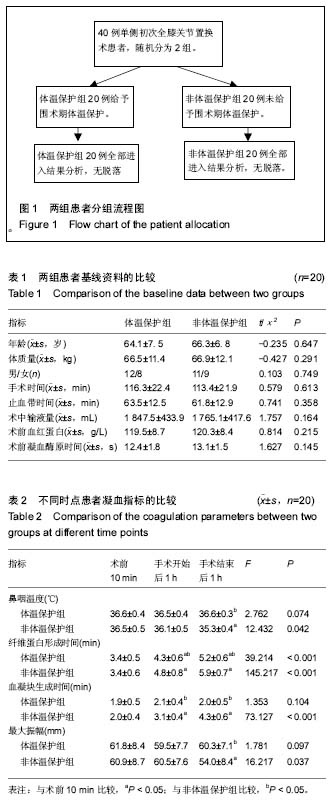
| [1] Leijtens B, Koeter M, Kremers K, et al. High incidence of postoperative hypothermia in total knee and total hip arthroplasty:A prospective observational study. J Arthroplasty. 2013;28(6) :895-898.[2] Winkler M, Akca O,Birkenberq B, et al. Aggressive warming reduces blood loss during hip arthroplasty. Anesth Analg. 2000;91(4):978-984.[3] 刘丹,汪涛,何开华.老年患者全膝关节置换围术期不同输血输液温度对术后恢复质量的影响[J].临床麻醉学杂志,2016,32(2): 122-125.[4] 黄家谷,张克,田华,等.单侧初次全膝关节置换后隐形失血的因素分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(26):3823-3829.[5] 王建祥,金宝城,王友,等.人工膝关节置换术中静滴氨甲环酸对围术期失血量的影响[J].山东医药,2015,55(2):46-47.[6] 时利军,高福强,孙伟,等.鸡尾酒疗法减少全膝关节置换后隐性失血[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(3):329-334.[7] 闵鹏,彭银虓,胡江海,等.氨甲环酸对单次全膝关节置换失血量的影响及安全性评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(17): 2655-2660.[8] 高福强,李子剑,刘延青,等 初次全膝关节置换术后肢体肿胀程度与隐形失血量的相关性研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2011, 19(3):199-202.[9] 刘立柱,宋世锋,张伟. 不同预防方案对初次单侧膝关节置换患者围术期失血量影响的比较[J].医学综述,2016,22(21):4345-4347.[10] 卞春喜,耿秋丽,马永成,等 氨甲环酸关节腔内灌注联合2小时引流管夹闭在初次单侧全膝关节置换术后失血量的临床研究[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2016,13(1):10-12.[11] 蔡元真,朱锦宇,朱庆生.人工全膝关节置换术围手术期失血量的影响因素及预防[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2013,7(1): 132-134.[12] Hofer CK, Wom M,Tavakoli R,et al.Influence of body core temperature on blood loss and transfusion requirements during off pump coronary artery by pass grafting :a comparison of 3 warming systems .J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2005;129(4):838-843.[13] Anderson TA, Fuzaylov G. Perioperative anesthesia management of the burn patient. Surg Clin North Am. 2014; 94(4):851-861.[14] Emetick TH,Ozaki M,Sessler DI,et al.Epidural anesthesia increases apparent leg temperature and decreases the shivering threshold. Anesthesiology. 1994;81(2):289-298.[15] Munday J,Hines SJ, Chang AM. Evidence utilisation project: management of inadvertent perioperative hypothermia.The challenges of implementing best practice recommendations in the perioperative environment. Int J Evid Based Healthc. 2013;11(4):305-311.[16] Jana D, Petr K, Marketa B, et al.The influence of deep hypothermia on inflammatory status,tissue hypoxia and endocrine function of adipose tissue during cardiac surgery. Cryobiology. 2014;68(2):269-275.[17] Tedesco NS,Korpi FP,Pazdernik VK,et al.Relationship between hypothermia and blood loss in adult patients undergoing open lumbar spine surgery.J Am Osteopath Assoc.2014;114(11):828-838.[18] 龚建峰,朱维铭. 低温酸中毒与凝血机制障碍[J].中国实用外科杂志,2010, 30(2) :96-98.[19] Schmied H , Kurz A, Sessler DI,et al. Mild hypothermia increases blood loss and transfusion requirements during total hip arthroplasty. Lancet. 1996;347(1):289-292.[20] Staikou C , Paraskeva A, Drakos E,et al. Impact of graded hypothermia on coagulation and fibrinolysis. J Surg Res. 2011; 167(1):125-130.[21] 许文言,吴晓丹,陈彦青,等.围术期体温保护对腹腔镜胃癌根治术患者凝血功能的影响[J].创伤与急诊电子杂志, 2015,3(4): 51-57.[22] 张黄丽,葛衡江.血栓弹力图和D-二聚体在髋关节置换术患者围术期的变化[J]. 武警医学院学报,2009,18(4) :311-314.[23] 耿玮,张志刚,皮斌,等.血栓弹力图与传统凝血检查监测围关节置换期的凝血状态[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(48): 7709-7716.[24] Nates JL,Cattano D,Chelly JE,et al.Study of acute hemocoagulation changes in a porcine endotoxemic shock model using thrombelastography.Transl Res.2015;165(5): 549-557.[25] Campbell JE,Aden JK,Cap AP.Acute traumatic coagulopathy:Whole blood thrombelastography measures the tip of the iceberg.J Trauma Acute Care Surg.2015;78(5): 955-961.