中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (6): 924-928.doi: 10.12307/2022.178
• 脊柱植入物Spinal implants • 上一篇 下一篇
应用体表地形图量化腰椎间盘突出症腰型客观化指标:下腰曲线弹性固定转折点的三维成角
马 超1,王 飞2,刘晓民3,王子昀2,许 奎2,杨文东2,冯 伟2
- 1北京中医药大学,北京市 100029;2空军特色医学中心中西医结合正骨科,北京市 100142;3北京工业大学电子信息与控制工程学院,北京市 100024
Quantification of the objective index of lumbar disc herniation with body surface topography map: three-dimensional angulation of the elastically fixed turning point of the lower back curve
Ma Chao1, Wang Fei2, Liu Xiaomin3, Wang Ziyun2, Xu Kui2, Yang Wendong2, Feng Wei2
- 1Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China; 2Department of Orthopedics of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Air Force Special Medical Center, Beijing 100142, China; 3School of Electronic Information and Control Engineering, Beijing University of Technology, Beijing 100024, China
摘要:
文题释义:
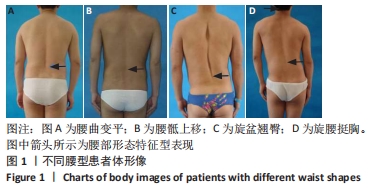
下腰曲线转折点的三维成角:对Ⅲ、Ⅳ型腰椎间盘突出症患者而言,单(多)个椎体发生位移,棘突连线所呈直线中断,成角形成一或多个折线,同时造成脊柱畸形曲线弹性固定,经下腰曲线弹性固定转折点的脊沟曲线、截面曲线在冠状面、矢状面、轴面的投影线与人体竖直线和水平线所形成的夹角。该角的大小决定了两侧椎旁肌形态对称性、髂嵴两侧高低对称性以及人体脊柱旋转的程度。
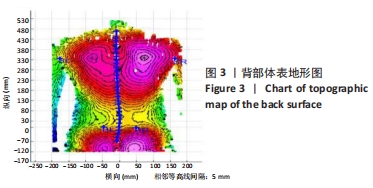
体表地形图:基于双目立体视觉方法,可以产生代表物体表面形状的等高线波纹,随体表形状不同而变形,可用于脊柱变形引发背部表面不对称性的测量,定量分析脊柱侧凸和旋转角度,实现人体背部形态及脊柱非侵入性的数字化和直观再现。
背景:腰椎间盘突出症患者背部形态呈现特征性表现,目前对腰型的判断主要通过望诊观察、采用定性描述,冯天有教授从望诊角度总结出“腰型”四步规律——腰曲变平、腰骶(功能)上移、旋盆翘臀、旋腰挺胸。
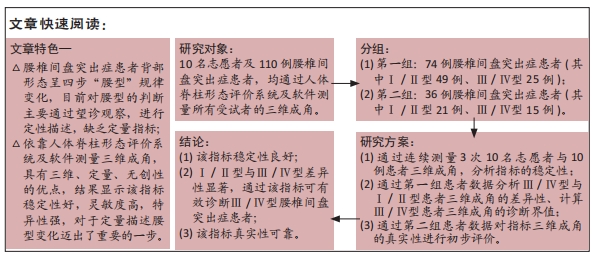
目的:测量Ⅲ/Ⅳ型与Ⅰ/Ⅱ型腰椎间盘突出症患者下腰曲线转折点的三维成角,分析通过三维成角判断腰型的可行性。
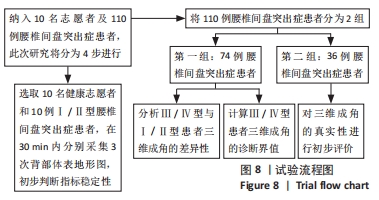
方法:顺次纳入住院腰椎间盘突出症患者110例,其中Ⅰ/Ⅱ腰型70例,Ⅲ/Ⅳ腰型40例。通过人体脊柱形态评价系统采集患者背部体表地形图,应用分析软件测量患者三维成角,初步判断三维成角的稳定性,计算Ⅲ/Ⅳ型与Ⅰ/Ⅱ型患者三维成角的差异性及诊断临界值,并对三维成角的真实性进行初步评价。
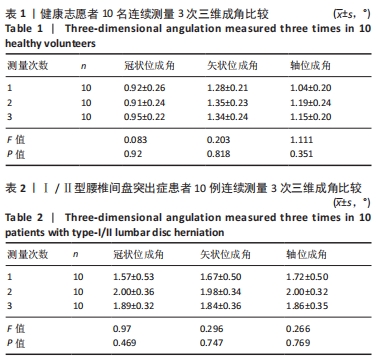
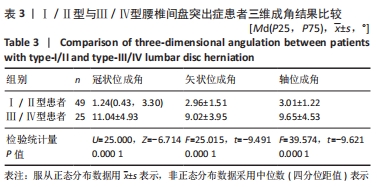
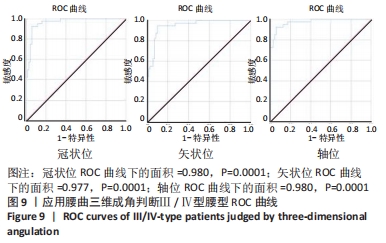
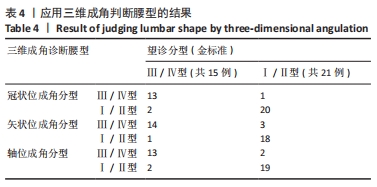
结果与结论:①此次指标稳定性良好,3次三维成角测量数据比较,差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);②Ⅲ/Ⅳ型与Ⅰ/Ⅱ型患者的三维成角差异极显著:冠状位成角Ⅲ/Ⅳ型平均11.04°,远大于Ⅰ/Ⅱ型(中位数1.24°);矢状位成角Ⅲ/Ⅳ型平均9.02°,远大于Ⅰ/Ⅱ型(平均数2.96°);轴位成角Ⅲ/Ⅳ型平均9.65°,远大于Ⅰ/Ⅱ型(平均数3.01°);③依据ROC曲线值得出Ⅲ/Ⅳ型腰型患者的三维成角(冠状位、矢状位、轴位)的诊断临界值分别为5.43°,4.77°,4.83°。此次三维成角结果真实性可靠,冠状位、矢状位、轴位成角结果显示:灵敏度分别为86.66%,93.33%,86.66%;特异度分别为95.23%,85.72%,90.47%;约登指数分别为0.818,0.790,0.771;总符合率分别为91.66%,88.88%,88.88%;④该研究利用人体背部体表三维地形图技术,分析通过三维成角判断腰型的可行性,发现该指标稳定性好,尤其能够反映旋盆翘臀和旋腰挺胸型的特征,该角度作为一个腰椎间盘突出症腰型分类的关键指标,对于定量描述腰型变化迈出了重要的一步。
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3665-9133 (马超)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: