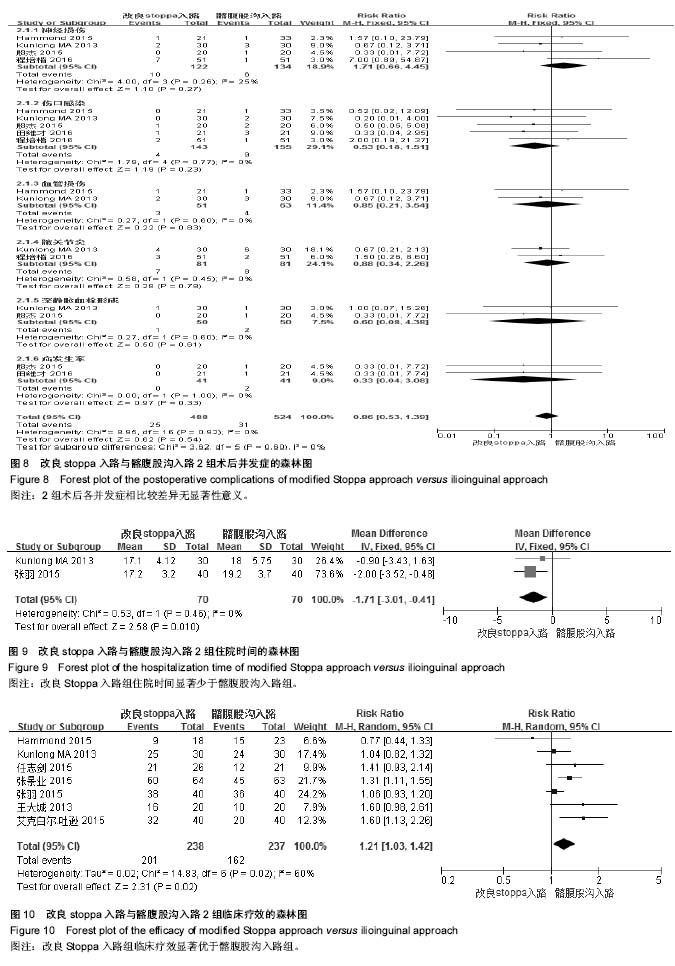
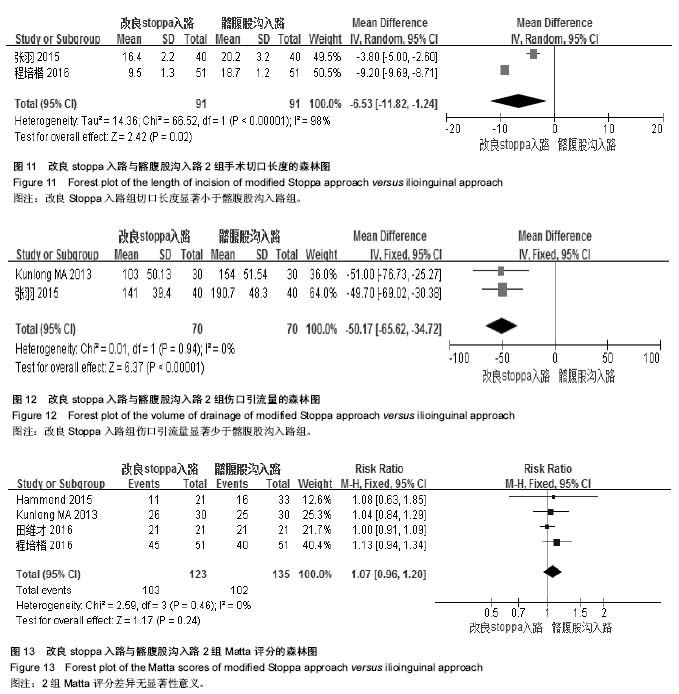
| [1] Laird A, Keating JF. Acetabular fractures: a 16-year prospective epidemiological study.J Bone Joint Surg Br.2005;87(7): 969-973.[2] Balogh Z, King KL, Mackay P, et al. The epidemiology of pelvic ring fractures: a population-based study. J Trauma.2007;63(5): 1066-1073; discussion 1072-1063.[3] 柯铁. Stoppa入路联合髂骨螺钉治疗复杂骨盆骨折31例[J].福建医药杂志, 2016, 38(3): 32-34.[4] 陈明.不稳定型骨盆骨折的手术方式探讨[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2013, 15(5): 445-447.[5] 周东生. 髋臼骨折的治疗进展及思考[J].中国骨伤,2016, 29(4): 293-297.[6] Guerado E, Cano JR, Cruz E. Fractures of the acetabulum in elderly patients: An update.Injury,2012, 43(SUPPL. 2): S33-S41.[7] 崔志民. 微创固定治疗不稳定骨盆骨折40例临床研究[J].中外医学研究, 2013, 11(21): 190-191.[8] 魏帅帅. 新改良Stoppa入路治疗骨盆、髋臼骨折[J].临床骨科杂志, 2012, 15(3): 264-267.[9] 钱荣勋. 改良Stoppa入路与腹股沟入路行髋臼骨折切开复位内固定术的比较[J]. 实用骨科杂志, 2015, 21(9): 784-788.[10] Zha GC, Sun JY, Dong SJ. Predictors of clinical outcomes after surgical treatment of displaced acetabular fractures in the elderly.J Orthop Res. 2013;31(4):588-595.[11] Lao A, Putman S, Soenen M, et al. The ilio-inguinal approach for recent acetabular fractures: ultrasound evaluation of the ilio-psoas muscle and complications in 24 consecutive patients. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res.2014; 100(4):375-378.[12] Oh H-K, Choo SK, Kim J-J, et al. Stoppa Approach for Anterior Plate Fixation in Unstable Pelvic Ring Injury. Clin Orthop Surg. 2016;8(3):243-248.[13] Elmadag M, Uzer G, Yildiz F, et al.Safety of modified Stoppa approach for Ganz periacetabular osteotomy: A preliminary cadaveric study. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2016;50(4): 409-414.[14] Elmadag M, Guzel Y, Aksoy Y, et al. Surgical Treatment of Displaced Acetabular Fractures Using a Modified Stoppa Approach. Orthopedics.2016;39(2): e340-345.[15] Bastian JD, Savic M, Cullmann JL, et al. Surgical exposures and options for instrumentation in acetabular fracture fixation: Pararectus approach versus the modified Stoppa. Injury. 2016; 47(3):695-701. [16] Letournel E. Acetabulum fractures: classification and management.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1980;(151): 81-106.