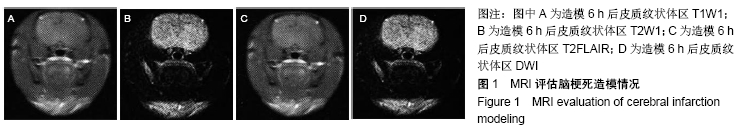
中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (19): 2972-2977.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2057
• 脐带脐血干细胞 umbilical cord blood stem cells • 上一篇 下一篇
人脐血间充质干细胞移植脑梗死大鼠神经功能的恢复及脑组织端粒酶反转录酶表达
余 恒,周 涛
- 襄阳市中心医院,湖北省文理学院附属医院北院区神经内科,湖北省襄阳市 441003
Effects of umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on recovery of nerve function and telomerase reverse transcriptase expression in brain tissue of cerebral infarction rats
Yu Heng, Zhou Tao
- Department of Neurology, Xiangyang Central Hospital, North Branch of Affiliated Hospital of Hubei University of Arts and Science, Xiangyang 441003, Hubei Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
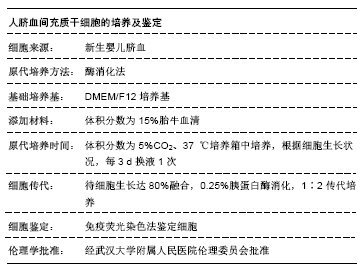
人脐血来源间充质干细胞的优势:脐血从孕妇分娩后的胎盘、脐带残端收集,对于产妇和新生儿均没有任何痛苦和不良影响,也不会涉及社会、伦理及法律方面的争论;脐血受胎盘屏障的保护,其成分被病毒、细菌污染的概率低。
端粒酶:细胞中负责端粒延长的一种酶,是基本的核蛋白反转录酶,在保持端粒稳定、基因组完整、细胞长期活性和潜在的继续增殖能力等方面有重要作用。
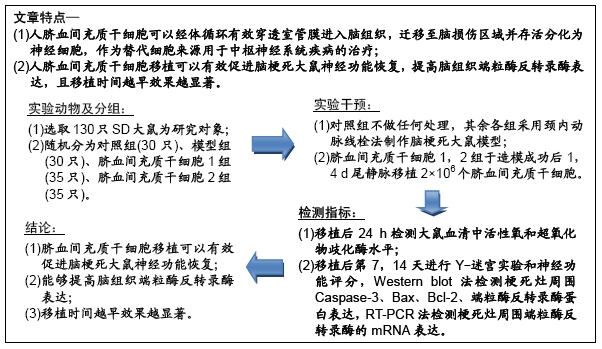
背景:脐血间充质干细胞可以经体循环有效穿透室管膜进入脑组织,迁移至脑损伤区域并存活分化为神经细胞,作为替代细胞来源用于中枢神经系统疾病的治疗。
目的:探讨人脐血间充质干细胞移植对脑梗死大鼠神经功能恢复及脑组织端粒酶反转录酶表达的影响。
