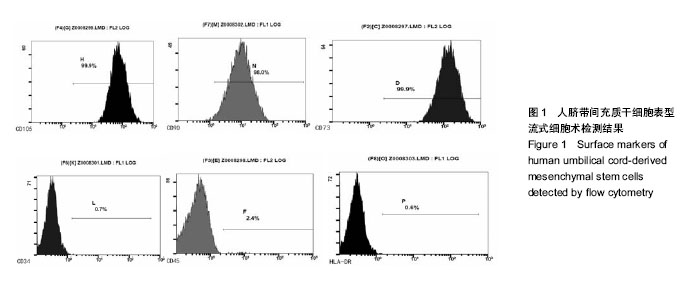
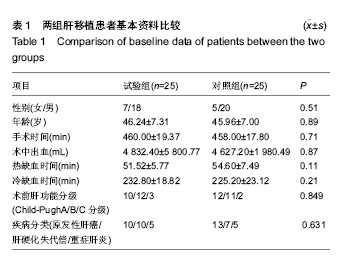
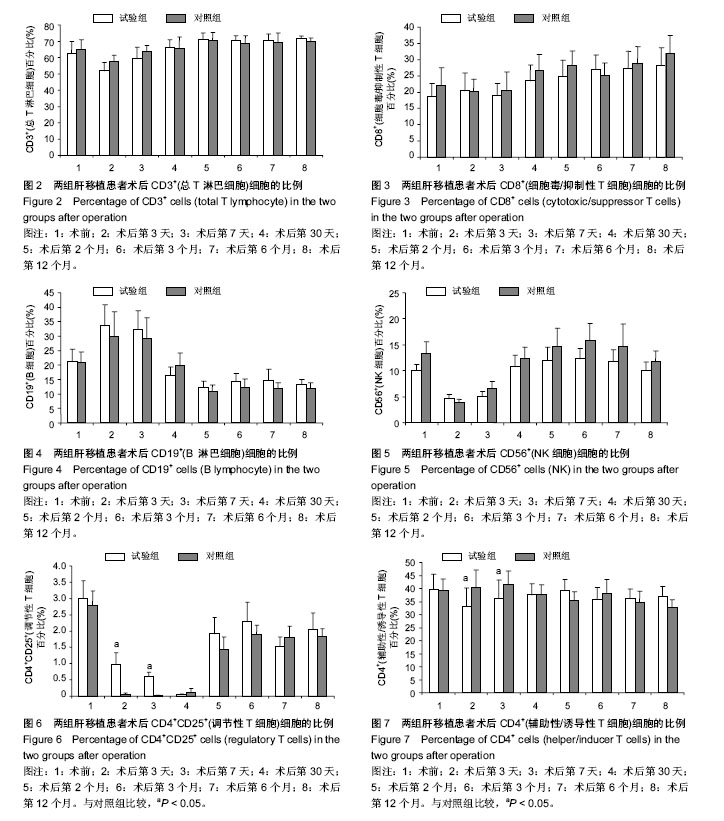
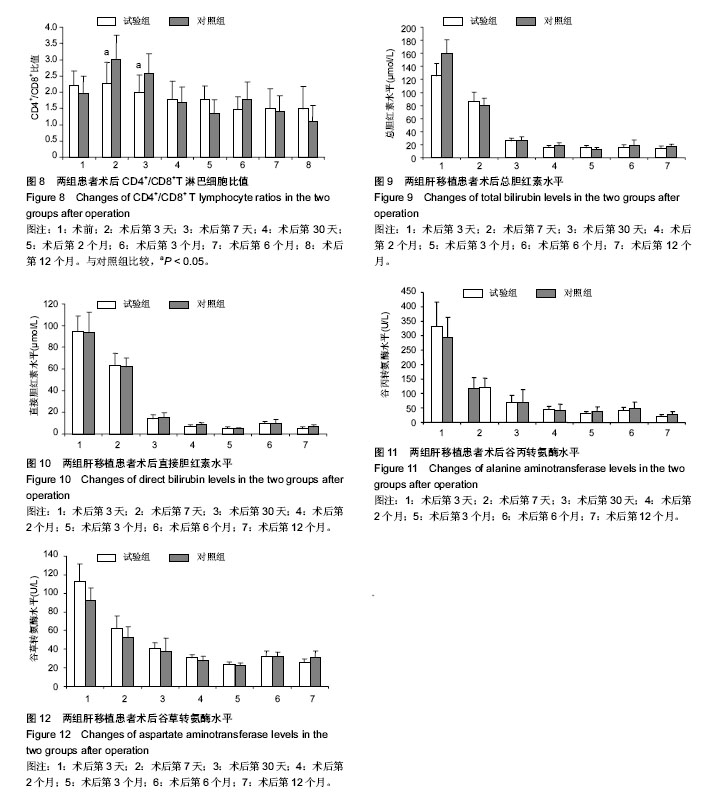
| [1] Piselli P, Busnach G, Fratino L, et al. De novo malignancies after organ transplantation: focus on viral infections. Curr Mol Med. 2013;13(7):1217-1227.[2] Zhang Z, Lin H, Shi M, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells improve liver function and ascites in decompensated liver cirrhosis patients.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;27 Suppl 2:112-120.[3] Casiraghi F, Perico N, Remuzzi G. Mesenchymal stromal cells to promote solid organ transplantation tolerance. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2013;18(1):51-58.[4] Qu X, Liu X, Cheng K, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit Th17 cell differentiation by IL-10 secretion. Exp Hematol. 2012;40(9):761-770.[5] Zhang B, Liu R, Shi D, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells induce mature dendritic cells into a novel Jagged-2-dependent regulatory dendritic cell population. Blood. 2009;113(1):46-57.[6] Liu X, Qu X, Chen Y, et al. Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells induce the generation of novel IL-10-dependent regulatory dendritic cells by SOCS3 activation. J Immunol. 2012;189(3): 1182-1192.[7] Liu X, Ren S, Qu X, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit Th17 cells differentiation via IFN-γ-mediated SOCS3 activation. Immunol Res. 2015;61(3):219-229.[8] Liu X, Ren S, Ge C, et al. Sca-1+Lin-CD117- mesenchymal stem/stromal cells induce the generation of novel IRF8-controlled regulatory dendritic cells through Notch-RBP-J signaling. J Immunol. 2015;194(9):4298-4308.[9] Casiraghi F, Azzollini N, Cassis P, et al. Pretransplant infusion of mesenchymal stem cells prolongs the survival of a semiallogeneic heart transplant through the generation of regulatory T cells. J Immunol. 2008;181(6):3933-3946.[10] Chabannes D, Hill M, Merieau E, et al. A role for heme oxygenase-1 in the immunosuppressive effect of adult rat and human mesenchymal stem cells. Blood. 2007;110(10): 3691-3694.[11] Inoue S, Popp FC, Koehl GE, et al. Immunomodulatory effects of mesenchymal stem cells in a rat organ transplant model. Transplantation. 2006;81(11):1589-1595.[12] Popp FC, Eggenhofer E, Renner P, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells can induce long-term acceptance of solid organ allografts in synergy with low-dose mycophenolate. Transpl Immunol. 2008;20(1-2):55-60.[13] Zhou HP, Yi DH, Yu SQ, et al. Administration of donor-derived mesenchymal stem cells can prolong the survival of rat cardiac allograft. Transplant Proc. 2006;38(9):3046-3051.[14] Ding Y, Xu D, Feng G, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells prevent the rejection of fully allogenic islet grafts by the immunosuppressive activity of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9. Diabetes. 2009;58(8):1797-1806.[15] Ge W, Jiang J, Arp J, et al. Regulatory T-cell generation and kidney allograft tolerance induced by mesenchymal stem cells associated with indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase expression. Transplantation. 