| [1] Jansson A, Pernestig AK, Nilsson P, et al. Toward quantifying the thymic dysfunctional state in mouse models of inflammatory bowel disease .Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2013;19(4):881-888.[2] Coussens LM, Werb Z. Inflammation and cancer. Nature. 2002;420(6917):860-867. [3] 王玉芳,欧阳钦,胡仁伟,等.炎症性肠病流行病学研究进展[J].胃肠病学,2013,18(1): 48-51.[4] Wallace KL, Zheng LB, Kanazawa Y, et al. Immunopathology of inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2014; 20(1):6-21.[5] Pedros C, Gaud G, Bernard I, et al. An Epistatic Interaction between Themis1 and Vav1 Modulates Regulatory T Cell Function and Inflammatory Bowel Disease Development. J Immunol. 2015;195(4):1608-1616. [6] 李家玉,卢启明.炎症性肠病的内科治疗进展[J].甘肃医药,2015, 34(2):98-101. [7] 黄缘.炎症性肠病的治疗现状[J].世界华人消化杂志,2015, 23(26):4150-4154.[8] Larijani B, Esfahani EN, Amini P, et al. Stem cell therapy in treatment of different diseases. Acta Med Iran. 2012;50(2): 79-96.[9] Srivastava AS, Feng Z, Mishra R, et al. Embryonic stem cells ameliorate piroxicam-induced colitis in IL10-/- KO mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;361(4):953-959.[10] 徐隽,智发朝.炎症性肠病治疗新进展—干细胞治疗[J]. 现代消化及介入诊疗,2015,20(4):447-451. [11] Gazouli M, Roubelakis MG, Theodoropoulos GE. Stem cells as potential targeted therapy for inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2014;20(5):952-955.[12] Cassinotti A, Annaloro C, Ardizzone S, et al. Autologous haematopoietic stem cell transplantation without CD34+ cell selection in refractory Crohn's disease. Gut. 2008;57(2): 211-217.[13] Hommes DW, Duijvestein M, Zelinkova Z, et al. Long-term follow-up of autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for severe refractory Crohn's disease. J Crohns Colitis. 2011;5(6):543-549.[14] Snowden JA, Saccardi R, Allez M, et al. Haematopoietic SCT in severe autoimmune diseases: updated guidelines of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2012;47(6):770-790.[15] Hawkey CJ, Allez M, Clark MM, et al. Autologous Hematopoetic Stem Cell Transplantation for Refractory Crohn Disease: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2015;314(23): 2524-2534.[16] 李楠.脐带间充质干细胞与炎症性肠病[J].山东医药,2011, 51(16):8-9.[17] Kim HS, Shin TH, Lee BC, et al. Human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells reduce colitis in mice by activating NOD2 signaling to COX2. Gastroenterology. 2013;145(6): 1392-1403.[18] Corridoni D, Kodani T, Rodriguez-Palacios A, et al. Dysregulated NOD2 predisposes SAMP1/YitFc mice to chronic intestinal inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(42):16999-17004.[19] 彭凯玥,钱晓文,吴冰冰.脐血干细胞移植治疗白介素10受体A基因突变导致的极早发型炎症性肠病1例病例报告并文献复习[J].中国循证儿科杂志,2016,11(3):171-176.[20] Rahimzadeh A, Mirakabad FS, Movassaghpour A, et al. Biotechnological and biomedical applications of mesenchymal stem cells as a therapeutic system. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2016;44(2):559-570.[21] Irhimeh MR, Cooney J. Management of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Using Stem Cell Therapy. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;11(1):72-77.[22] Forbes GM, Sturm MJ, Leong RW, et al. A phase 2 study of allogeneic mesenchymal stromal cells for luminal Crohn's disease refractory to biologic therapy. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;12(1):64-71.[23] Castelo-Branco MT, Soares ID, Lopes DV, et al. Intraperitoneal but not intravenous cryopreserved mesenchymal stromal cells home to the inflamed colon and ameliorate experimental colitis. PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e33360.[24] 葛翠翠,王慧娜,杜丽欣,等.人脐带间充质干细胞对炎症性肠病小鼠模型的治疗作用[J].生物技术通讯,2014,25(6):813-816.[25] Lalu MM, McIntyre L, Pugliese C, et al. Safety of cell therapy with mesenchymal stromal cells (SafeCell): a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. PLoS One. 2012; 7(10):e47559.[26] Taddio A, Tommasini A, Valencic E, et al. Failure of interferon-γ pre-treated mesenchymal stem cell treatment in a patient with Crohn's disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21(14):4379- 4384.