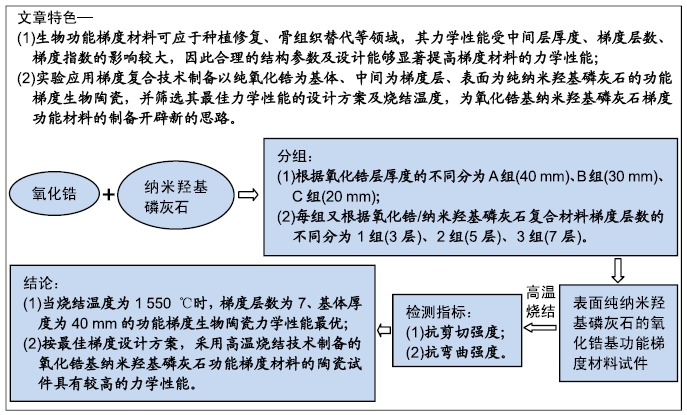
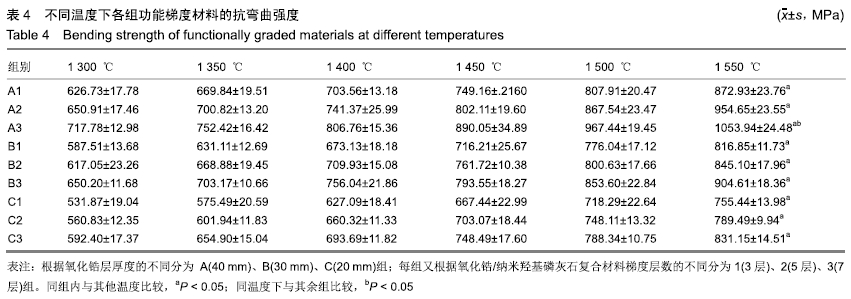
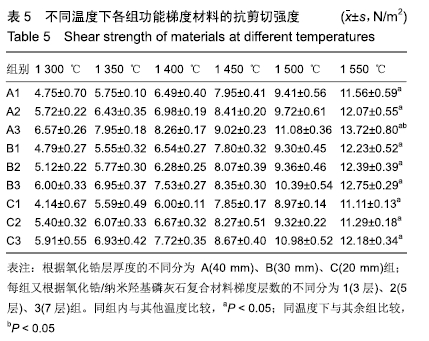
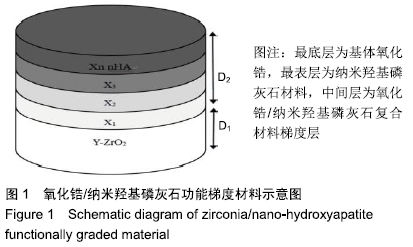
[1] 许力强,宋文植,孙宏晨.放电等离子烧结法制备牙科纳米氧化锆复相陶瓷力学性能研究[J].广东牙病防治,2014,22(8):440-412.
[2] 赵露,吴音,郭兴国,等.浸渗掺杂技术制备彩色氧化锆陶瓷[J].稀有金属材料与工程,2018,47(S1):375-378.
[3] 李敢,童昕,秦海燕,等.前牙区钛基台与氧化锆基台修复对种植体周围组织影响的短期评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(30): 4811-4816.
[4] 王玉增,单志华.羟基磷灰石(HAP)的制备及应用概况[J].皮革科学与工程,2015,25(6):34-38.
[5] CARVALHO O, SOUSA F, MADEIRA S, et al. HAp-functionalized zirconia surfaces via hybrid laser process for dental applications.Opt Laser Technol.2018;106:157-167.
[6] 鲍雨梅,徐哲玉,马龙,等.氧化锆增强HA涂层的制备及其磨损性能[J].中国陶瓷,2016,52(4):58-63.
[7] 沈倩倩,潘育松.生物功能梯度材料的制备技术及性能评价[J].热加工工艺,2015,44(14):21-24.
[8] 钱超,樊英姿,孙健.三维打印制备钛/羟基磷灰石复合体及功能梯度材料[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(29):5364-5370.
[9] EVANS C, TWEHEYO R, MCGARRY J, et al.What are the experiences of seeking, receiving and providing FGM-related healthcare.Perspectives of health professionals and women/girls who have undergone FGM:protocol for a systematic review of qualitative evidence.BMJ Open. 2017; 7(1):018-170.
[10] BAYATI R, MOLAEI R, RICHMOND A, et al.Modification of properties of yttria stabilized zirconia ep itaxial thin films by excimer laser annealing.ACS Appl Mater Inter. 2014;6(24): 22316-22325.
[11] TOMAN M, TOKSAVUL S, SARIKANAT M, et al.Fracture resistance of endodontically treated teeth:effect of tooth coloured post material and surface conditioning.Eur J Prosthodont Restor Dent.2010;18(1):23-30.
[12] DANILENKO I, LASKO G, BRYKHANOVA I, et al.The Peculiarities of Structure Formation and Properties of Zirconia-Based Nanocomposites with Addition of Al 2 O 3 and NiO.Nanoscale Res Lett.2017;12(1):125-130.
[13] MIAO Y, YANG Z, LIANG B, et al.A novel in situ synthesis of SiBCN-Zr composites prepared by a sol-gel process and spark plasma sintering.Dalton T.2016;45(32):12739-12744.
[14] WANG T, TSOI JK.A novel zirconia fibre-reinforced resin composite for dental use. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2016; 53(5):151-160.
[15] LI X, YOSHIHARA K, DE MUNCK J, et al.Modified tricalcium silicate cement formulations with added zirconium oxide.Clin Oral Investig.2017;21(1):895-905.
[16] SPONCHIA G, MOSHTAGHIOUN BM, RIELLO P, et al. High-temperature compressive creep of novel fine-grained orthorhombic ZrO2 ceramics stabilized with 12 mol% Ta doping.J Eur Ceram Soc.2018;38(5):2445-2448.
[17] ZHOU C, DENG C, CHEN X, et al.Mechanical and biological properties of the micro-/nano-grain functionally graded hydroxyapatite bioceramics for bone tissue engineering.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater.2015;48(1):1-11.
[18] SANDOMIERSKI M, STRZEMIECKA B, CHEHIMI MM. Reactive Diazonium-Modified Silica Fillers for Polymers. Langmuir.2016;32(44):11646-11654.
[19] EWAIS EM, AMIN AM, AHMED YM, et al.Combined effect of magnesia and zirconia on the bioactivity of calcium silicate ceramics at C\S ratio less than unity.Mat Sci Eng C-Mater. 2017;70(2):155-160.
[20] 李清禄,李世荣.非保守功能梯度材料简支梁在过屈曲附近的振动响应[J].应用基础与工程科学学报,2019,27(1):95-103.
[21] MAHMOUDI M, SAIDI AR, HASHEMIPOUR MA.The use of functionally graded dental crowns to improve biocompatibility: a finite element analysis.Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin.2018;21(1):161-168.
[22] 李清禄,朱作权.陶瓷氧化锆和金属钛合金FGM变截面立柱的过屈曲数值模拟[J].功能材料,2017,48(2):2226-2230.
[23] BYKOV YV, EGOROV SV, EREMEEV AG, et al.Temperature profile optimization for microwave sintering of bulk Ni–Al2O3 functionally graded materials.J Mater Proc Tech. 2014;214(2): 210-216.
[24] BOLELLI G, BELLUCCI D, CANNILLO V, et al.Comparison between suspension plasma sprayed and high velocity suspension flame sprayed bioactive coatings.Surf Coat Tech. 2015;280(1):232-249.
[25] LIN D, LI Q, LI W, et al.Bone remodeling induced by dental implants of functionally graded material.J Biomed Mater Res B.2010;92(2):430-438.
[26] RAZA MR, SULONG AB, MUHAMAD N, et al.Effects of binder system and processing parameters on formability of porous Ti/HA composite through powder injection molding.Mater Design.2015;87(2):386-392.
[27] YOSHIHIKO H, KOUSUKE Z, HIDETOSHI F, et al.Fabrication and Compression Properties of Functionally Graded Copper Foam Made Using Friction Powder Sintering and Dissolution. J Mater Eng and Perform.2017;26(9).4508-4513.
[28] BAI D, LIU H, BAI H, et al.Powder metallurgy inspired low-temperature fabrication of high-performance stereocomplexed polylactide products with good optical transparency.Sci Rep-UK.2016;6(5):202-220.
[29] 万千.HA/316L不锈钢生物功能梯度材料的理化性能及体外生物活性研究[D].长沙:中南大学,2006.
[30] FERREIRA SC, CONDE A, ARENAS MA, et al.Anodization Mechanism on SiC Nanoparticle Matrix Composites Produced by Power Metallurgy.Mat.2014;7(12):8151-8167.
[31] 程西云,何俊,肖舒,等.梯度结构对氧化铝陶瓷涂层抗冲击载荷性能的影响[J].机械工程学报,2012,48(21):124-131.
[32] MARTELLI L, BERARDESCA E, MARTELLI M.Topical formulation of a new plant extract complex with refirming properties.Clinical and non-invasive evaluation in a double-blind trial.Inter J Cosmetic Sci.2008;22(3):424-430.
[33] FUJI T, TOHGO K, ARAKI H, et al.Fabrication and strength evaluation of biocompatible ceramic-metal composite material.J Solid Mech Mater Eng.2010;4(11):1699-1699.
[34] 冯晓娜,杨宪园,卢婷利,等.羟基磷灰石微载体的应用及制备[J].材料导报,2013,27(3):87.
[35] ALSAHHAF A, SPIES BC, VACH K.Fracture resistance of zirconia-based implant abutments after artificial long-term aging.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater.2017;66(4):224-232.
[36] 仇满德,王晓燕,李旭,等.水热法合成羟基磷灰石的微分析研究[J].人工晶体学报,2013,42(9):1965-1971.
[37] BHOWMICK A, PRAMANIK N, JANA P, et al.Development of bone-like zirconium oxide nanoceramic modified chitosan based porous nanocomposites for biomedical application.Int J Biol Macromol.2017,95(1):348-356.
[38] BERMÚDEZ-REYES B.Effect on growth and osteoblast mineralization of hydroxyapatite-zirconia(HA-ZrO2)obtained by a new low temperature system.Biomed Mater. 2018;13(3): 35-40.
[39] ZHANG L, HAN Y.Hydroxyaptite nanorods patterned ZrO2 bilayer coating on zirconium for the application of percutaneous implants.Colloid Surface B.2015;127(1):8-14.
[40] 史文涛,戴瑶,陈平波,等.鼻黏膜来源外胚间充质干细胞与磷酸钙骨水泥材料的体外相容性[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(33): 5350-5355.
[41] 刘宁,朱勇,刘昌奎,等.仿生磷酸钙缓释涂层改性三维支架的制备及性能研究[J].山西医科大学学报,2019,50(1):35-39.
[42] 陶剑,袁博,姜华.β-TCP/HA双相骨修复材料的Ames试验研究[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2013,10(5):1-4.
[43] KURTZ SM, DEVINE JN.PEEK biomaterials in trauma, orthopedic and spinal implants. Biomaterials. 2007;28(32): 4845-4869.
|