2010;90(12):1312-1320.[16] Ge W, Jiang J, Baroja ML, et al. Infusion of mesenchymal stem cells and rapamycin synergize to attenuate alloimmune responses and promote cardiac allograft tolerance. Am J Transplant. 2009;9(8):1760-1772.[17] Castorina A, Szychlinska MA, Marzagalli R, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells-based therapy as a potential treatment in neurodegenerative disorders: is the escape from senescence an answer. Neural Regen Res. 2015;10(6):850-858.[18] Lu LL, Liu YJ, Yang SG, et al. Isolation and characterization of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells with hematopoiesis-supportive function and other potentials. Haematologica. 2006;91(8):1017-1026.[19] Koç ON, Gerson SL, Cooper BW, et al. Rapid hematopoietic recovery after coinfusion of autologous- blood stem cells and culture-expanded marrow mesenchymal stem cells in advanced breast cancer patients receiving high-dose chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18(2):307-316.[20] 陈忠华.同种肝脏移植免疫特惠器官现象及其临床意义[J].中华肝脏病杂志,2005,13(3):221.[21] Calne R, Friend P, Moffatt S, et al. Prope tolerance, perioperative campath 1H, and low-dose cyclosporin monotherapy in renal allograft recipients. Lancet. 1998; 351(9117):1701-1702.[22] 何骁,黄宏,徐祥.间充质干细胞在炎症调节中的研究进展[J].中国细胞生物学学报, 2015,37(8):1173-1179.[23] Bradstreet RW, Toledo-Pereyra LH. Role of mesenchymal stem cells in partial liver transplantation. J Surg Res. 2014; 186(1):95-96.[24] Jonuleit H, Schmitt E, Kakirman H, et al. Infectious tolerance: human CD25(+) regulatory T cells convey suppressor activity to conventional CD4(+) T helper cells. J Exp Med. 2002; 196(2):255-260.[25] 谭浩翔.受体骨髓间充质干细胞输注在大鼠原位肝移植中的作用[D].广州:南方医科大学, 2007.[26] 吴卫真,谭建明,孙星慧,等.术前自体骨髓间充质干细胞输注用于肾移植诱导治疗的临床研究[J].中华器官移植杂志,2011,32(11): 647-650. [27] Hare JM, Traverse JH, Henry TD, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-escalation study of intravenous adult human mesenchymal stem cells (prochymal) after acute myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009; 54(24):2277-2286.[28] Le Blanc K, Frassoni F, Ball L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of steroid-resistant, severe, acute graft-versus-host disease: a phase II study. Lancet. 2008;371(9624):1579-1586.[29] Zhou YF, Bosch-Marce M, Okuyama H, et al. Spontaneous transformation of cultured mouse bone marrow-derived stromal cells. Cancer Res. 2006;66(22):10849-10854.[30] Garcia S, Bernad A, Martín MC, et al. Pitfalls in spontaneous in vitro transformation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Cell Res. 2010;316(9):1648-5160.[31] Miura M, Miura Y, Padilla-Nash HM, et al. Accumulated chromosomal instability in murine bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells leads to malignant transformation. Stem Cells. 2006;24(4):1095-1103.[32] Kim S, Kim HS, Lee E, et al. In vivo hepatic differentiation potential of human cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Mol Med. 2011;27(5):701-706.[33] Meier RP, Müller YD, Morel P, et al. Transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of liver diseases, is there enough evidence. Stem Cell Res. 2013;11(3):1348-1364. |
.jpg)
.jpg)