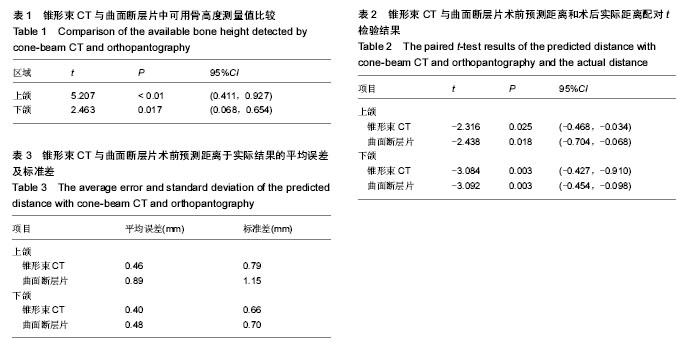
| [1] Oshida Y, Tuna EB, Aktören O, et al. Dental Implant Systems. Int J Mol Sci. 2010; 11(4): 1580-1678.[2] 王迪,杨文香,谢用江. 牙列缺损种植义齿修复的口腔健康相关生活质量分析[J]. 心理医生, 2016, 22(5):129-130.[3] Aunmeungtong W, Kumchai T, Strietzel FP, et al. Comparative Clinical Study of Conventional Dental Implants and Mini Dental Implants for Mandibular Overdentures: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2016.[4] Hu KS, Choi DY, Lee WJ, et al. Reliability of two different presurgical preparation methods for implant dentistry based on panoramic radiography and cone-beam computed tomography in cadavers.J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2012;42: 39-44.[5] Bruschi M, Steinmüller-Nethl D, Goriwoda W, et al. Composition and Modifications of Dental Implant Surfaces. J Oral Implants. 2015;2015(527426):1-14.[6] Gittens RA, Scheideler L, Rupp F, et al. A review on the wettability of dental implant surfaces II: Biological and clinical aspects. Acta Biomaterialia. 2014; 10(7):2907-2918.[7] Esposito M, Grusovin MG, Felice P, et al. Interventions for replacing missing teeth: horizontal and vertical bone augmentation techniques for dental implant treatment. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009;4:CD003607. [8] Esposito M, Grusovin MG, Rees J, et al. Effectiveness of sinus lift procedures for dental implant rehabilitation: a Cochrane systematic review. Eur J Oral Implantol.2010;3:7-26. [9] 唐礼,陈东晖.颌骨曲面断层片垂直方向放大率的临床分析[J].中国临床新医学,2009,2(11):1152-1154.[10] Cati? A, Celebi? A, Valenti?-Peruzovi? M, et al. Evaluation of Precision of Dimensional Measurements of the Mandible on Panoramic Radiographs: A Digital Radiographic Study. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1998;86(2): 242-248.[11] Eiu K, Zhuruli GN, Kuznetsov AV, et al. Study of stomatological status in patients of dental implantological clinic according to the data of orthopantomography and computer tomography. Stomatologiia. 2010;89(5):39-42.[12] Amarnath GS, Kumar U, Hilal M, et al. Comparison of Cone Beam Computed Tomography, Orthopantomography with Direct Ridge Mapping for Pre-Surgical Planning to Place Implants in Cadaveric Mandibles: An Ex-Vivo Study. J Int Oral Health. 2015;7(Suppl 1):38-42.[13] Dreiseidler T, Mischkowski RA, Neugebauer J, et al. Comparison of cone-beam imaging with orthopantomography and computerized tomography for assessment in presurgical implant dentistry. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24(2):216-225.[14] 杨艺强,刘琪,庄东鹏,等.数字化根尖片、曲面断层片、CBCT测量牙齿长度准确性的比较研究[J].临床放射学杂志, 2014, 33(9): 1434-1437.[15] Lindquist LW, Carlsson GE, Jemt T. A prospective 15-year follow-up study of mandibular fixed prostheses supported by osseointegrated implants. Clinical results and marginal bone loss. Clin Oral Implants Res.1996;7: 329-336. [16] Paula LK, Solondemello PA, Mattos CT, et al. Influence of magnification and superimposition of structures on cephalometric diagnosis. Dental Press J Orthod. 2015;20(2): 29.[17] 陆婧雅,王银龙,朱友明,等.曲面断层片和锥形束CT对下颌阻生第三磨牙与下颌神经管位置关系的研究[J]. 安徽医药, 2016, 20(4):695-698.[18] Chopra A, Mhapuskar AA, Marathe S, et al. Evaluation of Osseointegration in Implants using Digital Orthopantomogram and Cone Beam Computed Tomography. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2016;17(11):953-957. [19] Kernen F, Benic GI, Payer M, et al. Accuracy of Three-Dimensional Printed Templates for Guided Implant Placement Based on Matching a Surface Scan with CBCT. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2016;18(4):762-768. [20] Guerrero ME, Noriega J, Castro C, et al. Does cone-beam CT alter treatment plans? Comparison of preoperative implant planning using panoramic versus cone-beam CT images. Imaging Sci Dent. 2014;44: 121-128.[21] Sung CE, Cochran DL, Cheng WC, et al. Preoperative assessment of labial bone perforation for virtual immediate implant surgery in the maxillary esthetic zone: A computer simulation study. J Am Dent Assoc. 2015;146(11):808.[22] Vazquez L, Nizamaldin Y, Combescure C, et al. Accuracy of vertical height measurements on direct digital panoramic radiographs using posterior mandibular implants and metal balls as reference objects. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2013;42: 20110429.[23] 高萃,赵红艳,孙婷婷,等. 曲面断层片和锥形束CT对上颌阻生尖牙的定位分析[J]. 口腔医学研究, 2015, 31(2):171-174.[24] Yamada S, Uchida K, Iwamoto Y, et al. Panoramic radiography measurements, osteoporosis diagnoses and fractures in Japanese men and women. Oral Dis. 2015; 21(3):335–341.[25] Yun-Hoa J, Bong-Hae C. Assessment of maxillary third molars with panoramic radiography and cone-beam computed tomography. Imaging Sci Dent. 2015;45(4):233.[26] Reddy MS, Mayfield-Donahoo T, Vanderven FJ, et al. A comparison of the diagnostic advantages of panoramic radiography and computed tomography scanning for placement of root form dental implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1994; 5: 229-238. [27] 孙小玲,方平娟,孙仁义,等.锥形束CT与曲面断层片下颌神经管与牙槽骨嵴间距离的比较[J]. 温州医科大学学报, 2013, 43(11): 740-742.[28] 向梅, 张宇. 传统种植导板与3D打印种植导板的设计制作及精确性的分析[D].南方医科大学,2016.[29] Sarment DP, Sukovic P, Clinthorne N. accuracy of implant placement with a stereolithographic surgical guide. Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2003;18(4):571-557. [30] Luangchana P, Pornprasertsuk-Damrongsri S, Kiattavorncharoen S, et al. Accuracy of linear measurements using cone beam computed tomography and panoramic radiography in dental implant treatment planning. Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2015;30(6):1287-1294.[31] 陈佳张志宏刘红红,等.曲面体层片与锥形束 CT 对种植区骨量测量的临床评价[J].安徽医科大学学报,2015,50(3):393-395.[32] Dagassan-Berndt DC, Zitzmann NU, Walter C, et al. Implant treatment planning regarding augmentation procedures: panoramic radiographs vs. cone beam computed tomography images. Clin Oral Implants. 2015. doi: 10.1111/clr.12666. |
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)