| [1]Fukushima W, Fujioka M, Kubo T, et al. Nationwide epidemiologic survey of idiopathic osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468(10):2715-2724. [2]Issa K, Pivec R, Kapadia BH, et al. Osteonecrosis of the femoral head: the total hip replacement solution. Bone Joint J. 2013;95-B(11 SupplA):46-50. [3]Matsui M, Saito S, Ohzono K, et al. Experimental steroid-induced osteonecrosis in adult rabbits with hypersensitivity vasculitis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992;(277): 61-72. [4]Saito S, Inoue A, Ono K. Intramedullary haemorrhage as a possible cause of avascular necrosis of the femoral head. The histology of 16 femoral heads at the silent stage. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1987;69(3):346-351. [5]Kawai K, Tamaki A, Hirohata K. Steroid-induced accumulation of lipid in the osteocytes of the rabbit femoral head. A histochemical and electron microscopic study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1985;67(5):755-763. [6]Wang GJ, Sweet DE, Reger SI, et al. Fat-cell changes as a mechanism of avascular necrosis of the femoral head in cortisone-treated rabbits. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1977;59(6): 729-735. [7]Kahya MC, Naziro?lu M, Çi? B. Melatonin and selenium reduce plasma cytokine and brain oxidative stress levels in diabetic rats. Brain Inj. 2015;29(12):1490-1496. [8]Ebert R, Ulmer M, Zeck S, et al. Selenium supplementation restores the antioxidative capacity and prevents cell damage in bone marrow stromal cells in vitro. Stem Cells. 2006;24(5): 1226-1235. [9]Kim JH, Kang JC. Oxidative stress, neurotoxicity, and non-specific immune responses in juvenile red sea bream, Pagrus major, exposed to different waterborne selenium concentrations. Chemosphere. 2015;135:46-52. [10]Stohs SJ, Bagchi D. Oxidative mechanisms in the toxicity of metal ions. Free Radic Biol Med. 1995;18(2):321-336. [11]Yao L, Du Q, Yao H, et al. Roles of oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress in selenium deficiency-induced apoptosis in chicken liver. Biometals. 2015;28(2):255-265. [12]Zhang J, Wang X, Xu T. Elemental selenium at nano size (Nano-Se) as a potential chemopreventive agent with reduced risk of selenium toxicity: comparison with se-methylselenocysteine in mice. Toxicol Sci. 2008;101(1):22-31. [13]Liu X, Deng G, Wang Y, et al. A novel and facile synthesis of porous SiO2-coated ultrasmall Se particles as a drug delivery nanoplatform for efficient synergistic treatment of cancer cells. Nanoscale. 2016;8(16):8536-8541. [14]龚君佐,屠重棋,段宏,等.Fe3O4纳米粒子的组织相容性及组织分布研究[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(52):7872-7877.[15]Ichiseki T, Kaneuji A, Ueda Y, et al. Osteonecrosis development in a novel rat model characterized by a single application of oxidative stress. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63(7): 2138-2141.