| [1] 王爽,杨慧霞.妊娠期糖尿病发病的危险因素分析[J].中华妇产科杂志,2014,49(5):321-324.[2] HAPO Study Cooperative Research Group, Metzger BE, Lowe LP, et al. Hyperglycemia and adverse pregnancy outcomes. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(19):1991-2002.[3] Banas A. Purification of adipose tissue mesenchymal stem cells and differentiation toward hepatic-like cells. Methods Mol Biol. 2012;826:61-72.[4] Sacchetti B, Funari A, Michienzi S, et al. Self-renewing osteoprogenitors in bone marrow sinusoids can organize a hematopoietic microenvironment. Cell. 2007;131(2): 324-336.[5] Barlow S, Brooke G, Chatterjee K, et al. Comparison of human placenta- and bone marrow-derived multipotent mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2008;17(6): 1095-1107.[6] Chao KC, Chao KF, Fu YS, et al. Islet-like clusters derived from mesenchymal stem cells in Wharton's Jelly of the human umbilical cord for transplantation to control type 1 diabetes. PLoS One. 2008;3(1):e1451.[7] Sun B, Meng XH, Liu R, et al. Mechanism study for hypoxia induced differentiation of insulin-producing cells from umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;466(3):444-449.[8] Lee LK, Ueno M, Van Handel B, et al. Placenta as a newly identified source of hematopoietic stem cells. Curr Opin Hematol. 2010;17(4):313-318.[9] Parolini O, Alviano F, Bagnara GP, et al. Concise review: isolation and characterization of cells from human term placenta: outcome of the first international Workshop on Placenta Derived Stem Cells. Stem Cells. 2008;26(2): 300-311.[10] Ende N, Chen R, Reddi AS. Effect of human umbilical cord blood cells on glycemia and insulitis in type 1 diabetic mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;325(3):665-669.[11] Kadam S, Muthyala S, Nair P, et al. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and islet-like cell clusters generated from these cells as a novel source for stem cell therapy in diabetes. Rev Diabet Stud. 2010;7(2):168-182.[12] Hashemian SJ, Kouhnavard M, Nasli-Esfahani E. Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Rising Concerns over Their Application in Treatment of Type One Diabetes Mellitus. J Diabetes Res. 2015;2015:675103.[13] 杨慧霞.妊娠合并糖尿病临床实践指南[M].第2版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2013:22-36.[14] 中华医学会妇产科学分会产科学组/围产医学分会妊娠合并糖尿病协作组.妊娠合并糖尿病诊治指南(2014)[J].糖尿病临床, 2014,8(11):489-498.[15] 刘洋, 李艳琪, 王洪一, 等. 胎盘源间充质干细胞分离提取的新方法[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2015, 19(10): 1608-1612.[16] 李小燕. 脐带间充质干细胞诱导分化为胰岛样细胞及对妊娠期糖尿病大鼠的降糖效果的研究[D].南京:南京医科大学,2013.[17] Abdul Aziz SH, John CM, Mohamed Yusof NI, et al. Animal Model of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus with Pathophysiological Resemblance to the Human Condition Induced by Multiple Factors (Nutritional, Pharmacological, and Stress) in Rats. Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:9704607. [18] 刘科宇,王春华,杜智敏.链脲佐菌素致大鼠高血糖模型的实验研究[J].哈尔滨医科大学报,2006,40(4):272-274.[19] Zhang C, Zhou C, Wu XJ, et al. Human CD133-positive hematopoietic progenitor cells initiate growth and metastasis of colorectal cancer cells. Carcinogenesis. 2014;35(12): 2771-2777.[20] Joseph M, Das M, Kanji S, et al. Retention of stemness and vasculogenic potential of human umbilical cord blood stem cells after repeated expansions on PES-nanofiber matrices. Biomaterials. 2014;35(30):8566-8575.[21] González-González M, Rito-Palomares M, Méndez Quintero O. Partition behavior of CD133(+) stem cells from human umbilical cord blood in aqueous two-phase systems: In route to establish novel stem cell primary recovery strategies. Biotechnol Prog. 2014;30(3):700-707.[22] Maslova EV, Andreeva ER, Andrianova IV, et al. Enrichment of umbilical cord blood mononuclears with hemopoietic precursors in co-culture with mesenchymal stromal cells from human adipose tissue. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2014b;156(4): 584-589.[23] Paczkowska E, Kaczyńska K, Pius-Sadowska E, et al. Humoral activity of cord blood-derived stem/progenitor cells: implications for stem cell-based adjuvant therapy of neurodegenerative disorders. PLoS One. 2013;8(12):e83833.[24] Kamei N, Kwon SM, Alev C, et al. Ex-vivo expanded human blood-derived CD133+ cells promote repair of injured spinal cord. J Neurol Sci. 2013;328(1-2):41-50.[25] Scherer PE, Williams S, Fogliano M, et al. A novel serum protein similar to C1q, produced exclusively in adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1995;270(45):26746-26749.[26] Unger RH. Role of glucagon in the pathogenesis of diabetes: the status of the controversy. Metabolism. 1978;27(11): 1691-1709.[27] Ali S, Drucker DJ. Benefits and limitations of reducing glucagon action for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2009;296(3):E415-421.[28] 安雅莉,李光伟,刘雪丽,等.胰岛细胞抗体亚型与胰岛素、胰高血糖素分泌的关联[J].中华内分泌代谢杂志,2004,20(3):190-192. |
.jpg)
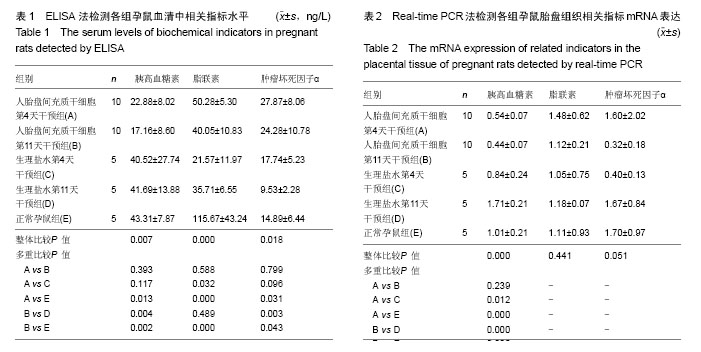
.jpg)