| [1] 刘继中,王臻,胡蕴玉.异体骨关节移植修复肢体大段骨缺损的术后并发症[J].中华外科杂志,2000,38(5):332-335.[2] Petersen BE, Bowen WC, Patrene KD, et al. Bone marrow as a potential source of hepatic oval cells. Science. 1999; 284(5417):1168-1170.[3] Jiang Y, Jahagirdar BN, Reinhardt RL, et al. Pluripotency of mesenchymal stem cells derived from adult marrow. Nature. 2002;418(6893):41-49. [4] Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell. 2009;136(2):215-233. [5] Fabian MR, Sonenberg N, Filipowicz W. Regulation of mRNA translation and stability by microRNAs. Annu Rev Biochem. 2010;79:351-379. [6] Bentwich I. A postulated role for microRNA in cellular differentiation. FASEB J. 2005;19(8):875-879.[7] Ma Y, Qin H, Cui Y. MiR-34a targets GAS1 to promote cell proliferation and inhibit apoptosis in papillary thyroid carcinoma via PI3K/Akt/Bad pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;441(4):958-963.[8] Nakasa T, Ishikawa M, Shi M, et al. Acceleration of muscle regeneration by local injection of muscle-specific microRNAs in rat skeletal muscle injury model. J Cell Mol Med. 2010; 14(10):2495-2505. [9] Hassan MQ, Maeda Y, Taipaleenmaki H, et al. miR-218 directs a Wnt signaling circuit to promote differentiation of osteoblasts and osteomimicry of metastatic cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(50):42084-42092. [10] Su X, Liao L, Shuai Y, et al. MiR-26a functions oppositely in osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs and ADSCs depending on distinct activation and roles of Wnt and BMP signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2015;6:e1851. [11] Wang QF, Huang Y, He GC, et al. Osteoblast differentiation of rabbit adipose-derived stem cells by polyethylenimine- mediated BMP-2 gene transfection in vitro. Genet Mol Res. 2017;16(1). [12] Wang X, Niu D, Hu C, et al. Polyethyleneimine-Based Nanocarriers for Gene Delivery. Curr Pharm Des. 2015; 21(42):6140-6156.[13] Wang M, Guo Y, Yu M, et al. Photoluminescent and biodegradable polycitrate-polyethylene glycol- polyethyleneimine polymers as highly biocompatible and efficient vectors for bioimaging-guided siRNA and miRNA delivery. Acta Biomater. 2017;54:69-80. [14] Liu L, Zheng M, Librizzi D, et al. Efficient and Tumor Targeted siRNA Delivery by Polyethylenimine-graft-polycaprolactone- block-poly(ethylene glycol)-folate (PEI-PCL-PEG-Fol). Mol Pharm. 2016;13(1): 134-143. [15] Boussif O, Lezoualc'h F, Zanta MA, et al. A versatile vector for gene and oligonucleotide transfer into cells in culture and in vivo: polyethylenimine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995;92(16): 7297-7301.[16] Wang X, Niu D, Hu C, et al. Polyethyleneimine-Based Nanocarriers for Gene Delivery. Curr Pharm Des. 2015; 21(42):6140-6156.[17] Liang G, Li Y, Feng W, et al. Polyethyleneimine-coated quantum dots for miRNA delivery and its enhanced suppression in HepG2 cells. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016;11:6079-6088. [18] Parmar MB, Arteaga Ballesteros BE, Fu T, et al. Multiple siRNA delivery against cell cycle and anti-apoptosis proteins using lipid-substituted polyethylenimine in triple-negative breast cancer and nonmalignant cells. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2016;104(12):3031-3044. [19] Neu M, Fischer D, Kissel T. Recent advances in rational gene transfer vector design based on poly(ethylene imine) and its derivatives. J Gene Med. 2005;7(8):992-1009.