[16]Huang SL, Jiao J, Yan HW. Hydrogen-rich saline attenuates steroid-associated femoral head necrosis through inhibition of oxidative stress in a rabbit model. Exp Ther Med. 2016;11(1): 177-182. [17]Li GY, Feng Y, Cheng TS, et al. Edaravone, a novel free radical scavenger, prevents steroid-induced osteonecrosis in rabbits. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2013;52(3):438-447. [18]Lu BB, Li KH. Lipoic acid prevents steroid-induced osteonecrosis in rabbits. Rheumatol Int. 2012;32(6):1679-1683. [19]Liu H, Yang X, Zhang Y, et al. Fullerol antagonizes dexamethasone-induced oxidative stress and adipogenesis while enhancing osteogenesis in a cloned bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell. J Orthop Res. 2012;30(7):1051-1057. [20]Uzun G, Mutluoglu M, Ersen O, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy in the treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head: a review of the current literature. Undersea Hyperb Med. 2016;43(3):189-199. [21]Nakamura K, Nakajima Y, Nakamura Y. Characterization of two similar differential tumor markers based on phosphofructokinase activity arising from the influence of cancer patient serum. Cancer Detect Prev. 1988;13(3-4):239-250. [22]Ding H, Wang T, Xu D, et al. Dexamethasone-induced apoptosis of osteocytic and osteoblastic cells is mediated by TAK1 activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015; 460(2):157-163. [23]Zhen YF, Wang GD, Zhu LQ, et al. P53 dependent mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening is required for dexamethasone-induced death of osteoblasts. J Cell Physiol. 2014;229(10):1475-1483. [24]Liang D, Xiang L, Yang M, et al. ZnT7 can protect MC3T3-E1 cells from oxidative stress-induced apoptosis via PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK signaling pathways. Cell Signal. 2013;25(5): 1126-1135. [25]Zhu ZH, Song WQ, Zhang CQ, et al. Dimethyloxaloylglycine increases bone repair capacity of adipose-derived stem cells in the treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Exp Ther Med. 2016;12(5):2843-2850. [26]鲁静,武士科,陈光,等.玻璃酸钠壳聚糖纳米粒对烧伤角膜新生血管生长的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(52):7803-7808.[27]Heath JR. Nanotechnologies for biomedical science and translational medicine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112 (47):14436-14443. [28]Westmeier D, Stauber RH, Docter D. The concept of bio-corona in modulating the toxicity of engineered nanomaterials (ENM). Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2016; 299:53-57. [29]Estevez H, Garcia-Lidon JC, Luque-Garcia JL, et al. Effects of chitosan-stabilized selenium nanoparticles on cell proliferation, apoptosis and cell cycle pattern in HepG2 cells: comparison with other selenospecies. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2014;122:184-193. [30]Srivastava N, Mukhopadhyay M. Green synthesis and structural characterization of selenium nanoparticles and assessment of their antimicrobial property. