中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (4): 641-649.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.04.025
• 组织构建循证医学 evidence-based medicine in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
引导组织再生联合植骨修复治疗牙周骨内缺损效果的Meta分析
沈 玥,何攀龙,魏奕茹,热依拉•居热提,古丽努尔•阿吾提
- 新疆医科大学第一附属医院牙周粘膜科,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830054
Effects of guided tissue regeneration combined with bone graft in the repair of periodontal bone defects: a Meta-analysis
Shen Yue, He Pan-long, Wei Yi-ru, Reyila•Jureti, Gulinuer•Awuti
- Department of Periodontics & Oral Medicine, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
引导组织再生术:是指用外科的方法放置一个物理屏障来选择性地分隔不同的牙周组织,阻止牙龈上皮和牙龈结缔组织向根面生长,造成空间,诱导具有牙周组织再生潜力的牙周膜细胞冠向移动并生长分化,实现牙周膜、牙槽骨、牙骨质再生,形成牙周新附着。
单纯的引导组织再生:常不能使缺损的牙周组织获得重建,近年来在施行牙周再生性手术时会联合使用一些骨替代材料充填骨缺损部分,起到占位和支架作用,为引导牙周组织再生提供一定的空间,在牙周膜细胞冠向移动,生长分化形成牙周新附着的同时,更加有利于成骨细胞增殖,并完成成骨。
文题释义:
引导组织再生术:是指用外科的方法放置一个物理屏障来选择性地分隔不同的牙周组织,阻止牙龈上皮和牙龈结缔组织向根面生长,造成空间,诱导具有牙周组织再生潜力的牙周膜细胞冠向移动并生长分化,实现牙周膜、牙槽骨、牙骨质再生,形成牙周新附着。
单纯的引导组织再生:常不能使缺损的牙周组织获得重建,近年来在施行牙周再生性手术时会联合使用一些骨替代材料充填骨缺损部分,起到占位和支架作用,为引导牙周组织再生提供一定的空间,在牙周膜细胞冠向移动,生长分化形成牙周新附着的同时,更加有利于成骨细胞增殖,并完成成骨。
