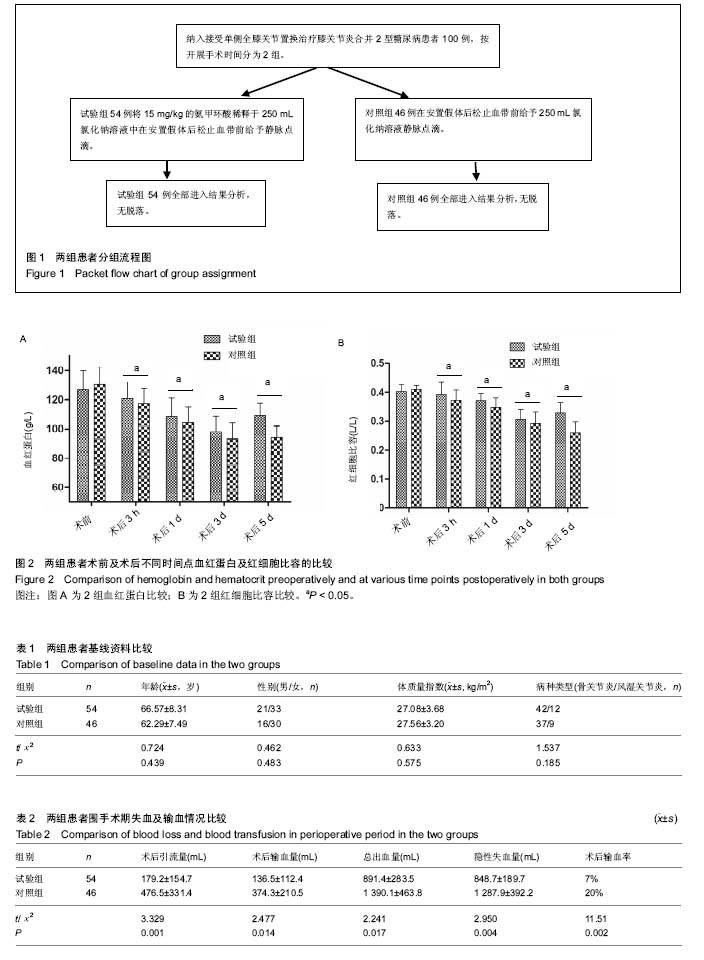
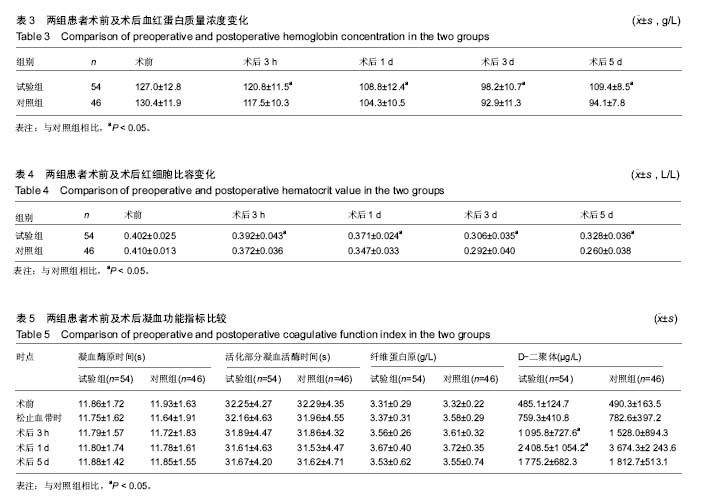
| [1] Choi YJ, Ra HJ. Patient Satisfaction after Total Knee Arthroplasty. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2016;28(1):1-15.[2] Moráis S, Ortega-Andreu M, Padilla-Eguiluz NG, et al. Blood transfusion after primary total knee arthroplasty can be significantly minimised through a multimodal blood-loss prevention approach. Int Orthop. 2014;38(2):347-354.[3] Lotke PA, Faralli VJ, Orenstein EM, et al. Blood loss after total knee replacement. Effects of tourniquet release and continuous passive motion. J Bone Joint Surg. 1991; 73(7): 1037-1040.[4] 陈森, 彭昊, 李建平,等. 全膝关节置换术中使用止血带对围手术期失血量影响的 Meta分析[J]. 中华关节外科杂志:电子版, 2015,9(4):62-65.[5] Sentilhes L, Lasocki S, Ducloy-Bouthors AS, et al. Tranexamic acid for the prevention and treatment of postpartum haemorrhage. Br J Anaesthesia. 2015;114(4): 576-587. [6] Bagsby DT, Samujh CA, Vissing JL, et al. Tranexamic Acid Decreases Incidence of Blood Transfusion in Simultaneous Bilateral Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2015;30(12): 2106-2109.[7] Gausden EB, Garner MR, Warner SJ, et al. Tranexamic acid in hip fracture patients: a protocol for a randomised, placebo controlled trial on the efficacy of tranexamic acid in reducing blood loss in hip fracture patients. BMJ Open. 2016;6(6): e010676.[8] 黄亮达, 魏亦兵, 王思群,等. 氨甲环酸在全膝关节置换术中的研究进展[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2015, 23(1):60-63.[9] 刘亚非,陈百成,孙然,等. 糖尿病患者人工全膝关节置换术围手术期处理措施与方法探讨[J]. 第三军医大学学报, 2007, 29(17): 1724-1726.[10] 中华医学会骨科学分会. 中国骨科大手术静脉血栓栓塞症预防指南[J]. 中华骨科杂志, 2016, 3(2):70-72.[11] Nadler SB, Hidalgo JH, Bloch T. Prediction of blood volume in normal human adults. Surgery. 1962;51(2):224-232.[12] Gross JB. Estimating allowable blood loss: corrected for dilution. Anesthesiology. 1983;58(3):277-280.[13] de Achaval S, Kallen MA, Amick B, et al. Patients' expectations about total knee arthroplasty outcomes. H Health Expect. 2016;19(2):299-308.[14] 徐鸿尧, 赵建宁, 包倪荣. 人工膝关节置换术对严重骨关节炎及类风湿性关节炎引起的膝关节畸形的疗效比较和术后风险评估[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2015, 23(3):211-214.[15] 林治平, 汤炀炀, 谭宏昌, 等. 单髁置换术与全膝关节置换术治疗膝单间室骨性关节炎的疗效比较[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2016,31(4):424-425.[16] Yan C, Chan P, Fu C, et al. Effect of tourniquet use on blood loss and post-operative function in total knee arthroplasty. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24:S518-S518.[17] 岳辰, 周宗科, 裴福兴,等. 中国髋、膝关节置换术围术期抗纤溶药序贯抗凝血药应用方案的专家共识[J]. 中国骨与关节外科, 2015, 8(4):281-285.[18] 李宗泽, 田京. 减少全膝关节置换术围手术期出血的研究进展[J]. 中华关节外科杂志:电子版, 2015,9(5):655-658.[19] 伍旭林, 朱伟民, 唐本森,等. 全膝关节置换术后早期不同引流管夹闭时间的临床研究[J]. 