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2015;38(9):1723-1730. [31]Wang H, Zhang J, Yu H. Elemental selenium at nano size possesses lower toxicity without compromising the fundamental effect on selenoenzymes: comparison with selenomethionine in mice. Free Radic Biol Med. 2007; 42(10):1524-1533. [32]Zhang J, Wang X, Xu T. Elemental selenium at nano size (Nano-Se) as a potential chemopreventive agent with reduced risk of selenium toxicity: comparison with se-methylselenocysteine in mice. Toxicol Sci. 2008;101(1): 22-31. [33]He Y, Chen S, Liu Z, et al, Wang M. Toxicity of selenium nanoparticles in male Sprague-Dawley rats at supranutritional and nonlethal levels. Life Sci. 2014;115(1-2):44-51. [34]Peng D, Zhang J, Liu Q, et al. Size effect of elemental selenium nanoparticles (Nano-Se) at supranutritional levels on selenium accumulation and glutathione S-transferase activity. J Inorg Biochem. 2007;101(10):1457-1463. [35]Robinson E, Kaushal S, Alaboson J, et al. Combinatorial release of dexamethasone and amiodarone from a nano-structured parylene-C film to reduce perioperative inflammation and atrial fibrillation. Nanoscale. 2016;8(7): 4267-4275. [36]Kim K, Jo MC, Jeong S, et al. Externally controlled drug release using a gold nanorod contained composite membrane. Nanoscale. 2016;8(23):11949-11955. [37]Li J, Zhou H, Wang J, et al. Oxidative stress-mediated selective antimicrobial ability of nano-VO2 against Gram-positive bacteria for environmental and biomedical applications. Nanoscale. 2016;8(23):11907-11923. [38]Zhou W, Cao Y, Sui D, et al. Ultrastable BSA-capped gold nanoclusters with a polymer-like shielding layer against reactive oxygen species in living cells. Nanoscale. 2016; 8(18):9614-9620. [39]Hassanin KM, Abd El-Kawi SH, Hashem KS. The prospective protective effect of selenium nanoparticles against chromium-induced oxidative and cellular damage in rat thyroid. Int J Nanomedicine. 2013;8:1713-1720. [40]Liu H, Li X, Qin F, et al. Selenium suppresses oxidative-stress-enhanced vascular smooth muscle cell calcification by inhibiting the activation of the PI3K/AKT and ERK signaling pathways and endoplasmic reticulum stress. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2014;19(3):375-388. [41]Min-Chang G, Wei-Hong T, Zhen X, et al. Effects of Selenium-Enriched Protein from Ganoderma lucidum on the Levels of IL-1 β and TNF-α, Oxidative Stress, and NF-κB Activation in Ovalbumin-Induced Asthmatic Mice. Evid Based Complement lternat Med. 2014;2014:182817. |
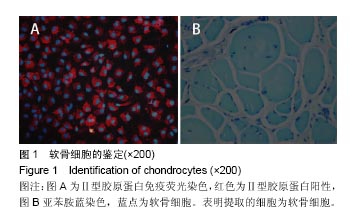
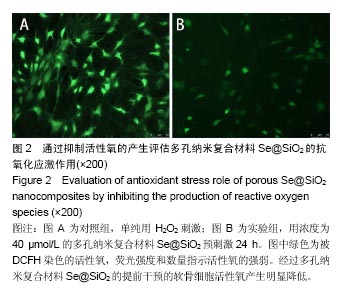
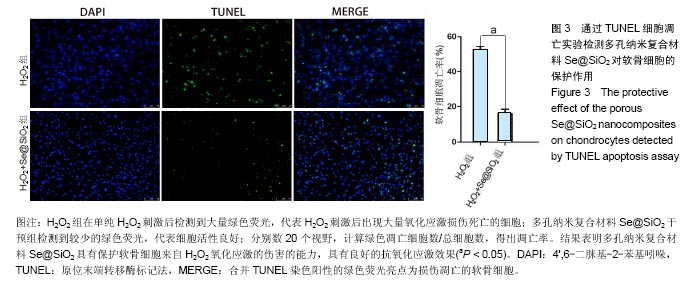
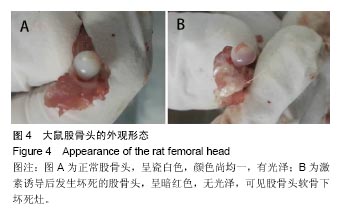
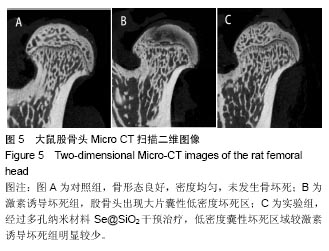
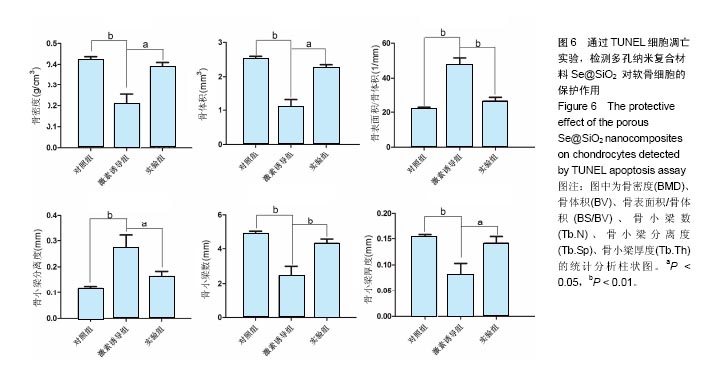
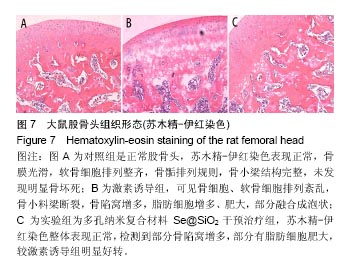
.jpg)
.jpg)