[17] Matta JM. Operative treatment of acetabular fractures through the ilioinguinal approach. A 10-year perspective. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1994;(305):10-19.[18] Briffa N, Pearce R, Hill AM, et al. Outcomes of acetabular fracture fixation with ten years' follow-up[J]. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery - Series B.2011;93B(2): 229-236.[19] Rocca G, Spina M. Anterior combined endopelvic (ACE) approach for the treatment of the acetabular and pelvic ring fractures: A new proposal. Injury. 2014;45 Suppl 6:S9-S15. [20] Matta JM. Fractures of the acetabulum: accuracy of reduction and clinical results in patients managed operatively within three weeks after the injury.J Bone Joint Surg Am.1996;78(11):1632-1645.[21] Kothe M, Lein T, Weber AT, et al. [Morel-Lavallee lesion. A grave soft tissue injury]Unfallchirurg.2006;109(1): 82-86.[22] Cole JD, Bolhofner BR.Acetabular fracture fixation via a modified Stoppa limited intrapelvic approach. Description of operative technique and preliminary treatment results. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1994;(305):112-123.[23] Hirvensalo E, Lindahl J, Bostman O. A new approach to the internal fixation of unstable pelvic fractures.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1993;(297): 28-32.[24] Shazar N, Eshed I, Ackshota N, et al. Comparison of acetabular fracture reduction quality by the ilioinguinal or the anterior intrapelvic (modified Rives-Stoppa) surgical approaches. J Orthop Trauma. 2014;28(6):313-319.[25] Andersen RC, O'Toole RV, Nascone JW, et al.Modified stoppa approach for acetabular fractures with anterior and posterior column displacement: Quantification of radiographic reduction and analysis of interobserver variability. J Orthop Trauma. 2010;24(5):271-278.[26] Sagi HC, Afsari A, Dziadosz D. The anterior intra-pelvic (modified rives-stoppa) approach for fixation of acetabular fractures.J Orthop Trauma. 2010;24(5):263-270.[27] Archdeacon MT,Kazemi N,Guy P,et al.The modified stoppa approach for acetabular fracture. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2011 Mar;19(3):170-175.[28] Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary?. Control Clin Trials. 1996;17(1): 1-12.[29] 田维才. 改良Stoppa入路在髋臼及骨盆骨折手术治疗中的应用[J].大家健康(下旬版),2016, 10(8): 111-111.[30] 王大城. 经改良Stoppa入路治疗骨盆髋臼骨折的疗效观察[J].中国医药指南, 2013,11(23):103-104.[31] 艾克白尔•吐逊. 改良Stoppa入路手术用于髋臼骨折中的有效性及可行性[J].中国伤残医学, 2015, 23(18): 47-48.[32] 任志剑. 经改良Stoppa入路治疗骨盆髋臼骨折的效果分析[J].中外医学研究, 2015, 13(3): 19-20.[33] 杨自龙. 改良Stoppa入路方式在骨盆骨折、髋臼骨折治疗中的应用效果探讨[J]. 当代医学, 2015, 21(3): 81-82.[34] 殷杰. 改良Stoppa入路手术方法治疗骨盆髋臼骨折的临床疗效分析[J].陕西医学杂志, 2015, (9): 1224-1226.[35] 张景业. 改良Stoppa入路治疗骨盆髋臼骨折的临床观察[J].当代医学, 2015, 21(33): 32-33.[36] 张羽. 髂腹股沟入路和改良Stoppa入路治疗髋臼骨折的效果对比[J]. 当代医学, 2015, 21(20): 75-76.[37] 程培楷. 新型改良Stoppa入路治疗髋臼骨折合并同侧骨盆骨折的临床效果[J]. 牡丹江医学院学报, 2016, 37(3): 84-85.[38] Ma K, Luan F, Wang X, et al. Randomized, controlled trial of the modified Stoppa versus the ilioinguinal approach for acetabular fractures. Orthopedics.2013;36(10): e1307-1315.[39] Hammad AS,El-Khadrawe TA.Accuracy of reduction and early clinical outcome in acetabular fractures treated by the standard ilio-inguinal versus the Stoppa/iliac approaches. Injury.2015;46(2): 320-326.[40] Xu Y,Lin C,Zhang L,et al.Anterograde fixation module for posterior acetabular column fracture: Computer-assisted determination of optimal entry point, angle, and length for screw insertion. Medical Science Monitor. 2016; 22: 3106-3112.[41] Elmada M, Güzel Y, Ali Acar M, et al.The Stoppa approach versus the ilioinguinal approach for anterior acetabular fractures: A case control study assessing blood loss complications and function outcomes. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2014;100(6):675-680.[42] 李坤. 改良Stoppa入路和髂腹股沟入路治疗髋臼骨折临床疗效的Meta分析[J]. 大连医科大学硕士学位论文,2015.[43] 王小健, 苏云星, 郭秀生,等. 经髂腹股沟入路与+Stoppa+入路治疗移位型髋臼骨折临床疗效的+Meta+分析[J].中华解剖与临床杂志, 2016, 21(5): 426-431[44] Nayak SB, Deepthinath R, Prasad AM, et al.A South Indian cadaveric study on obturator neurovascular bundle with a special emphasis on high prevalence of 'venous corona mortis'.Injury.2016;47(7): 1452-1455.[45] Darmanis S, Lewis A, Mansoor A, et al. Corona mortis: An anatomical study with clinical implications in approaches to the pelvis and acetabulum. Clinical Anatomy.2007;20(4): 433-439.[46] 王钢. Stoppa入路在骨盆髋臼骨折中的应用及典型病例分析[C].第五届上海国际骨科前沿技术与临床转化学术会议论文集,上海:2011:134,133. |
.jpg)


.jpg)