[27] Valencic E, Piscianz E, Andolina M, et al. The immunosuppressive effect of Wharton's jelly stromal cells depends on the timing of their licensing and on lymphocyte activation. Cytotherapy. 2010;12(2):154-160.[28] Lin Y, Lin L, Wang Q, et al. Transplantation of human umbilical mesenchymal stem cells attenuates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2015;42(1):76-86.[29] Tang RJ, Shen SN, Zhao XY, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells-regulated Treg cells suppress colitis-associated colorectal cancer. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;6:71.[30] Banerjee A, Bizzaro D, Burra P, et al. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells modulate dextran sulfate sodium induced acute colitis in immunodeficient mice. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;6:79.[31] Zhuang Y, Li D, Fu J, et al. Comparison of biological properties of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells from early and late passages: immunomodulatory ability is enhanced in aged cells. Mol Med Rep. 2015;11(1):166-174.[32] Fuenzalida P, Kurte M, Fernández-O'ryan C, et al. Toll-like receptor 3 pre-conditioning increases the therapeutic efficacy of umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cells in a dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis model. Cytotherapy. 2016; 18(5):630-641.[33] 郭婧,晁康,康健,等.过表达IL-17RLM的人脐带间充质干细胞对TNBS诱导的结肠炎小鼠脾脏淋巴细胞的免疫调节作用[J].中国病理生理杂志,2016,32(6):961-970.[34] Chen Y, Song Y, Miao H, et al. Gene delivery with IFN-γ-expression plasmids enhances the therapeutic effects of MSCs on DSS-induced mouse colitis. Inflamm Res. 2015; 64(9):671-681.[35] 刘静,韩冬梅,薛梅,等.脐带间充质干细胞输注治疗顽固性溃疡性结肠炎[J].组织工程与重建外科杂志,2011,7(5):258-260.[36] Fayyad-Kazan H, Faour WH, Badran B, et al. The immunomodulatory properties of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells are defined according to multiple immunobiological criteria. Inflamm Res. 2016;65(6):501-510.[37] 段江洁,王蓓,张建华,等.胎儿肠壁结缔组织诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向肠上皮细胞的分化[J]. 第三军医大学学报,2008,30(18): 1718-1721.[38] 张夏梦,寿折星,石月萍,等.骨髓间充质干细胞对溃疡性结肠炎大鼠结肠组织血管内皮的修复作用[J].世界华人消化杂志,2013, 21(28):2908-2914.[39] 刘星星,范恒,唐庆,等.过表达CXCR4的间充质干细胞缓解实验性结肠炎[J]. 世界华人消化杂志,2016, 24(8):1233-1240.[40] Forte D, Ciciarello M, Valerii MC, et al. Human cord blood-derived platelet lysate enhances the therapeutic activity of adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells isolated from Crohn's disease patients in a mouse model of colitis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;6:170.[41] Mizushima T, Takahashi H, Takeyama H, et al. A clinical trial of autologous adipose-derived regenerative cell transplantation for a postoperative enterocutaneous fistula. Surg Today. 2016;46(7):835-842.[42] Lee WY, Park KJ, Cho YB, et al. Autologous adipose tissue-derived stem cells treatment demonstrated favorable and sustainable therapeutic effect for Crohn's fistula. Stem Cells. 2013;31(11):2575-2581.[43] Herreros MD, Garcia-Arranz M, Guadalajara H, et al. Autologous expanded adipose-derived stem cells for the treatment of complex cryptoglandular perianal fistulas: a phase III randomized clinical trial (FATT 1: fistula Advanced Therapy Trial 1) and long-term evaluation. Dis Colon Rectum. 2012;55(7):762-772.[44] 祝芳,曲波,金世柱,等.肠道干细胞与炎症性肠病的关系[J].胃肠病学和肝病学杂志,2013,22(8):717-719.[45] Barker N, van Es JH, Kuipers J, et al. Identification of stem cells in small intestine and colon by marker gene Lgr5. Nature. 2007;449(7165):1003-1007.[46] Shaker A, Rubin DC. One step closer to gut repair. Nature. 2014;485(7397):181-182.[47] Takahashi K, Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell. 2006;126(4):663-676.[48] Wagnerova A, Gardlik R. In vivo reprogramming in inflammatory bowel disease. Gene Ther. 2013;20(12): 1111-1118.[49] Munir H, McGettrick HM. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for Autoimmune Disease: Risks and Rewards. Stem Cells Dev. 2015;24(18):2091-2100. |
.jpg)
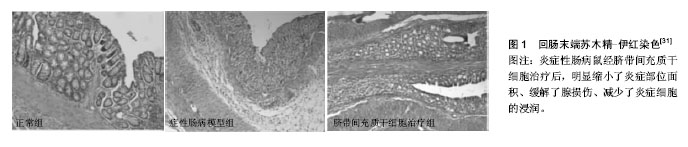
.jpg)