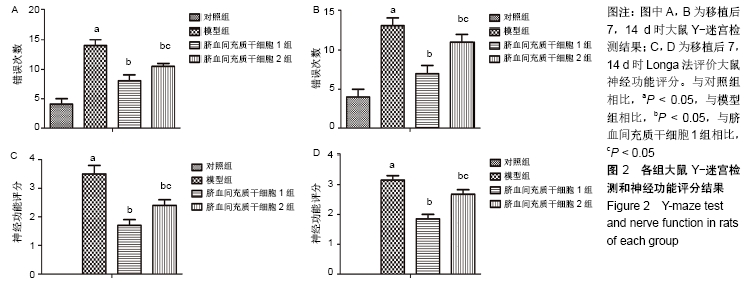
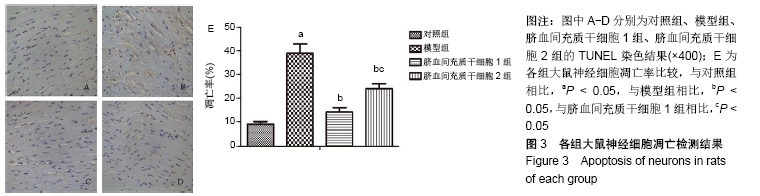
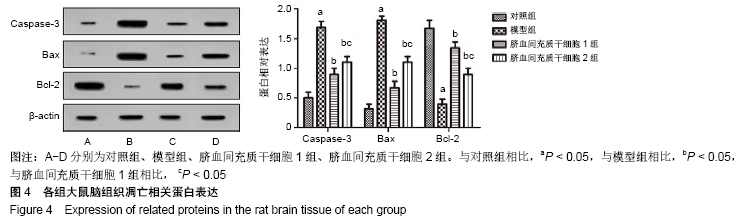
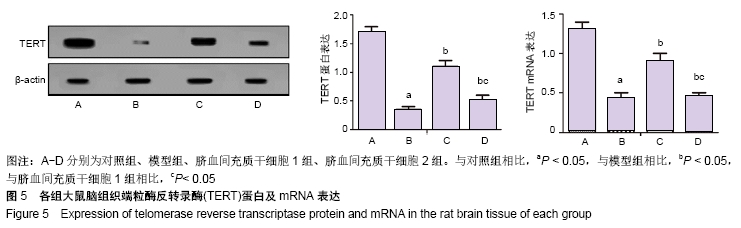
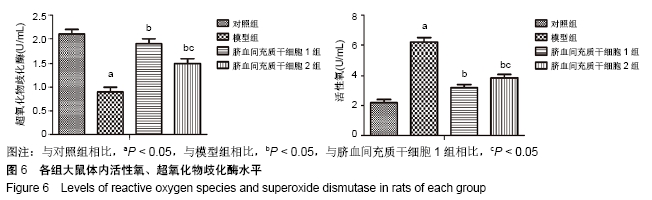
方法:选取130只大鼠为研究对象,随机分为对照组(30只)、模型组(30只)、脐血间充质干细胞1组(35只)、脐血间充质干细胞2组(35只);对照组不做任何处理,其余各组采用颈内动脉线栓法制作脑梗死大鼠模型,脐血间充质干细胞1,2组于造模成功后1,4 d尾静脉移植2×106个脐血间充质干细胞;移植后24 h检测大鼠血清中活性氧和超氧化物歧化酶水平,移植后第7,14天进行Y-迷宫实验和神经功能评分,采用TUNEL法检测病灶中心神经细胞凋亡率,Western blot法检测梗死灶周围Caspase-3、Bax、Bcl-2、端粒酶反转录酶蛋白表达,RT-PCR法检测梗死灶周围端粒酶反转录酶的mRNA表达。
结果与结论:①与对照组相比,模型组大鼠Y-迷宫实验错误次数、神经功能评分、细胞凋亡指数、Caspase-3、Bax蛋白表达、活性氧水平均显著升高(P < 0.05),Bcl-2、端粒酶反转录酶蛋白以及mRNA表达、超氧化物歧化酶水平均显著降低(P < 0.05);②与模型组相比,脐血间充质干细胞1组和脐血间充质干细胞2组大鼠Y-迷宫实验错误次数、神经功能评分、细胞凋亡指数、Caspase-3、Bax蛋白表达、活性氧水平均显著降低(P < 0.05),Bcl-2、端粒酶反转录酶蛋白以及mRNA表达、超氧化物歧化酶水平均显著升高(P < 0.05);③与脐血间充质干细胞2组相比,脐血间充质干细胞1组大鼠Y-迷宫实验错误次数、神经功能评分、细胞凋亡指数、Caspase-3、Bax蛋白表达、活性氧水平均显著降低(P < 0.05),Bcl-2、端粒酶反转录酶蛋白以及mRNA表达、超氧化物歧化酶水平均显著升高(P < 0.05);④结果表明,脐血间充质干细胞移植可以有效促进脑梗死大鼠神经功能恢复,能够提高脑组织端粒酶反转录酶表达,移植时间越早效果越显著。
ORCID: 0000-0002-4902-1553(余恒)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: