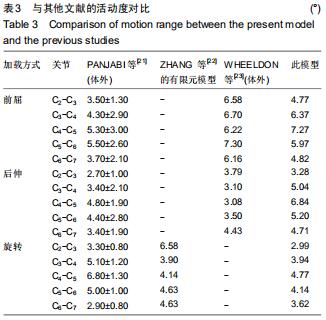
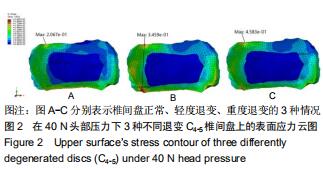
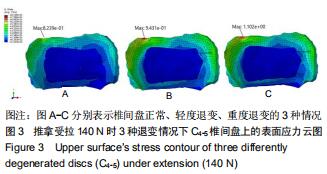
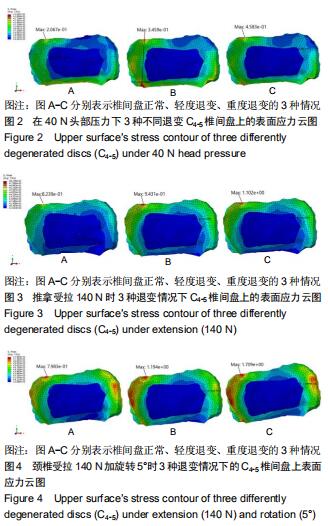
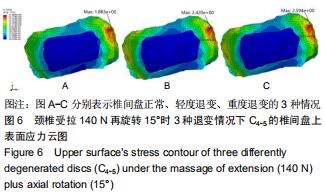
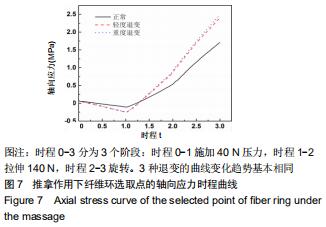
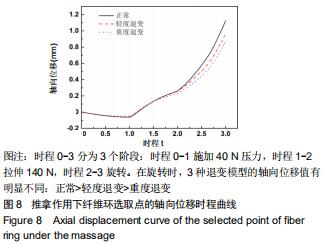
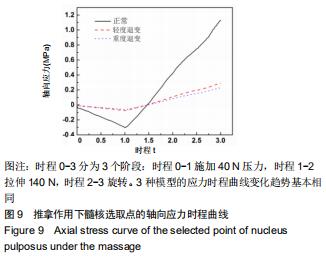
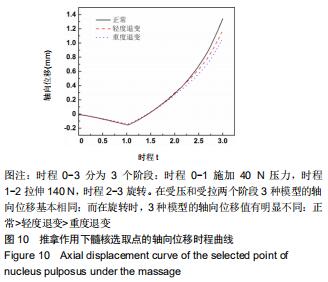
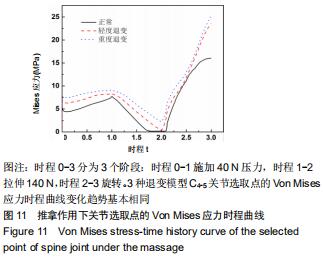
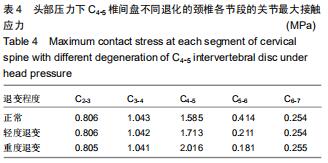
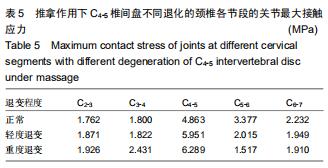
|
[1] 姜广宗,李学锋,聂林,等.利用MIMICS和ABAQUS建立正常人颈椎的三维有限元模型[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2013,21(11): 1114-1120.
[2] 中华外科杂志编辑部. 颈椎病的手术治疗及围手术期管理专家共识(2018)[J].中华外科杂志,2018,56(12):881-884.
[3] 乔秀秀,于秀娟,张蕊杰,等.大学生颈椎病现状调查及防治对策[J].科技资讯,2017,15(29):204-205+207.
[4] 吕艳伟,李文桓,田伟,等.基于不同核函数构建的退行性颈椎病支持向量机高危人群筛查模型的比较[J].中国卫生统计,2018, 35(3):368-371.
[5] 余洋.颈椎病的治疗与护理研究现状[J].海南医学,2018,29(20): 2949-2951.
[6] 罗勇骏,杨海源,唐鹏宇,等.青年人颈椎病的临床特点及前路手术疗效观察[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2017,25(7):583-589.
[7] 陈佳雯,汪慧,董菡珺,等.医务人员常见疾病现状调查分析[J].重庆医学,2018,47(26):3450-3452+3457.
[8] 张琪,金鸿宾,范桐顺,等.推拿手法治疗颈椎病机制研究[J].河南中医,2018,38(8):1248-1251.
[9] LING TH, ZAKARIA AF, ABDULLAH AT. Is neck massage safe? A rare case of tetraplegia and spinal shock after neck manipulation. J Orthop Surg. 2017;25(1):230949901769045.
