[1] RAMPONI DR, MCSWIGAN T. Tibial plateau fractures. Adv Emerg Nurs J. 2018;40(3):155-161.
[2] HE QF, SUN H, SHU LY, et al. Tibial plateau fractures in elderly people: an institutional retrospective study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018;13(1):276.
[3] BIGGI F, DI FABIO S, D’ANTIMO C, et al. Tibial plateau fractures: internal fixation with locking plates and the MIPO technique. Injury. 2010; 41(11):1178-1182.
[4] KUGELMAN DN, QATU AM, STRAUSS EJ, et al. Knee stiffness after tibial plateau fractures: predictors and outcomes (OTA-41). J Orthop Trauma. 2018; 32(11):e421-e427.
[5] ADAMS JDJ, LOEFFLER MF. Soft tissue injury considerations in the treatment of tibial plateau fractures. Orthop Clin North Am. 2020;51(4): 471-479.
[6] MTHETHWA J, CHIKATE A. A review of the management of tibial plateau fractures. Musculoskelet Surg. 2018;102(2):119-127.
[7] 张英泽.胫骨平台骨折诊疗创新与发展再探索[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2020,22(8):662-664.
[8] KRAUSE M, MüLLER G, FROSCH KH. Surgical approaches to tibial plateau fractures. Unfallchirurg. 2018;121(7):569-582.
[9] MENGHI A, MAZZITELLI G, MARZETTI E, et al. Complex tibial plateau fractures: a retrospective study and proposal of treatment algorithm. Injury. 2017;48 Suppl 3:S1-S6.
[10] ELSOE R, JOHANSEN MB, LARSEN P. Tibial plateau fractures are associated with a long-lasting increased risk of total knee arthroplasty a matched cohort study of 7,950 tibial plateau fractures. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019;27(5):805-809.
[11] BALOCH SR, RAFI MS, JUNAID J, et al. Ilizarov fixation method of tibia plateau fractures: a prospective observational study. Cureus. 2020; 12(10):e11277.
[12] ZHAO XW, MA JX, MA XL, et al. A meta-analysis of external fixation versus open reduction and internal fixation for complex tibial plateau fractures. Int J Surg. 2017;39:65-73.
[13] BOUTEFNOUCHET T, LAKDAWALA AS, MAKRIDES P. Outcomes following the treatment of bicondylar tibial plateau fractures with fine wire circular frame external fixation compared to open reduction and internal fixation: a systematic review. J Orthop. 2016;13(3):193-199.
[14] MARION-MARTINS AD, PINHO DLM. Interprofessional simulation effects for healthcare students: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nurse Educ Today. 2020;94:104568.
[15] AHEARN N, OPPY A, HALLIDAY R, et al. The outcome following fixation of bicondylar tibial plateau fractures. Bone Joint J. 2014;96-b(7):956-962.
[16] BERTRAND ML, PASCUAL-LóPEZ FJ, GUERADO E. Severe tibial plateau fractures (Schatzker V-VI): open reduction and internal fixation versus hybrid external fixation. Injury. 2017;48 Suppl 6: S81-S85.
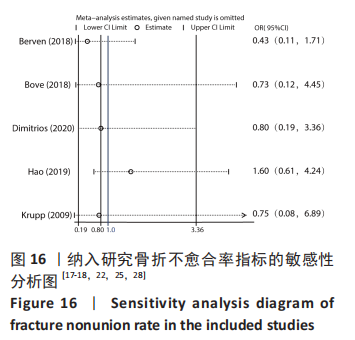
[17] BERVEN H, BRIX M, IZADPANAH K, et al. Comparing case-control study for treatment of proximal tibia fractures with a complete metaphyseal component in two centers with different distinct strategies: fixation with Ilizarov frame or locking plates. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018; 13(1):121.
[18] BOVE F, SALA F, CAPITANI P, et al. Treatment of fractures of the tibial plateau (Schatzker VI) with external fixators versus plate osteosynthesis. Injury. 2018;49 Suppl 3:S12-S18.
[19] CHAN C, KEATING J. Comparison of outcomes of operatively treated bicondylar tibial plateau fractures by external fixation and internal fixation. Malays Orthop J. 2012;6(1):7-12.
[20] CONSERVA V, VICENTI G, ALLEGRETTI G, et al. Retrospective review of tibial plateau fractures treated by two methods without staging. Injury. 2015;46(10):1951-1956.
