| [1] Bartsch G, Yoo JJ, De Coppi P, et al. Propagation, expansion, and multilineage differentiation of human somatic stem cells from dermal progenitors. Stem Cells Dev. 2005;14(3):337- 348.[2] Peters BA, Diaz LA, Polyak K, et al. Contribution of bone marrow-derived endothelial cells to human tumor vasculature. Nat Med. 2005;11(3):261-262.[3] Young HE, Steele TA, Bray RA, et al. Human reserve pluripotent mesenchymal stem cells are present in the connective tissues of skeletal muscle and dermis derived from fetal, adult, and geriatric donors. Anat Rec. 2001;264(1): 51-62. [4] De Ugarte DA, Morizono K, Elbarbary A, et al. Comparison of multi-lineage cells from human adipose tissue and bone marrow. Cells Tissues Organs. 2003;174(3):101-109.[5] Li L, Tian H, Chen Z, et al. Inhibition of lung cancer cell proliferation mediated by human mesenchymal stem cells. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2011;43(2):143-148.[6] Lin TM, Chang HW, Wang KH, et al. Isolation and identification of mesenchymal stem cells from human lipoma tissue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;361(4):883- 889.[7] Gibbs CP, Kukekov VG, Reith JD, et al. Stem-like cells in bone sarcomas: implications for tumorigenesis. Neoplasia. 2005; 7(11):967-976.[8] Sun X, Cai H, Qian H, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells isolated from human uterine cervix cancer tissues. Cell Biol Int. 2011; 35(2):119-123.[9] Cao H, Xu W, Qian H, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-like cells derived from human gastric cancer tissues. Cancer Lett. 2009; 274(1):61-71.[10] 赫捷,赵平,陈万青.中国肿瘤登记年报[M].北京:军事医学科学出版社,2012.[11] Curtis MA, Kam M, Nannmark U, et al. Human neuroblasts migrate to the olfactory bulb via a lateral ventricular extension. Science. 2007;315(5816):1243-1249.[12] Wang SP, Wang ZH, Peng DY, et al. Therapeutic effect of mesenchymal stem cells in rats with intracerebral hemorrhage: reduced apoptosis and enhanced neuroprotection. Mol Med Rep. 2012;6(4):848-854.[13] 朱伟.骨髓间质干细胞在肿瘤进展和肿瘤微环境中的作用及机制[D].镇江:江苏大学,2010.[14] 狄国虎.间充质干细胞(MSCs)用于肿瘤化疗辅助治疗及与肿瘤生长关系的实验研究[D].天津:天津大学,2012.[15] 王勇.人脐带间充质干细胞对人食管癌细胞的抑制作用研究[D]. 北京:北京协和医学院,2011.[16] 刘富磊.人脐带间充质干细胞裂解液在体外对食管癌EC9706细胞增殖与迁移的抑制作用[D]. 新乡:新乡医学院,2014.[17] Bissell MJ, Radisky D. Putting tumours in context. Nat Rev Cancer. 2001;1(1):46-54.[18] Kidd S, Spaeth E, Dembinski JL, et al. Direct evidence of mesenchymal stem cell tropism for tumor and wounding microenvironments using in vivo bioluminescent imaging. Stem Cells. 2009;27(10):2614-2623.[19] Nakamizo A, Marini F, Amano T, et al. Human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of gliomas. Cancer Res. 2005;65(8):3307-3318.[20] Hung SC, Deng WP, Yang WK, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell targeting of microscopic tumors and tumor stroma development monitored by noninvasive in vivo positron emission tomography imaging. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11(21): 7749-7756.[21] Karnoub AE, Dash AB, Vo AP, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells within tumour stroma promote breast cancer metastasis. Nature. 