| [1] Dhawan A, Puppi J, Hughes RD, et al. Human hepatocyte transplantation: current experience and future challenges. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;7(5):288-298.[2] Tralhão JG, Abrantes AM, Hoti E, et al. Hepatectomy and liver regeneration: from experimental research to clinical application. ANZ J Surg. 2014;84(9):665-671.[3] Pham PV. Adipose stem cells in the clinic. Biomedical Research Therapy. 2014;1(2):57-70.[4] Kubo N, Narumi S, Kijima H, et al. Efficacy of adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells for fulminant hepatitis in mice induced by concanavalin A. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;27(1):165-172.[5] Harn HJ, Lin SZ, Hung SH, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells can abrogate chemical-induced liver fibrosis and facilitate recovery of liver function. Cell Transplant. 2012;21(12): 2753-2764.[6] Zuk PA, Zhu M, Mizuno H, et al. Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies. Tissue Eng. 2001;7(2):211-228.[7] Banas A, Teratani T, Yamamoto Y, et al. Rapid hepatic fate specification of adipose-derived stem cells and their therapeutic potential for liver failure. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;24(1):70-77.[8] Yukawa H, Noguchi H, Oishi K, et al. Cell transplantation of adipose tissue-derived stem cells in combination with heparin attenuated acute liver failure in mice. Cell Transplant. 2009; 18(5):611-618.[9] Ranganath SH, Levy O, Inamdar MS, et al. Harnessing the mesenchymal stem cell secretome for the treatment of cardiovascular disease. Cell Stem Cell. 2012;10(3):244-258.[10] Chung H, Hong DP, Jung JY, et al. Comprehensive analysis of differential gene expression profiles on carbon tetrachloride-induced rat liver injury and regeneration. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2005;206(1):27-42.[11] 杨志峰,杨清玲, 陈昌杰. 趋化因子SDF-1与受体CXCR4的研究进展[J]. 分子诊断与治疗杂志, 2011, 3(1):58-61.[12] Ezzat T, Dhar DK, Malago M, et al. Dynamic tracking of stem cells in an acute liver failure model. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18(6):507-516.[13] Berry PA, Antoniades CG, Hussain MJ, et al. Admission levels and early changes in serum interleukin-10 are predictive of poor outcome in acute liver failure and decompensated cirrhosis. Liver Int. 2010;30(5):733-740.[14] Tögel F, Hu Z, Weiss K, et al. Administered mesenchymal stem cells protect against ischemic acute renal failure through differentiation-independent mechanisms. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2005;289(1):F31-42.