齐齐哈尔医学院学报, 2016, 37(13): 1684-1685.[20] Dahuja A, Dahuja G, Jaswal V, et al. A prospective study on role of tranexamic acid in reducing postoperative blood loss in total knee arthroplasty and its effect on coagulation profile. J Arthroplasty.2014;29(4):733-735.[21] Tzatzairis TK, Drosos GI, Kotsios SE, et al. Intravenous vs Topical Tranexamic Acid in Total Knee Arthroplasty Without Tourniquet Application: A Randomized Controlled Study. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(11):2465-2470.[22] 杨红明, 李兵, 殷巍,等. 氨甲环酸对减少肝切除术中出血的临床研究[J]. 华西医学, 2010, 25(9):1698-1700.[23] 卢志华, 熊传芝, 颜连启,等. 全膝置换围手术期失血量因素分析[J]. 北华大学学报:自然科学版, 2016, 17(2):236-239.[24] 陈校国, 肖扬, 伍旭辉,等. 氨甲环酸用于创伤外科的研究进展[J]. 中华创伤杂志, 2016, 32(5):469-473.[25] Moskal JT, Harris RN, Capps SG. Transfusion Cost Savings with Tranexamic Acid in Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty from 2009 to 2012. J Arthroplasty.2014;30(3):365-368.[26] Shen PF, Hou WL, Chen JB, et al. Effectiveness and Safety of Tranexamic Acid for Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Prospective Randomized Controlled Trial. Med Sci Monit. 2015;21: 576-581.[27] Nielsen CS, Jans Ø, Ørsnes T, et al. Combined Intra-Articular and Intravenous Tranexamic Acid Reduces Blood Loss in Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. J Bone Joint Surg. 2016;98(10): 835-841.[28] 张欢, 任凯晶, 樊庆阳. 氨甲环酸对全膝关节置换术后出血的影响[J]. 天津医科大学学报, 2015,21(6):535-537. [29] Huang GP, Jia XF, Zhou X, et al. Tranexamic Acid Reduces Hidden Blood Loss in Patients Undergoing Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Comparative Study and Meta-Analysis. Med Sci Monit. 2016;22:797-802.[30] 胡旭栋, 裴福兴, 沈彬,等. 氨甲环酸减少全膝关节置换术失血量的有效性和安全性评价[J]. 中国骨与关节外科, 2013,6(s1): 52-56.[31] Cap AP, Baer DG, Orman JA, et al. Tranexamic acid for trauma patients: a critical review of the literature. J Trauma. 2011;71(1 Suppl):9-14.[32] 孙程, 陆海明, 吕杰,等. 氨甲环酸在初次全髋关节置换术中的应用[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2015, 23(2):139-143.[33] 李波. 全膝关节置换手术中应用氨甲环酸术后出血量及凝血变化研究[D]. 山东大学, 2015.[34] 鲁强, 彭昊, 尹东,等. 不同剂量氨甲环酸在全膝关节置换术中的疗效比较[J]. 临床外科杂志, 2016, 24(4):296-298.[35] 王清山, 徐海斌, 黄媛霞,等. 氨甲环酸减少膝关节置换术术后失血效果观察[J]. 人民军医, 2015,58(11):1305-1307.[36] 张延杰, 郝军, 高文香. 不同剂量氨甲环酸对全膝关节置换术后失血量的影响[J]. 山东医药, 2013, 53(19):53-55.[37] 席少华, 周朝波, 赵桂林. 不同应用方式的氨甲环酸在全膝关节置换术中的止血效果比较[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2015, 31(2): 294-296.[38] 王鑫瑞, 王涛, 张志强. 全膝关节置换围置换期氨甲环酸的临床应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(44):7188-7192.[39] 石永进, 王全彬, 邱庆虎. 氨甲环酸不同途径用药对全膝关节置换术失血量的影响[J]. 中国中西医结合外科杂志, 2016, 22(2):135-138.[40] 姬健钧, 杨自权, 赵永亮,等. 氨甲环酸在全膝关节置换术中应用策略的研究进展[J]. 中国骨伤, 2016, 29(10):963-967. |
.jpg)
.jpg)