2007;449(7162):557-563.[22] Bagley RG, Weber W, Rouleau C, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow express tumor endothelial and stromal markers. Int J Oncol. 2009;34(3):619-627.[23] Lieubeau B, Heymann MF, Henry F, et al. Immunomodulatory effects of tumor-associated fibroblasts in colorectal-tumor development. Int J Cancer. 1999;81(4):629-636.[24] Jeon ES, Moon HJ, Lee MJ, et al. Cancer-derived lysophosphatidic acid stimulates differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells to myofibroblast-like cells. Stem Cells. 2008;26(3):789-797.[25] Kinnaird T, Stabile E, Burnett MS, et al. Marrow-derived stromal cells express genes encoding a broad spectrum of arteriogenic cytokines and promote in vitro and in vivo arteriogenesis through paracrine mechanisms. Circ Res. 2004;94(5):678-685.[26] Birnbaum T, Roider J, Schankin CJ, et al. Malignant gliomas actively recruit bone marrow stromal cells by secreting angiogenic cytokines. J Neurooncol. 2007;83(3):241-247.[27] Au P, Tam J, Fukumura D, et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells facilitate engineering of long-lasting functional vasculature. Blood. 2008;111(9):4551-4558.[28] Loebinger MR, Eddaoudi A, Davies D, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell delivery of TRAIL can eliminate metastatic cancer. Cancer Res. 2009;69(10):4134-4142.[29] Wang N, Fallavollita L, Nguyen L, et al. Autologous bone marrow stromal cells genetically engineered to secrete an igf-I receptor decoy prevent the growth of liver metastases. Mol Ther. 2009;17(7):1241-1249.[30] Li X, Lu Y, Huang W, et al. In vitro effect of adenovirus-mediated human Gamma Interferon gene transfer into human mesenchymal stem cells for chronic myelogenous leukemia. Hematol Oncol. 2006;24(3):151-158.[31] Lu YR, Yuan Y, Wang XJ, et al. The growth inhibitory effect of mesenchymal stem cells on tumor cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Biol Ther. 2008;7(2):245-251.[32] Cho JA, Park H, Kim HK, et al. Hyperthermia-treated mesenchymal stem cells exert antitumor effects on human carcinoma cell line. Cancer. 2009;115(2):311-323.[33] Khakoo AY, Pati S, Anderson SA, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells exert potent antitumorigenic effects in a model of Kaposi's sarcoma. J Exp Med. 2006;203(5):1235-1247.[34] Djouad F, Plence P, Bony C, et al. Immunosuppressive effect of mesenchymal stem cells favors tumor growth in allogeneic animals.Blood. 2003;102(10):3837-3844.[35] Sato T, Sakai T, Noguchi Y, et al. Tumor-stromal cell contact promotes invasion of human uterine cervical carcinoma cells by augmenting the expression and activation of stromal matrix metalloproteinases. Gynecol Oncol. 2004;92(1):47-56.[36] Hall BM, Fortney JE, Taylor L, et al. Stromal cells expressing elevated VCAM-1 enhance survival of B lineage tumor cells. Cancer Lett. 2004;207(2):229-239. |
.jpg)
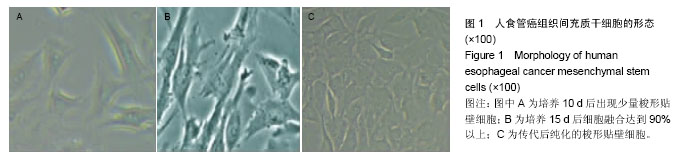
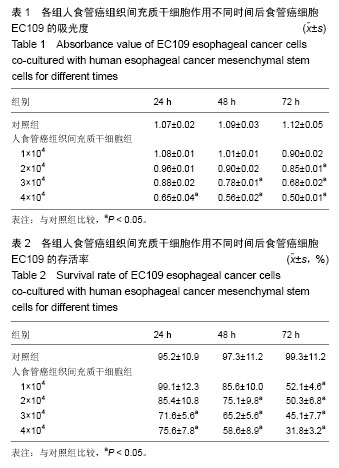
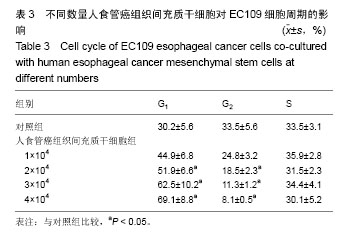
.jpg)