中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (23): 3730-3735.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.23.021
• 骨与关节生物力学 bone and joint biomechanics • 上一篇 下一篇
不同体质量指数正常人的足底压力特征
钟慧敏1,黄 萍2
- 1华东师范大学物理与材料科学学院,上海市 200241;2上海市伤骨科研究所,上海交通大学医学院附属瑞金医院,上海市中西医结合防治骨与关节病损重点实验室,上海市 200025
Plantar pressure of normal people with different body mass index
Zhong Hui-min1, Huang Ping2
- 1School of Physics and Materials Science, East China Normal University, Shanghai 200241, China; 2Shanghai Institute of Traumatology and Orthopaedics, Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai Key Laboratory for Prevention and Treatment of Bone and Joint Diseases with Integrated Chinese-Western Medicine, Shanghai 200025, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
体质量指数:是指体质量与身高平方得出的值,简称BMI(英文为Body Mass Index),当需要比较及分析一个人的体质量对于不同高度的人所带来的健康影响时,体质量指数值是一个中立而可靠的指标。体质量指数是世界公认的一种评定肥胖程度的分级方法,世界卫生组织(WHO)也以体质量指数来对肥胖或超重进行定义。
足底压力:人体在静止站立或者动态行走时在自身重力的作用下,足底在垂直方向上受到一个地面的反作用力,这个力就是足底压力。运用压力测量仪器对人体各体态或不同运动状态下的足底压力的力学、几何学、时间参数值进行测定、分析、研究,揭示不同的足底压力分布特征。美国足部医学会的研究报告显示,一个正常人步行时足部所承担的地面反作用力达到1.5倍体质量,跑步时更达到三至四倍体质量。正常人行走时动态足底最大压力主要位于第2-3跖骨和足跟。步行时足底与支撑面之间的压力分布反映了下肢乃至全身的生理、结构和功能等方面的信息。
摘要
背景:体质量是影响足底压力非常重要的一个因素,多种不同体质量足底压力的系统研究尚未见报道。
目的:检测不同体质量正常人的足底压力情况,为足底压力的应用研究提供参考指标。
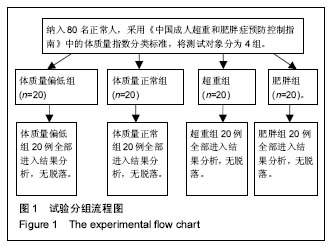
方法:采用比利时RSscan INTERNATIONAL公司生产的Footscan 2 m平板足底压力分布测试系统,对80名不同体质量正常人进行动态足底压力测试。根据《中国成人超重和肥胖症预防控制指南》中的分类标准,将测试对象分为4组,即体质量偏低组、体质量正常组、超重组、肥胖组,每组20人,进行比较分析。
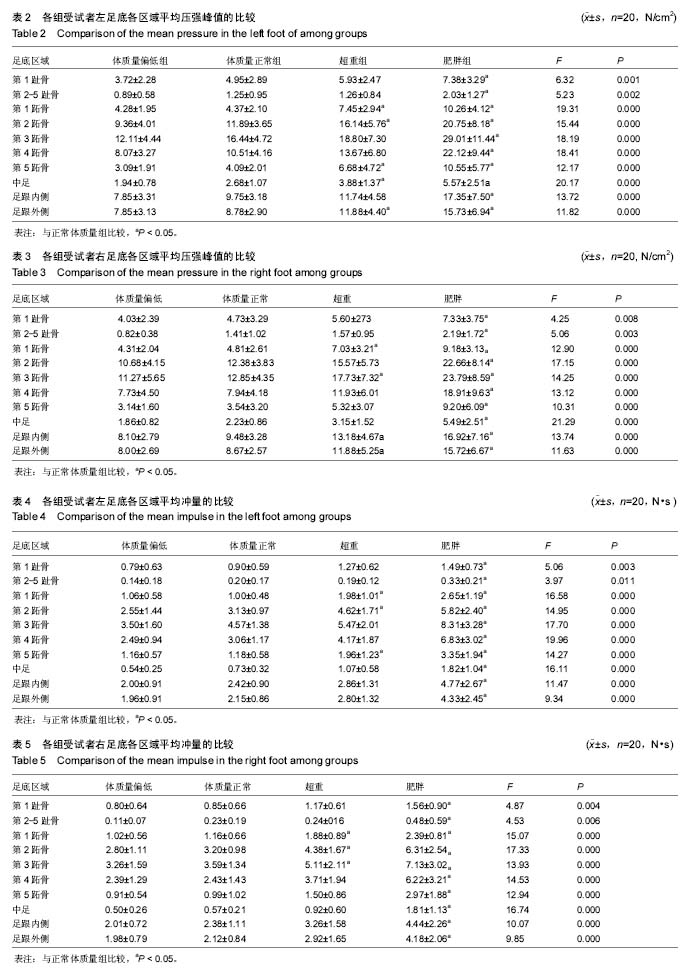
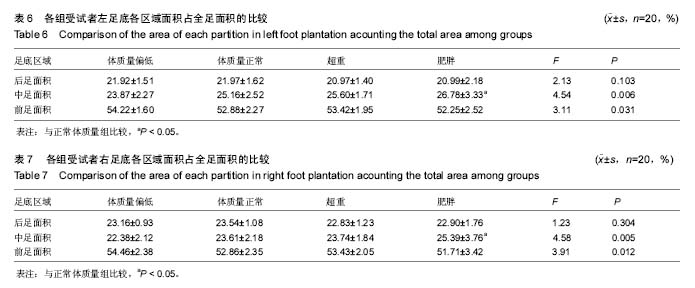
结果与结论:①足底各区域压强峰值和冲量随着受试者体质量指数的增加而增大,差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05);与体质量正常者相比,超重者足底部分区域、肥胖者足底各区域压强增高(P < 0.05);②中足底接触面积占全足底接触面积的百分比随着受试者体质量指数的增加而增大,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01);与体质量正常者相比,肥胖者中足底接触面积占全足底接触面积的百分比增高(P < 0.05);③结果显示,超重特别是肥胖者由于体质量大,其步行时足底压强和冲量相应增高,时间长会造成足部病理性改变;肥胖者体质量大造成足弓下降,中足与地面接触面积增大,易产生扁平足。提示超重特别是肥胖者,要注意控制体质量,适当运动,穿合适的鞋,保护好足,防止足部损伤和扁平足的发生。
ORCID:0000-0001-9701-2734(钟慧敏)
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)