[21] SOCIETY COT. Open reduction and internal fixation compared with circular fixator application for bicondylar tibial plateau fractures. Results of a multicenter, prospective, randomized clinical trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(12):2613-2623.
[22] HAO ZC, XIA Y, XIA DM, et al. Treatment of open tibial diaphyseal fractures by external fixation combined with limited internal fixation versus simple external fixation: a retrospective cohort study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019; 20(1):311.
[23] JANSEN H, FREY SP, DOHT S, et al. Medium-term results after complex intra-articular fractures of the tibial plateau. J Orthop Sci. 2013;18(4):569-577.
[24] KODANDAPANI K. Ilizarov and locking plate fixation for closed bicondylar tibial plateau fracturesa prospective study. J Evol Med Dent Sci. 2017;6(64):4670-4675.
[25] KRUPP RJ, MALKANI AL, ROBERTS CS, et al. Treatment of bicondylar tibia plateau fractures using locked plating versus external fixation. Orthopedics. 2009. doi: 10.3928/01477447-20090624-11.
[26] LIN L, LIU Y, LIN C, et al. Comparison of three fixation methods in treatment of tibial fracture in adolescents. ANZ J Surg. 2018;88(6):E480-E485.
[27] PUN TB, KRISHNAMOORTHY VP, POONNOOSE PM, et al. Outcome of Schatzker type V and VI tibial plateau fractures. Indian J Orthop. 2014; 48(1):35-41.
[28] EVANGELOPOULOS D, CHALIKIAS S, MICHALOS M, et al. Medium-term results after surgical treatment of high-energy tibial plateau fractures. J Knee Surg. 2020;33(4): 394-398.
[29] TAHIR M, KUMAR S, SHAIKH SA, et al. Comparison of postoperative outcomes between open reduction and internal fixation and ilizarov for schatzker type V and type VI fractures. Cureus. 2019;11(6):e4902.
[30] YOUNG MJ, BARRACK RL. Complications of internal fixation of tibial plateau fractures. Orthop Rev. 1994;23(2):149-154.
[31] JENSEN DB, RUDE C, DUUS B, et al. Tibial plateau fractures. A comparison of conservative and surgical treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1990; 72(1):49-52.
[32] HALL JA, BEUERLEIN MJ, MCKEE MD. Open reduction and internal fixation compared with circular fixator application for bicondylar tibial plateau fractures. Surgical technique. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91 Suppl 2 Pt 1:74-88.
[33] KEIGHTLEY AJ, NAWAZ SZ, JACOB JT, et al. Ilizarov management of Schatzker IV to VI fractures of the tibial plateau: 105 fractures at a mean follow-up of 7.8 years. Bone Joint J. 2015;97-b(12):1693-1697.
[34] CHIN TY, BARDANA D, BAILEY M, et al. Functional outcome of tibial plateau fractures treated with the fine-wire fixator. Injury. 2005;36(12):1467-1475.
[35] METCALFE D, HICKSON CJ, MCKEE L, et al. External versus internal fixation for bicondylar tibial plateau fractures: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop Traumatol. 2015;16(4):275-285.
[36] COLE PA, ZLOWODZKI M, KREGOR PJ. Treatment of proximal tibia fractures using the less invasive stabilization system: surgical experience and early clinical results in 77 fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2004;18(8):528-535.
[37] MORANDI MM, LANDI S, KILAGHBIAN V, et al. Schatzker type VI tibial plateau fractures and the Ilizarov circular external fixator. Bull Hosp Jt Dis. 1997;56(1):46-48.
[38] CATAGNI MA, OTTAVIANI G, MAGGIONI M. Treatment strategies for complex fractures of the tibial plateau with external circular fixation and limited internal fixation. J Trauma. 2007;63(5):1043-1053.
[39] LIU F, TAO R, CAO Y, et al. The role of LISS (less invasive stabilisation system) in the treatment of peri-knee fractures. Injury. 2009;40(11):1187-1194.
[40] MAHADEVA D, COSTA ML, GAFFEY A. Open reduction and internal fixation versus hybrid fixation for bicondylar/severe tibial plateau fractures: a systematic review of the literature. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2008;128(10): 1169-1175.
[41] PHISITKUL P, MCKINLEY TO, NEPOLA JV, et al. Complications of locking plate fixation in complex proximal tibia injuries. J Orthop Trauma. 2007;21(2):83-91.
[42] GAUDINEZ RF, MALLIK AR, SZPORN M. Hybrid external fixation of comminuted tibial plateau fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996;(328): 203-210. |