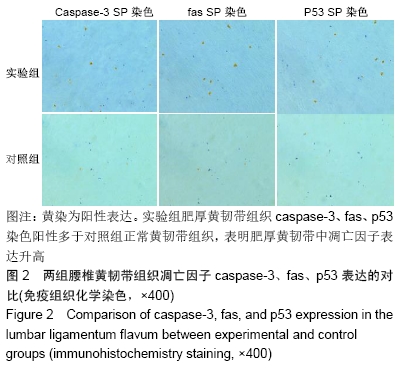
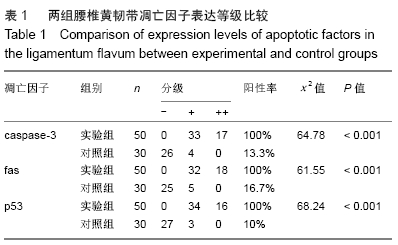
[1] ANDRESEN AK, ERNST C, ANDERSEN M.Lumbar spinal stenosis. Ugeskr Laeger.2016;178(41).pii: V04160245.
[2] 王伟敦,倪斌,于沈敏.腰椎管狭窄症与黄韧带的病理关系研究分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2003,11(10):664-666.
[3] 阚敏慧,程爱国,杜宁.CT横断面测量分析腰椎管狭窄症与黄韧带肥厚的关系[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(52):9756-9759.
[4] 阚敏慧,王小锐,程爱国.黄韧带肥厚与腰椎管狭窄症关系的研究[J].天津医药,2011,39(3):202-204.
[5] SAKAMAKI T, SAIRYO K, SAKAI T, et al. Measurements of ligamentum flavum thickening at lumbar spine using MRI. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2009;129(10):1415-1419.
[6] ALTINKAYA N, YILDIRIM T, DEMIR S, et al. Factors associated with the thickness of the ligamentum flavum: is ligamentum flavum thickening due to hypertrophy or buckling?Spine.2011;36(16):E1093-1097.
[7] ABBAS J, HAMOUD K, MASHARAWI YM, et al. Ligamentum Flavum Thickness in Normal and Stenotic Lumbar Spines. Spine.2010; 35(12): 1225-1230.
[8] 周纲,张玉坤,黄卫民.中国新疆地区腰椎管狭窄患者腰椎黄韧带肥厚的危险因素分析:回顾性、单中心、病例分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2017, 21(19):2993-2998.
[9] SAIRYO K, BIYANI A, GOEL VK, et al. Lumbar ligamentum flavum hypertrophy is due to accumulation of inflammation-related scar tissue. Spine.2007;32(11):340-347.
[10] HAYASHI K, SUZUKI A, ABDULLAH AHMADI S, et al. Mechanical stress induces elastic fibre disruption and cartilage matrix increase in ligamentum flavum. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):13092.
[11] SHUNZHI Y, ZHONGHAI L, NING Y. Mechanical stress affects the osteogenic differentiation of human ligamentum flavum cells via the BMP Smad1 signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(5):7692-7698.
[12] 蒋玉权,刘继春,叶晓健,等. 肥厚腰椎黄韧带中成纤维细胞生长因子、转化生长因子及结缔组织生长因子的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(46): 7452-7457.
[13] HUR JW, BAE T, YE S, et al. Myofibroblast in the ligamentum flavum hypertrophic activity.Eur Spine J. 2017; 26:2021-2030.
[14] LÖHR M, HAMPL JA, LEE JY, et al. Hypertrophy of the lumbar ligamentum flavum is associated with inflammation-related TGF-β expression.Acta Neurochir(Wien).2011;153(1):134-141.
[15] AMUDONG A, MUHEREMU A, ABUDOUREXITI T.Hypertrophy of the ligamentum flavum and expression of transforming growth factor beta. Int Med Res.2017;45(6):2036-2041.
[16] NAKAMA S, KIKUCHI M, YASHIRO T, et al.Regional difference in the appearance of apoptotic cell death in the ligamentum flavum of the human cervical spine.Med Mol Morphol. 2005;38(3):173-180.
[17] LIU J,YAO Y,DING H,et al.Oxymatrine triggers apoptosis by regulating Bcl-2 family proteins and activating caspase-3/caspase-9 pathway in human leukemia HL 60 cells.Tumor Biology.2014;35(6):5409-5415.
[18] 赵英伦,马元,莫森,等.腰椎间盘突出症患者血清中Caspase-3和Caspase-9活性研究[J].现代检验医学杂志,2018,33(2):13-15.
[19] 叶君健,林金贵.退变腰椎间盘组织细胞凋亡及相关基因Fas和Bcl-2蛋白的表达[J].福建医科大学学报,2007,41(6):506-508.
[20] PARK JB, KIM K, HAN C, et al.Expression ofFasreceptorondisccellsin herniated lumbar disctissue.Spine.2001;26(2):142-146.
[21] PARK JB, CHANG H,KIM KW.Expression ofFas Iigend and apoptosis of disc cells in herniated lumbar disc tissue.Spine.2001;26(6):618-621.
[22] 李小川,李雷,王欢,等. Fas/FasL基因在退变腰椎间盘组织中的表达及诱导凋亡作用[J].中华医学杂志, 2005,85(24):1718-1720.
[23] 吕浩然,刘尚礼,黄东生,等.Fas在退变的兔椎间盘终板凋亡中的表达及作用通路研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,2016,(1):195-197.
[24] 孙廷哲,陈春,沈萍萍.细胞凋亡中p53转录依赖与非依赖性调控[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2008, 30(3):301-306.
[25] LU XY, DING XH, ZHONG LJ, et al. Expression and significance of VEGF and p53 in degenerate intervertebral disc tissue.Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2013;6(1):79-81.
[26] TAKASHI Y, HIROAKI H, KENICHIRO K, et al. Notochordal cell disappearance and modes of apoptotic cell death in a rat tail static compression-induced disc degeneration model.Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(1): R31.
[27] KOSAKA H, SAIRYO K, BIYANI A, et al.Pathomechanism of loss of elasticity and hypertrophy of lumbar igamentum flavum in elderly patients with lumbar spinal canal stenosis.Spine.2007;25(4):2805-2811.
[28] LIANG W, YE D, DAI L, et al.Overexpression of hTERT extends replicative capacity of human nucleus pulposus cells, and protects against serum starvation-induced apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. Cell Biochem. 2012;113:2112-2121.
|