.jpg) 文题释义:
引导组织再生术:是指用外科的方法放置一个物理屏障来选择性地分隔不同的牙周组织,阻止牙龈上皮和牙龈结缔组织向根面生长,造成空间,诱导具有牙周组织再生潜力的牙周膜细胞冠向移动并生长分化,实现牙周膜、牙槽骨、牙骨质再生,形成牙周新附着。
单纯的引导组织再生:常不能使缺损的牙周组织获得重建,近年来在施行牙周再生性手术时会联合使用一些骨替代材料充填骨缺损部分,起到占位和支架作用,为引导牙周组织再生提供一定的空间,在牙周膜细胞冠向移动,生长分化形成牙周新附着的同时,更加有利于成骨细胞增殖,并完成成骨。
文题释义:
引导组织再生术:是指用外科的方法放置一个物理屏障来选择性地分隔不同的牙周组织,阻止牙龈上皮和牙龈结缔组织向根面生长,造成空间,诱导具有牙周组织再生潜力的牙周膜细胞冠向移动并生长分化,实现牙周膜、牙槽骨、牙骨质再生,形成牙周新附着。
单纯的引导组织再生:常不能使缺损的牙周组织获得重建,近年来在施行牙周再生性手术时会联合使用一些骨替代材料充填骨缺损部分,起到占位和支架作用,为引导牙周组织再生提供一定的空间,在牙周膜细胞冠向移动,生长分化形成牙周新附着的同时,更加有利于成骨细胞增殖,并完成成骨。摘要
背景:引导组织再生术及植骨术是目前治疗中重度牙周炎导致的牙周骨缺损的研究热点,但临床研究存在样本量较小的问题,会导致研究结果存在差异。
目的:系统评价引导组织再生术联合植骨术治疗牙周骨内缺损的效果,探讨该方法的可行性,为临床应用提供循证依据。
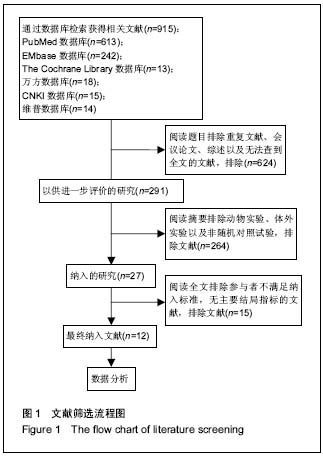
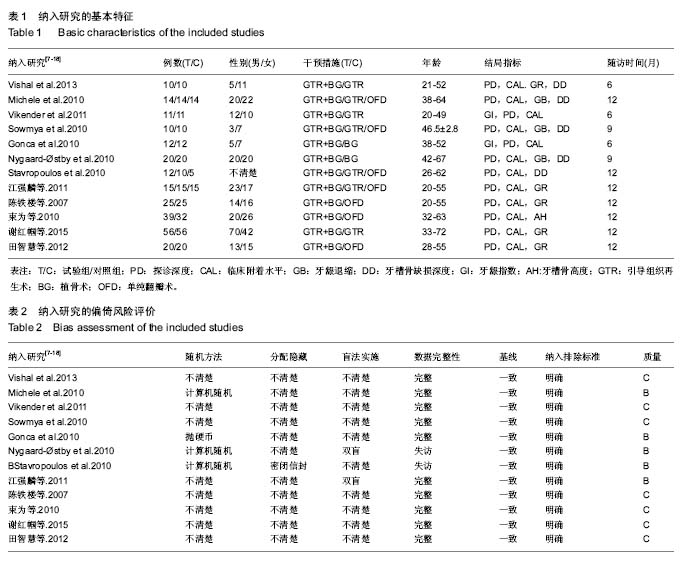
方法:计算机检索PubMed、Cochrane library、EMbase、中国知网、维普及万方数据库,英文检索词包括“guided tissue regeneration,bone grafts,periodontal bone defects”;中文检索词包“引导组织再生术,植骨术,牙周骨内缺损”,查找有关引导组织再生与联合植骨术治疗牙周骨内缺损的相关研究,检索时间为2000至 2016 年。由2位研究者独立筛选文献、提取资料和评价纳入研究的偏倚风险后,对纳入的12篇随机对照试验进行文献质量评价,采用 RevMan 5.3统计学软件进行meta分析。
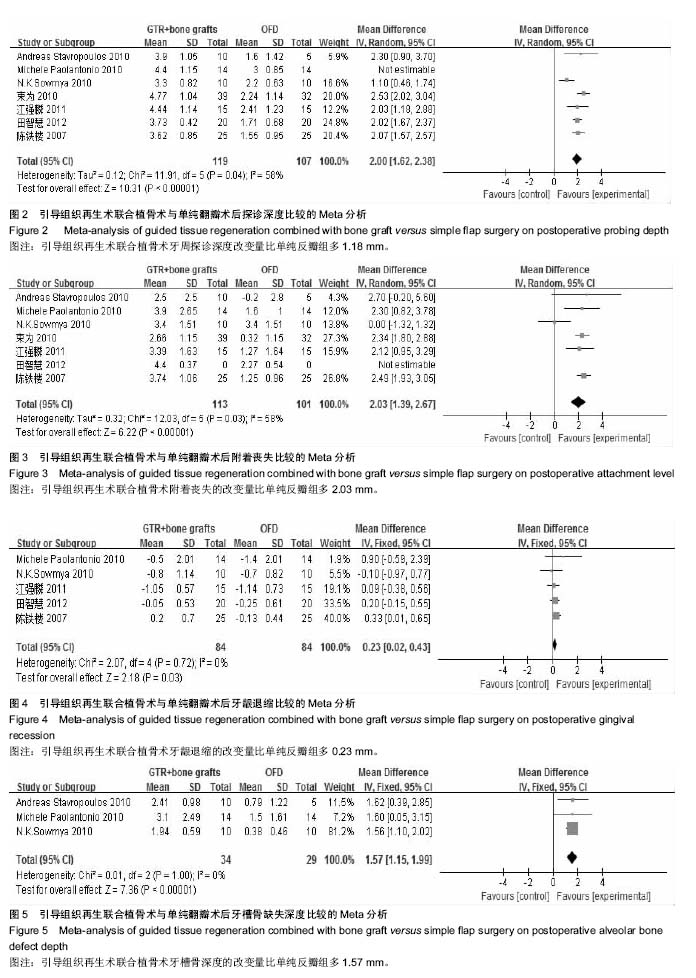
