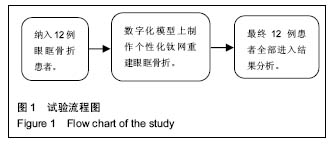
| [1]许雯,赵传亮,金玲,等.单纯性眶壁爆裂骨折的临床分析[J].临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志,2015,29(5):418-421.[2]Chaudhary R, Upendran M, Campion N, et al. The role of computerised tomography in predicting visual outcome in ocular trauma patients. Eye (Lond). 2015;29(7):867-871.[3]Pagnoni M, Marenco M, Ramieri V, et al. Late treatment of orbital fractures: a new analysis for surgical planning. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2014;34(6):439-445.[4]张云绮,贾保军,敖建华,等. 3D打印技术在下颌骨缺损修复中应用的初步临床研究[J].口腔医学研究,2016,32(5):517-523.[5]张庆福,刘刚,刘国勤.个体化3D打印钛合金下颌骨植入体的设计制作与临床应用[J].口腔医学研究,2015,31(1):48-51.[6]韩宝红.被动牵拉试验在眼眶爆裂性骨折修复手术中的应用[J].国际眼科杂志,2014,14(5):959-960[7]王兆艳,阴正勤,魏世辉,等.预成形钛网在眼眶骨折眶壁修复中的应用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2013, 33(7): 1071-1074.[8]刘观华,张志强,范钦华,等.眼眶骨折修复的人工材料的研究进展[J].临床眼科杂志,2015,23(1):87-89.[9]Totir M, Ciuluvica R, Dinu I, et al. Biomaterials for orbital fractures repair. J Med Life. 2015;8(1):41-43.[10]Yi WS, Xu XL, Ma JR, et al. Reconstruction of complex orbital fracture with titanium implants. Int J Ophthalmol. 2012;5(4): 488-492.[11]Degala S, Shetty SK, Biddappa L. Reconstruction of Post-traumatic Internal Orbital Wall Defects with Titanium Mesh. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2013;12(4):418-423.[12]孙凯建,王春霞,王雅文,等.应用个体化预成型钛网修复眶下壁骨折的临床分析[J].国际眼科杂志,2016,16(4):745-747.[13]陈明,柴广睿,王梦,等.应用AO三维预成型钛网治疗眼眶骨折的临床研究[J].国际眼科杂志,2015,15(1):112-116.[14]Boyette JR, Pemberton JD, Bonilla-Velez J. Management of orbital fractures: challenges and solutions. Clin Ophthalmol. 2015;9:2127-2137.[15]管吉,杨树欣,管叶,等.3D打印技术在医疗领域的研究进展[J].中国医疗设备,2014,29(4):71-72.[16]Thomas DJ,Azmi MABM,Tehrani Z. 3D additive manufacture of oral and maxillofacial surgical models for preoperative planning. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology. 2014;71(9-12):1643-1651.[17]秦勉,刘亚雄,贺健康,等. 数字化设计与3-D打印技术在个性化医疗中的应用[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2014,28(3):286-291.[18]黄立,林李嵩,王志红,等.基于眼球三维空间精确定位测量的外伤性眼眶缺损的个体化重建[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志, 2014, 12(2):136-143. [19]Wan KH, Chong KK, Young AL.The Role of Computer-Assisted Technology in Post-Traumatic Orbital Reconstruction: A PRISMA-driven Systematic Review. Sci Rep. 2015;5:17914.[20]陈春艳,张力,鲍海宏.计算机三维塑形钛网在眶壁缺损修复中的临床应用[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2016,32(4):237-238.[21]张翔,陈伟,曹罡,等.计算机辅助快速成型钛网在眼眶爆裂骨折整复中的应用[J].医学研究生学报,2016,29(4):407-410. [22]Susarla SM, Duncan K, Mahoney NR, et al. Virtual Surgical Planning for Orbital Reconstruction. Middle East Afr J Ophthalmol. 2015;22(4):442-446.[23]Zavattero E, Ramieri G, Roccia F, et al. Comparison of the Outcomes of Complex Orbital Fracture Repair with and without a Surgical Navigation System: A Prospective Cohort Study with Historical Controls. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017; 139(4):957-965.[24]Oh TS, Jeong WS, Chang TJ, et al. Customized Orbital Wall Reconstruction Using Three-Dimensionally Printed Rapid Prototype Model in Patients With Orbital Wall Fracture. J Craniofac Surg. 2016;27(8):2020-2024.[25]Callahan AB, Campbell AA, Petris C, et al. Low-Cost 3D Printing Orbital Implant Templates in Secondary Orbital Reconstructions.Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017 Feb 22. [Epub ahead of print][26]彭昌福,李婵.CAD/CAM技术在眼眶重建中的应用研究[J].国际眼科杂志,2016,16(5):993-995.[27]Jansen J, Schreurs R, Dubois L, et al. Orbital volume analysis: validation of a semi-automatic software segmentation method. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2016;11(1):11-18.[28]Shyu VB, Hsu CE, Chen CH, et al. 3D-assisted quantitative assessment of orbital volume using an open-source software platform in a Taiwanese population. PLoS One. 2015;10(3): e0119589.[29]蒋丽琼,何小琴,刘桂琴,等.利用Image J软件测量眼眶脂肪体积[J].中国CT和MRI杂志,2016,14(3):11-13.[30]傅杰,赵佳威.眼眶骨折整复重建前后视力和眼球运动功能研究[J].国际眼科杂志,2016,16(2):367-369.[31]孙黎波,肖金刚,兰玉燕,等.个性化钛网联合多孔高密度聚乙烯矫眼眶骨折伴眼球内陷畸形[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2015,33(3): 272-275.[32]Peng MY, Merbs SL, Grant MP, et al. Orbital fracture repair outcomes with preformed titanium mesh implants and comparison to porous polyethylene coated titanium sheets.J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2017;45(2):271-274. |
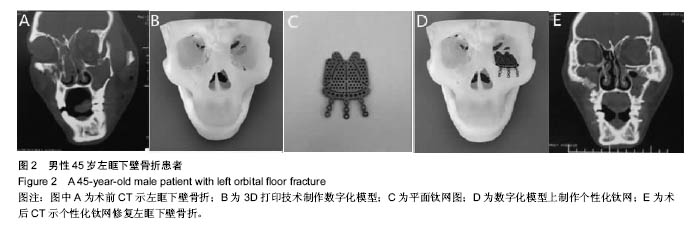
.jpg)
.jpg)