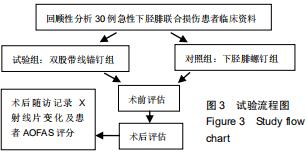
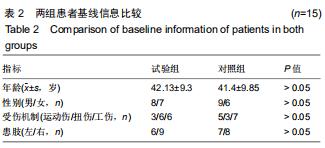
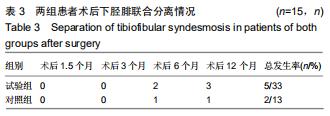
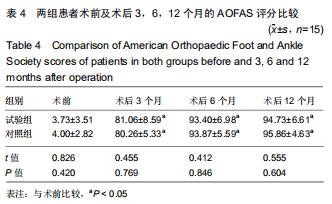
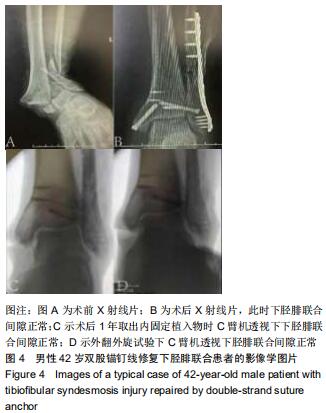
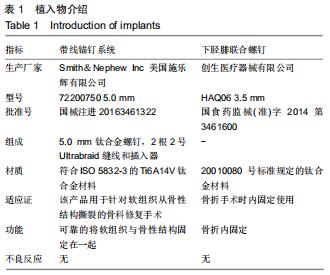
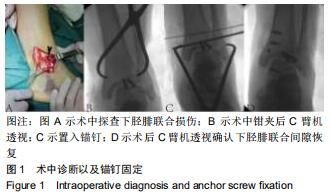
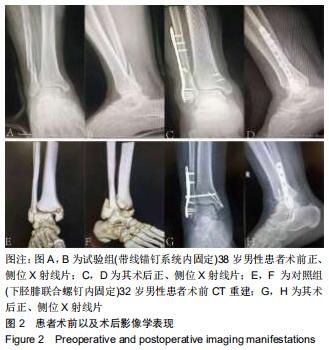
|
[1] TENFORDE AS, YIN A, HUNT KJ. Foot and ankle injuries in runners. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am.2016;27(1):121-137.
[2] BARR KP, HARRAST MA. Evidence-based treatment of foot and ankle injuries in runners. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2005;16(3):779-799.
[3] HUNT KJ, HURWIT D, ROBELL K, et al. Incidence and epidemiology of foot and ankle injuries in elite collegiate athletes. Am J Sports Med. 2017;45(2):426-433.
[4] YUEN CP, LUI TH. Distal tibiofibular syndesmosis: anatomy, biomechanics, injury and management. Open Orthop J. 2017; 11:670-677.
[5] CLANTON TO, WILLIAMS BT, BACKUS JD, et al. Biomechanical analysis of the individual ligament contributions to syndesmotic stability. Foot Ankle Int. 2017; 38(1):66-75.
[6] CLANTON TO, WHITLOW SR, WILLIAMS BT, et al. Biomechanical comparison of 3 current ankle syndesmosis repair techniques. Foot Ankle Int. 2017; 38(2): 200-207.
[7] VAN ZUUREN WJ, SCHEPERS T, BEUMER A, et al. Acute syndesmotic instability in ankle fractures: A review. Foot Ankle Surg. 2017;23(3):135-141.
[8] SOLAN MC, DAVIES MS, SAKELLARIOU A. Syndesmosis stabilisation: screws versus flexible fixation. Foot Ankle Clin. 2017; 22(1): 35-63.
[9] LI M, COLLIER RC, HILL BW, et al. Comparing different surgical techniques for addressing the posterior malleolus in supination external rotation ankle fractures and the need for syndesmotic screw fixation. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2017;56(4): 730-734.
[10] POGLIACOMI F, ARTONI C, RICCOBONI S,et al. The management of syndesmotic screw in ankle fractures. Acta Biomed. 2018;90(1-S):146-149.
[11] NEARY KC, MORMINO MA, WANG H. Suture button fixation versus syndesmotic screws in supination-external rotation type 4 injuries: a cost-effectiveness analysis. Am J Sports Med. 2017;45(1):210-217.