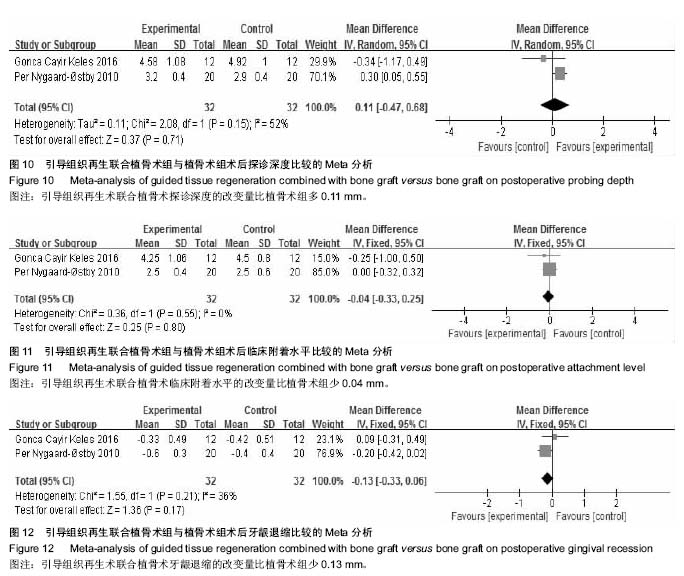
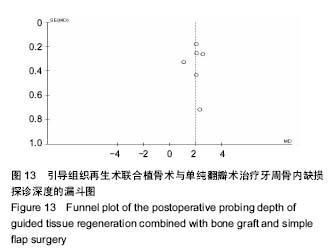
结果与结论:共纳入12个研究,总计414颗患牙,其中试验组228颗,对照组216颗。Meta分析结果显示,引导组织再生术联合植骨术组较单纯翻瓣术组可使牙周探诊深度降低1.18 mm、牙龈退缩减少0.23 mm、牙槽骨缺损深度降低1.57 mm,临床附着水平增加2.03 mm(P < 0.05);引导组织再生术联合植骨术较引导组织再生术在探诊深度增加0.34 mm和牙槽骨缺损深度降低0.73 mm(P > 0.05),牙龈退缩减少0.35 mm,临床附着水平有所增加0.63 mm(P < 0.05);引导组织再生术联合植骨术组较植骨术组在牙周探诊深度减少0.11 mm、临床附着水平增加0.04 mm和牙龈退缩增加0.13 mm(P > 0.05)。结果证实,在中重度牙周炎导致的牙周骨缺损的患者中,引导组织再生术联合植骨术较单纯翻瓣术以及引导组织再生术疗效更好,但较植骨术无明显统计学差异。此次Meta分析结果尚未对使用的膜材料及骨材料及骨替代品进行分类,仍缺少高质量大样本的随机对照试验予以证实。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-2537-1153(沈玥)
中图分类号:

.jpg) 文题释义:
引导组织再生术:是指用外科的方法放置一个物理屏障来选择性地分隔不同的牙周组织,阻止牙龈上皮和牙龈结缔组织向根面生长,造成空间,诱导具有牙周组织再生潜力的牙周膜细胞冠向移动并生长分化,实现牙周膜、牙槽骨、牙骨质再生,形成牙周新附着。
单纯的引导组织再生:常不能使缺损的牙周组织获得重建,近年来在施行牙周再生性手术时会联合使用一些骨替代材料充填骨缺损部分,起到占位和支架作用,为引导牙周组织再生提供一定的空间,在牙周膜细胞冠向移动,生长分化形成牙周新附着的同时,更加有利于成骨细胞增殖,并完成成骨。
文题释义:
引导组织再生术:是指用外科的方法放置一个物理屏障来选择性地分隔不同的牙周组织,阻止牙龈上皮和牙龈结缔组织向根面生长,造成空间,诱导具有牙周组织再生潜力的牙周膜细胞冠向移动并生长分化,实现牙周膜、牙槽骨、牙骨质再生,形成牙周新附着。
单纯的引导组织再生:常不能使缺损的牙周组织获得重建,近年来在施行牙周再生性手术时会联合使用一些骨替代材料充填骨缺损部分,起到占位和支架作用,为引导牙周组织再生提供一定的空间,在牙周膜细胞冠向移动,生长分化形成牙周新附着的同时,更加有利于成骨细胞增殖,并完成成骨。