| [1]Grote S, Polzer H, Prall WC, et al. [Prevention of infection in the current treatment of open fractures: an evidence-based systematic analysis. Orthopade. 2012;41(1): 32-42.[2]Court-Brown CM, Rimmer S, Prakash U, et al.The epidemiology of open long bonefractures.Injury.1998;29(7): 529-534. [3]Pavoni GL, Giannella M, Falcone M, et al. Conservative medical therapy of prosthetic joint infections: retrospective analysis of an 8-year experience. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2004; 10(9): 831-837.[4]Lew DP, Waldvogel FA. Osteomyelitis. Lancet. 2004; 364 (9431): 369-379.[5]Patzakis MJ, Wilkins J. Factors influencing infection rate in open fracture wounds. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1989; 246:36Y40.[6]Smirnov AY, Savel'ev SE, Nori F.Diffusion-controlled generation of a proton-motive force across a biomembrane. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2009;80(1 Pt 1): 011916.[7]Jorge LS, Chueire AG, Rossit AR. Osteomyelitis: a current hallenge.Braz J Infect Dis.2010;14(3):310-315.[8]Calhoun JH, Manring MM, Shirtliff M. Osteomyelitis of the long bones.Semin Plast Surg.2009;23(2):59-72.[9]Saveli CC, Morgan SJ, Belknap RW, et al.Prophylactic antibiotics in open fractures: a pilot randomized clinical safety study. J Orthop Trauma. 2013;27:552-557.[10]唐良华.载万古霉素-PDLLA钢板与-HA钢板的研制及其机制探讨[D].第三军医大学,2009.[11]Zelle BA, Boni G. Safe surgical technique: intramedullary nail fixation of tibial shaft fractures.Patient Saf Surg.2015’9: 40.[12]Elamurugan TP, Jagdish S, Kate V. Chandra Parija S. Role of bone biopsy spec-imen culture in the management of diabetic foot osteomyelitis.Int J Surg 2011;9:214-216. [13]Hofmann A, Dietz SO, Pairon P, et al. The role of intramedullary nailing in treatment of open fractures.Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg.2015;41(1):39-47.[14]Singh D, Garg R, Bassi JL, Tripathi SK Open grade III fractures of tibia: outcome after early unreamed intramedullary nailing. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 2011; 21:321-325[15]Craig J, Fuchs T, Jenks M, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the additional benefit of local prophylactic antibiotic therapy for infection rates in open tibia fractures treated with intramedullary nailing.Int Orthop.2014;;38(5): 1025-1030.