[12] SCHEPERS T, VAN DER LINDEN H, VAN LIESHOUT EMM, et al. Technical aspects of the syndesmotic screw and their effect on functional outcome following acute distal tibiofibular syndesmosis injury. Injury. 2014;45(4):775-779.
[13] KELLETT JJ, LOVELL GA, ERIKSEN DA, et al. Diagnostic imaging of ankle syndesmosis injuries: A general review. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2018;62(2):159-168.
[14] SCHOENNAGEL BP, KARUL M, AVANESOV M, et al. Isolated syndesmotic injury in acute ankle trauma: comparison of plain film radiography with 3T MRI. Eur J Radiol. 2014;83(10):1856-1861.
[15] HERMANS JJ, WENTINK N, BEUMER A, et al. Correlation between radiological assessment of acute ankle fractures and syndesmotic injury on MRI. Skeletal Radiol. 2012;41(7): 787-801.
[16] RAMMELT S, MANKE E. Syndesmosis injuries at the ankle. Unfallchirurg. 2018;121(9):693-703.
[17] HERMANS JJ, BEUMER A, DE JONG TAW, et al. Anatomy of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis in adults: a pictorial essay with a multimodality approach. J Anat. 2010; 217(6): 633-645.
[18] KRAHENBUHL N, WEINBERG MW, DAVIDSON NP, et al. Imaging in syndesmotic injury: a systematic literature review. Skelet Radiol. 2018;47(5):631-648.
[19] LILYQUIST M, SHAW A, LATZ K, et al. Cadaveric Analysis of the Distal Tibiofibular Syndesmosis. Foot Ankle Int. 2016; 37(8): 882-890.
[20] MRÓZ I, KURZYDŁO W, BACHUL P, et al. Inferior tibiofibular joint (tibiofibular syndesmosis) - own studies and review of the literature. Folia Med Cracov. 2015;55(4):71-79.
[21] XIE L, XIE H, WANG J, et al. Comparison of suture button fixation and syndesmotic screw fixation in the treatment of distal tibiofibular syndesmosis injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Surg. 2018;60:120-131.
[22] LAMOTHE JM, BAXTER JR, MURPHY C, et al. Three-Dimensional Analysis of Fibular Motion After Fixation of Syndesmotic Injuries With a Screw or Suture-Button Construct. Foot Ankle Int. 2016;37(12):1350-1356.
[23] SOIN SP, KNIGHT TA, DINAH AF, et al. Suture-button versus screw fixation in a syndesmosis rupture model: a biomechanical comparison. Foot Ankle Int. 2009;30(4): 346-352.
[24] WALLEY KC, HOFMANN KJ, VELASCO BT, et al. Removal of hardware after syndesmotic screw fixation: a systematic literature review. Foot Ankle Spec. 2017;10(3):252-257.
[25] GENNIS E, KOENIG S, RODERICKS D, et al.The fate of the fixed syndesmosis over time. Foot Ankle Int. 2015;36(10): 1202-1208.
[26] KAFTANDZIEV I, SPASOV M, TRPESKI S, et al. Fate of the syndesmotic screw--Search for a prudent solution. Injury. 2015;46 Suppl 6:S125-S129.
[27] KOCADAL O, YUCEL M, PEPE M, et al. Evaluation of reduction accuracy of suture-button and screw fixation techniques for syndesmotic injuries. Foot Ankle Int. 2016; 37(12):1317-1325.
[28] 田勇,马骁,刘成.纽扣钢板内固定治疗下胫腓骨联合损伤[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2015,19(Z):46.
[29] 钱伟宏,罗毅文,姚志宏.双带绊纽扣钢板和金属螺钉治疗下胫腓联合损伤的疗效比较[J].临床骨科杂志,2016,19(6):735-737.
[30] 冯杰,曹鹏飞,何毅.手术治疗踝关节骨折合并下胫腓联合韧带损伤的效果观察[J].双足与保健,2019,28(3):32-33.
[31] 汤峰,王勤业,徐忠良,等.缝合锚弹性固定生理重建修复下胫腓联合损伤[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(30):56-61.
|