[26] Meyer MA,Ostrowski SR,Sorensen AM,et al.Fibrinogen in trauma, an evaluation of thrombelastography and rotational thromboelastometry fibrinogen assays.J Surg Res.2015; 194(2):581-590.[27] 高飞,严洁.血栓弹力图监测亚低温治疗对心肺复苏患者凝血功能的影响[J].中国急救医学,2016,36(11):1019-1022.[28] 李涓,程志刚.采用血栓弹力图评估不同麻醉方式对膝关节置换术患者血液凝固动态变化的影响[J]. 中国现代医学杂志, 2016, 26(16):114-117.[29] Felferning M, Blaicher A, Kettner SC.Effects of temperature on partial thromboplastin time in heparinized plasma in vitro. Eur Anesthesiol. 2001;18(7):467-470.[30] Kettner SC,Kozek SA,Groetzner JP, et al. Effects of hypothermia on thrombelastography in patients undergoing cardiopulmonary bypass. Br J Anaesth. 1998;80(3): 313-317.[31] 蒋建刚,蒋震伟,周立平,等.亚低温治疗对颅脑损伤后凝血功能的影响[J]. 江苏医药,2010, 36(22) :2697-2698.[32] 魏红艳,胡春林,李欣,等.亚低温对兔心肺复苏后凝血及脑微循环的影响[J]. 中华急诊医学杂志,2011,20(3) :259-263.[33] 袁伟,马华松,王晓平,等. 全膝关节置换后短期血栓预测:D-D二聚体与纤维蛋白降解产物的动态监测[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(17):2661-2666.[34] Pandey CK,Singh A,Kajal K,et al.Intraoperative blood loss in orthotopic liver transplantation:The predictive factors.World J Gastrointest Surg.2015;7(6):86-93.[35] Sun Y,Yang JC,Dang QL,et al.Association between frequency of blood tests and mortality rate in patients undergoing massive blood transfusion:a multicenter study in five regions of china.Int J Clin Exp Med.2015;8(5):8069-8077.[36] Brinkman AC, Ten Tusscher BL,de Waard MC,et al.Minimal effects on ex vivo coagulation during mild therapeutic hypothermia in post cardiac arrest patients.Resuscitation. 2014;85(10):1359-1363.[37] Kander T,Brokopp J,Friberg H,et al. Wide temperature range testing with ROTEM coagulation analyses.Ther Hypothermia Temp Manag.2014;4(3):125-130[38] 莫文耀,陈茂君. 早期使用梯度压力袜对预防颅脑手术后下肢深静脉血栓形成的作用[J]. 成都医学院学报,2014,9(5):569-571.[39] 汪润,刘鹏飞. 骨科术后下肢深静脉血栓形成与麻醉方式的关系分析[J]. 血栓与止血学,2016,22(3):341-343.[40] Azzam FJ, Krock JL.Thermal burns in two infants associated with a forced air warming system.Anesth Analg.1995;81(3): 661.[41] Woon S,Talke P.Amount of air infused to patient increases as fluid flow rates decrease when using the Hotline HL-90 fluid warmer. J Clin Monit Comput. 1999;15(3):149-152.[42] 彭敏,罗翠花. 输血输液加温器在上消化道出血患者中的应用与观察[J]. 临床医学工程,2012,19(6) :849-850.[43] 陈培莲,薛张刚.老年人围术期低温的危害与防治[J]. 老年医学与保健,2014,20(5):344-346.[44] 张玉杰,杨宇.老年患者前列腺电切手术期间体温保护的临床观察[J]. 第三军医大学学报,2016,38(18) :2096-2099.[45] Pu Y,Cen G,Sun J,et al.Warming with an underbody warming system reduces intraoperative hypothermia in patients undergoing laparoscopic gastrointestinal surgery:a randomized controlled study.Int J Nurs Stud.2014;51(2): 181-189.[46] Horosz B,Malec-Milewska M.Inadvertent intraoperative hypothermia.Anaesthesiol Intensive Ther.2013;45(1):38-43.[47] Hill JB,Sexton KW,Bartlett EL,et al.The clinical role of intraoperative core temperature in free tissue transfer.Ann Plast Surg.2015;75(6):620-624.[48] Rowley B,Kerr M,Van Poperin J,et al.Perioperative warming in surgical patients:a comparison of interventions.Clin Nurs Res.2015;24(4)432-441.[49] Waechle RM,Russo SG,Sliwa B,et al.Perioperative thermal management in Germany varies depending on the hospital size.Anaesthesist.2015;64(8):612-622.[50] Jo YY,Chang YJ,Kim YB,et al.Effect of preoperative forced-air warming on hypothermia in elderly patients undergoing transurethral resection of the prostate.Urol J.2015;12(5): 2366-2370.[51] Vanni SM, Braz JR, Modolo NS, et al. Preoperative combined with intraoperative skin-surace warming avoids hypothermia caused by general anesthesia and surgery. J Clin Anesth. 2003;15(2):119-125. |
.jpg)
.jpg)