[20] Qi H, Aguiar DJ, Williams SM, et al. Identification of genes responsible for osteoblast differentiation from human mesodermal progenitor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(6):3305-3310. [21] Garg P, Mazur MM1, Buck AC1, et al. Prospective Review of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Differentiation into Osteoblasts. Orthop Surg. 2017;9(1):13-19. [22] Fu X, Jin L, Wang X, et al. MicroRNA-26a targets ten eleven translocation enzymes and is regulated during pancreatic cell differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(44): 17892-17897.[23] Li H, Xie H, Liu W, et al. A novel microRNA targeting HDAC5 regulates osteoblast differentiation in mice and contributes to primary osteoporosis in humans. J Clin Invest. 2009;119(12): 3666-3677. [24] Hu R, Liu W, Li H, et al. A Runx2/miR-3960/miR-2861 regulatory feedback loop during mouse osteoblast differentiation. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(14):12328-12339. [25] Li Z, Hassan MQ, Jafferji M, et al. Biological functions of miR-29b contribute to positive regulation of osteoblast differentiation. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(23):15676-15684. [26] Li T, Li H, Wang Y, et al. microRNA-23a inhibits osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells by targeting LRP5. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2016; 72:55-62.[27] Tian F, Ji XL, Xiao WA, et al. CXCL13 Promotes Osteogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells by Inhibiting miR-23a Expression. Stem Cells Int. 2015;2015:632305.[28] Cao Y, LV Q, LV C. MicroRNA-153 suppresses the osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells by targeting bone morphogenetic protein receptor type II. Int J Mol Med. 2015;36(3):760-766. [29] Zuo B, Zhu J, Li J, et al. microRNA-103a functions as a mechanosensitive microRNA to inhibit bone formation through targeting Runx2. J Bone Miner Res. 2015;30(2):330-345. [30] Karbiener M, Pisani DF, Frontini A, et al. MicroRNA-26 family is required for human adipogenesis and drives characteristics of brown adipocytes. Stem Cells. 2014;32(6):1578-1590. [31] Hu F, Sun B, Xu P, et al. MiR-218 Induces Neuronal Differentiation of ASCs in a Temporally Sequential Manner with Fibroblast Growth Factor by Regulation of the Wnt Signaling Pathway. Sci Rep. 2017;7:39427.[32] Qu B, Xia X, Yan M, et al. miR-218 is involved in the negative regulation of osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption by partial suppression of p38MAPK-c-Fos-NFATc1 signaling: Potential role for osteopenic diseases. Exp Cell Res. 2015; 338(1):89-96. [33] Taipaleenmäki H, Farina NH, van Wijnen AJ, et al. Antagonizing miR-218-5p attenuates Wnt signaling and reduces metastatic bone disease of triple negative breast cancer cells. Oncotarget. 2016;7(48):79032-79046. [34] Sun F, Ma Y, Cai Z, et al. MiR-218 promotes osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cell through activation of Wnt signaling by targeting SFRP2. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2016;9(10):10188-10196.[35] Zhang WB, Zhong WJ, Wang L. A signal-amplification circuit between miR-218 and Wnt/β-catenin signal promotes human adipose tissue-derived stem cells osteogenic differentiation. Bone. 2014;58:59-66. |
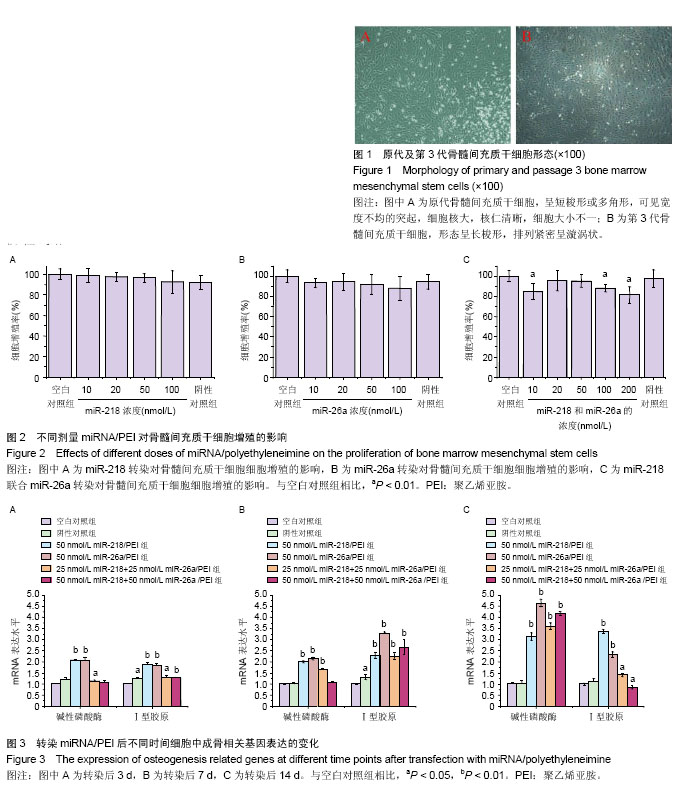
.jpg)
.jpg)
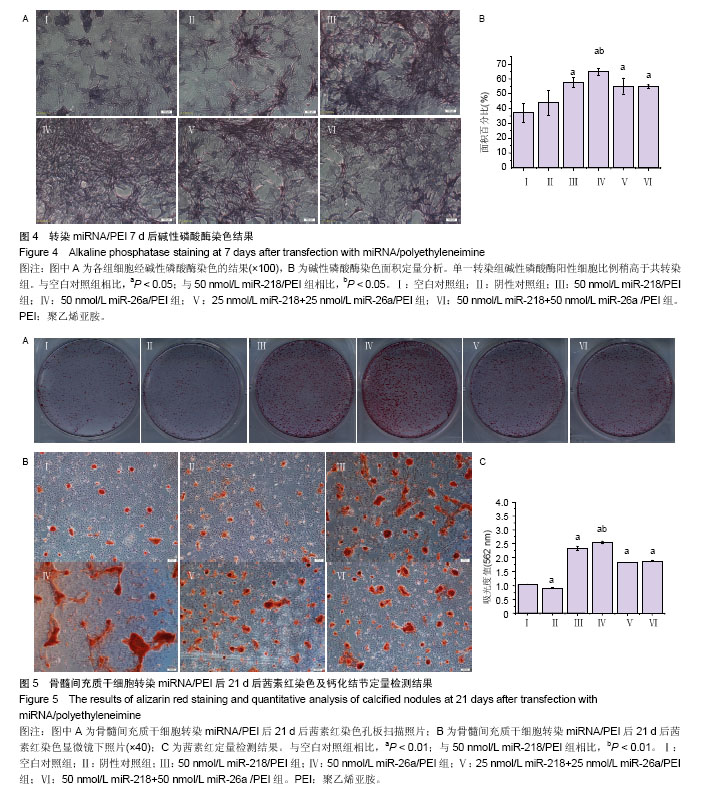
.jpg)