[16]Phaff M, Aird J, Rollinson PD. Delayed implants sepsis in HIV-positive patients following open fractures treated with orthopaedic implants.Injury 2015;46:590-594.[17]Mérens A, Rapp C, Delaune D,et al. Prevention of com-bat-related infections: Antimicrobial therapy in battlefield and barrier mea-sures in French military medical treatment facilities. Travel Med Infect Dis.2014;12:318-329.[18]Otchwemah R,Grams V,Tjardes T,et al.Bacterial contamination of open fractures- pathogens, antibiotic resistances and therapeuti -c regimes in four hospitals of the trauma network Cologne, Germany.Injury. 2015. 46 Suppl 4: S104-108.[19]张春,张俊,吕战虎,等.股骨骨折患者术后医院感染病原菌耐药特征与相关危险因素研究[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2016,26(2): 379-381. [20]王彤,王立新,白雪,等. 2014年骨科伤口感染患者病原菌分布耐药性分析[J].国际检验医学杂志,2015,36 (20):2989-2991.[21]Dunkel N, Pittet D, Tovmirzaeva L, et al. Short duration of antibiotic prophylaxis in open fractures does notenhance risk of subsequent infection. Bone Joint J.2013;95(6):831Y837.[22]Von EC, Proctor RA, Peters G. Coagulase-negative staphylococci. Pathogens have major role in nosocomial infections.Postgrad Med. 2001;110(4): 63-64, 69-70, 73-76.[23]Nanchahal J. Reply:Soft-tissue reconstruction of open fractures of the lower limb: muscle versus fasciocutaneous flaps. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013; 131(3): 448e-9e.[24]Mounasamy V,Fulco P,Desai P,et al.The successful use of vancomycin-impregnated cement beads in a patient with vancomycin systemic toxicity: a case report with review of literature.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2013;23 Suppl 2: S299-302.[25]林岚云,刘榕芳,肖秀峰.羟基磷灰石涂层的生物仿生法研究进展[J].硅酸盐通报,2005,24(1):70-75.[26]Hoiby N, Bjarnsholt T, Givskov M, et al. Antibiotic resistance of bacterial biofilms.Int J Antimicrob Agents.2010;35(4): 322-332.[27]Jensen T,Jakobsen T,Baas J,et al.Hydroxyapatite nanoparticles in poly-D,L-lactic acid coatings on porous titanium implants conducts bone formation.Biomed Mater Res A.2010;95(3): 665-672. |
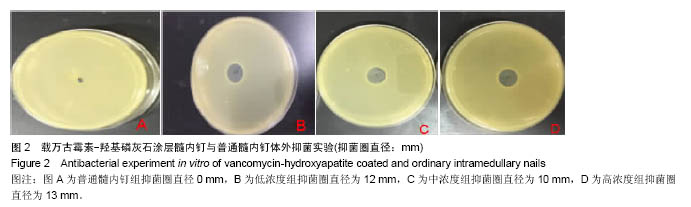
.jpg)
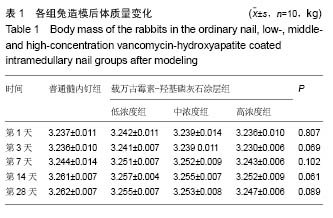
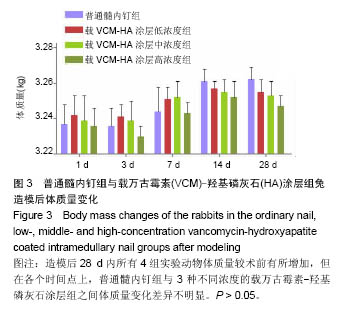
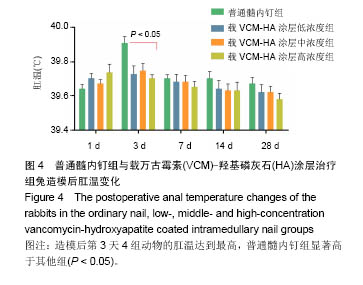

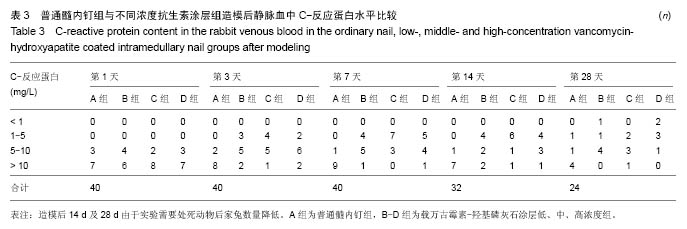
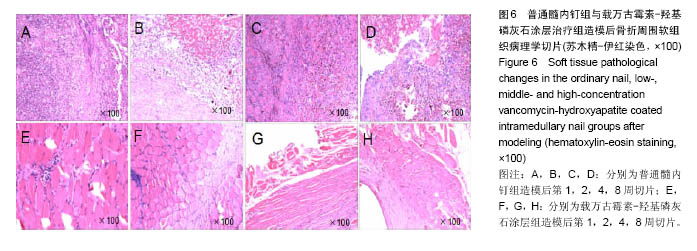
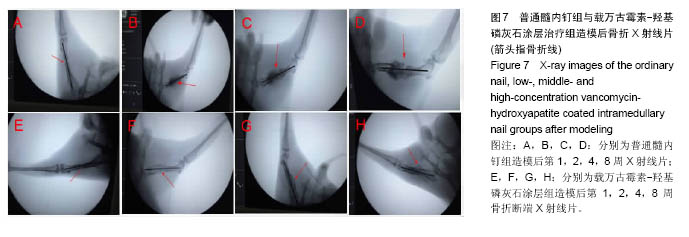
.jpg)
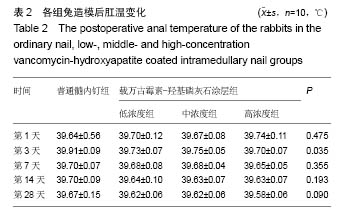
.jpg)