[10] 刘治华,许伟超,张新民,等.颈椎C2-7三维有限元模型的建立与最优角度牵引仿真研究[J].郑州大学学报(医学版), 2016,51(3): 359-363.
[11] 徐海涛. 腰椎手法推拿力的量化研究和有限元分析[D].广州:南方医科大学,2008.
[12] 邬黎平. 颈椎推拿的作用机理及优化研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2010.
[13] DENG Z, WANG K, WANG H, et al. A finite element study of traditional Chinese cervical manipulation. Eur Spine J. 2017; 26(7):1-10.
[14] 闫家智,吴志宏,汪学松,等.腰椎间盘退变后应力变化的有限元分析[J].中国医学科学院学报,2009,31(4):464-467.
[15] 王诗成,潘磊,黄必留,等.颈椎间盘退变对颈椎生物力学影响的有限元研究[J].颈腰痛杂志,2015,36(3):175-178.
[16] MUTHUKUMAR N. C1-C3 lateral mass fusion for type IIa and type III Hangman's fracture. J Craniovertebr Junction Spine. 2012;3(2): 62-66.
[17] LEE S, IM Y, KIM K, et al. Comparison of cervical spine biomechanics after fixed-and mobile-core artificial disc replacement:a finite element analysis.Spine.2011;36(9): 700-708.
[18] 苏再发,贾连顺,张美超,等.利用Mimics和Freeform建立下颈椎三维非线性有限元模型[J].脊柱外科杂志,2009,7(4):221-225.
[19] 刘海波,雷建银,张宝成,等.前后路内固定治疗Ⅱ型不稳定Hangman骨折的有限元分析[J].医用生物力学, 2015,30(4): 326-331.
[20] 赵亮,闫广华,瞿东滨,等.腰椎间盘退变对软骨终板生物力学特性影响的有限元分析[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2015,33(4): 455-460.
[21] PANJABI MM, CRISCO JJ, VASAVADA A, et al. Mechanical properties of the human cervical spine as shown by three-dimensional load-displacement curves. Spine. 2001; 26(24):2692-2700.
[22] ZHANG QH, TEO EC, NG HW, et al. Finite element analysis of moment-rotation relationships for human cervical spine. J Biomech. 2006;39(1):189-193.
[23] WHEELDON JA, PINTAR FA, KNOWLES S, et al. Experimental flexion/extension data corridors for validation of finite element models of the young, normal cervical spine. J Biomech. 2006;39(2):375-380.
[24] 曹贵君. ROI-C融合器内固定治疗Hangman骨折有限元分析与临床应用[D].青岛:青岛大学,2017.
[25] 李斌,赵文志,陈秉智.有限元分析:椎间盘退变对颈椎生物力学的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(11):1748-1752.
[26] 杜诗尧,周风金,倪斌,等.新型后路寰枢椎限制性非融合内固定系统的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(3):383-389.
[27] 蒋诗超,房敏,程英武,等.神经根型颈椎病动物模型国内研究进展及评价[J].中华中医药杂志,2012,27(12): 3052-3056.
[28] DEL PALOMAR AP, CALVO B, DOBLARÉ M. An accurate finite element model of the cervical spine under quasi-static loading. J Biomech. 2008; 41(3):523-531.
[29] JOHN JD, SARAVANA KUMAR G, YOGANANDAN N. Cervical spine morphology and ligament property variations: A finite element study of their influence on sagittal bending characteristics. J Biomech. 2019;85:18-26.
[30] KIM YH , KHUYAGBAATAR B, KIM K. Recent advances in finite element modeling of the human cervical spine. J Mech Sci Technol. 2018;32(1):1-10.
[31] NIKKHOO M, CHENG CH, WANG JL, et al. Development and validation of a geometrically personalized finite element model of the lower ligamentous cervical spine for clinical applications. Comput Biol Med. 2019;109:22-32.
[32] WANG XD, FENG MS, HU YC. Establishment and finite element analysis of a three-dimensional dynamic model of upper cervical spine instability: finite element of upper cervical instability. Orthop Surg. 2019;11(3):500-509.
[33] 刘伟聪,陈雄生,周盛源,等.正常人体C0-T1全颈椎有限元模型的构建及意义[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(11):1707-1712.
[34] 陈群响,倪斌,郭群峰,等.带肌肉组织全颈椎三维有限元模型的建立及分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2019,29(4):348-355.
[35] 陈威烨,王辉昊,梁飞凡,等.牵引治疗颈椎病的研究进展[J].中国康复医学杂志,2016,31(5):599-601.
[36] 邓真,王辉昊,牛文鑫,等.中医定点旋扳法对颈椎应力作用的有限元分析[A]. 第十二届全国生物力学学术会议暨第十四届全国生物流变学学术会议会议论文摘要汇编,2018.
[37] 王宽,邓真,王辉昊,等.力学测量在评估颈痛及手法治疗领域的应用[J].中国骨伤,2016,29(7):668-672.
[38] 孙树椿,张军,王立恒,等.旋转手法对颈椎髓核内压力影响的实验研究[J].中国骨伤,2010,23(1):34-38.
|