[15] Parekkadan B, van Poll D, Suganuma K, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived molecules reverse fulminant hepatic failure. PLoS One. 2007;2(9):e941.[16] Higashimoto M, Sakai Y, Takamura M, et al. Adipose tissue derived stromal stem cell therapy in murine ConA-derived hepatitis is dependent on myeloid-lineage and CD4+ T-cell suppression. Eur J Immunol. 2013;43(11):2956-2968.[17] Du Z, Wei C, Cheng K, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium reduces liver injury and enhances regeneration in reduced-size rat liver transplantation. J Surg Res. 2013;183(2):907-915.[18] Salomone F, Barbagallo I, Puzzo L, et al. Efficacy of adipose tissue-mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in rats with acetaminophen liver injury. Stem Cell Res. 2013;11(3): 1037-1044.[19] Weber LW, Boll M, Stampfl A. Hepatotoxicity and mechanism of action of haloalkanes: carbon tetrachloride as a toxicological model. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2003;33(2):105-136.[20] O'Garra A, Barrat FJ, Castro AG, et al. Strategies for use of IL-10 or its antagonists in human disease. Immunol Rev. 2008;223:114-131.[21] Serra MP, Marongiu F, Sini M, et al. Hepatocyte senescence in vivo following preconditioning for liver repopulation. Hepatology. 2012;56(2):760-768.[22] Serra MP, Marongiu F, Sini M, et al. Hepatocyte senescence induced by radiation and partial hepatectomy in rat liver. Int J Radiat Biol. 2014;90(10):876-883.[23] 马珊珊,刘静,姚宁,等. p16基因高表达对293细胞衰老的影响[J].郑州大学学报:医学版, 2014,49(5):622-625.[24] Yu SL, Kang MS, Kim HY, et al. The PCNA binding domain of Rad2p plays a role in mutagenesis by modulating the cell cycle in response to DNA damage. DNA Repair (Amst). 2014;16:1-10.[25] Seki A, Sakai Y, Komura T, et al. Adipose tissue-derived stem cells as a regenerative therapy for a mouse steatohepatitis- induced cirrhosis model. Hepatology. 2013;58(3):1133-1142.[26] Seki T, Yokoyama Y, Nagasaki H, et al. Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation promotes hepatic regeneration after hepatic ischemia-reperfusion and subsequent hepatectomy in rats. J Surg Res. 2012;178(1):63-70.[27] Koellensperger E, Niesen W, Kolbenschlag J, et al. Human adipose tissue derived stem cells promote liver regeneration in a rat model of toxic injury. Stem Cells Int. 2013;2013: 534263.[28] Liu T, Mu H, Shen Z, et al. Autologous adipose tissue?derived mesenchymal stem cells are involved in rat liver regeneration following repeat partial hepatectomy. Mol Med Rep. 2016; 13(3):2053-2059. |
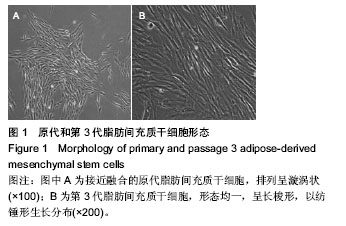
.jpg)
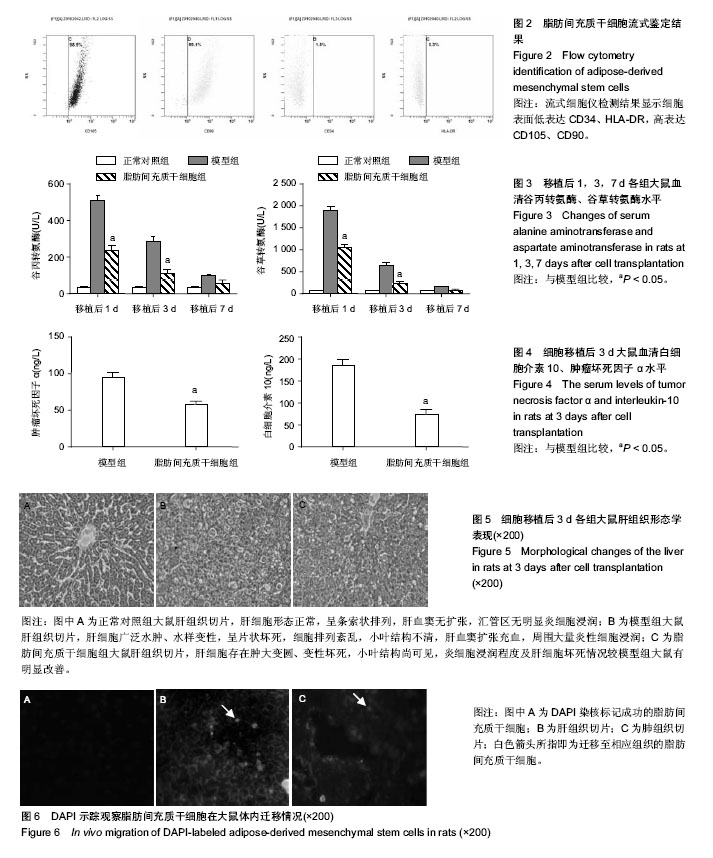
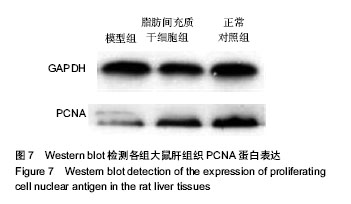
.jpg)