| [1] van Osch GJ, Brittberg M, Dennis JE,et al.Cartilage repair: past and future-lessons for regenerative medicine.J Cell Mol Med.2009;13(5):792-810.[2] Izadifar Z, Chen X, Kulyk W. Strategic Design and Fabrication of Engineered Scaffolds for Articular Cartilage Repair. J Funct Biomater.2012;3(4):799-838.[3] Duan L, Ma B, Liang Y, et al. Cytokine networking of chondrocyte dedifferentiation in vitro and its implications for cell-based cartilage therapy. Am J Transl Res.2015;7(2): 194-208.[4] Lindenmair A, Hatlapatka T, Kollwig G, et al. Mesenchymal Stem or Stromal Cells from Amnion and Umbilical Cord Tissue and Their Potential for Clinical Applications. Cells. 2012; 1(4):1061-1088. [5] Bieback K, Brinkmann I. Mesenchymal stromal cells from human perinatal tissues: From biology to cell therapy. World J Stem Cells.2010;2(4):81-92.[6] Barberini DJ, Freitas NP, Magnoni MS, et al. Equine mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow,adipose tissue and umbilical cord: immunophenotypic characterization and differentiation potential. Stem Cell Res Ther.2014;5(1):25. [7] Yang YH1, Lee AJ, Barabino GA. Coculture-Driven Mesenchymal Stem Cell- Differentiated Articular Chondrocyte-Like Cells Support Neocartilage Development. Stem Cells Transl Med.2012;1(11):843-854.[8] Levorson EJ, Santoro M, Kasper FK, et al. Direct and Indirect Co-culture of Chondrocytes and Mesenchymal Stem Cells for the Generation of Polymer/Extracellular Matrix Hybrid Constructs. Acta Biomater.2014;10(5):1824-1835.[9] Leyh M, Seitz A, Dürselen L, et al. Osteoarthritic cartilage explants affect extracellular matrix production and composition in cocultured bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and articular chondrocytes.Stem Cell Res Ther.2014;5(3):77. [10] Cooke ME, Allon AA, Cheng T, et al.Structured three-dimensional co-culture of mesenchymal stem cells with chondrocytes promotes chondrogenic differentiation without hypertrophy. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2011;19(10): 1210-1218.[11] Leyh M, Seitz A, Dürselen L, et al. Subchondral bone influences chondrogenic differentiation and collagen production of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and articular chondrocytes. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(5):453. [12] Rosenzweig DH, Matmati M, Khayat G, et al. Culture of Primary Bovine Chondrocytes on a Continuously Expanding Surface Inhibits Dedifferentiation.Tissue Eng Part A.2012; 18(23-24):2466-2476.[13] Wu L, Leijten J, van Blitterswijk CA, et al. Fibroblast Growth Factor-1 Is a Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Secreted Factor Stimulating Proliferation of Osteoarthritic Chondrocytes in Co-Culture. Stem Cells Dev.2013;22(17):2356-2367. [14] Qing C,Wei-ding C,Wei-min F. Co-culture of chondrocytes and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vitro enhances the expression of cartilaginous extracellular matrix components. Braz J Med Biol Res.2011;44(4):303-310.[15] Kang JS, Alliston T, Delston R, et al. Repression of Runx2 function by TGF-beta through recruitment of class II histone deacetylases by Smad3. EMBO J.2005;24(14):2543-2555.[16] 王泽民,黄江鸿,段莉,等.自体软骨细胞移植术治疗关节软骨损伤的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2015,23(4):328-331.[17] 王泽民,段莉,梁宇杰,等.自体软骨细胞复合Ⅰ型胶原支架体外动态培养的实验研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2015,23(18):1693- 1698. [18] Cao X, Xia H, Li N, et al. A mechanical refractory period of chondrocytes after dynamic hydrostatic pressure. Connect Tissue Res. 2015;56(3): 212-218.[19] Zhou Y, Liu SQ, Yu L, et al. Berberine prevents nitric oxide-induced rat chondrocyte apoptosis and cartilage degeneration in a rat osteoarthritis model via AMPK and p38 MAPK signaling. Apoptosis.2015;20(9):1187-1199.[20] Polur I, Kamiya Y, Xu M, et al. Oestrogen receptor beta mediates decreased occlusal loading induced inhibition of chondrocyte maturation in female mice. Arch Oral Biol.2015; 60(6):818-824.[21] Deng Z, Liu Y, Wang C, et al. Involvement of PI3K/Akt pathway in rat condylar chondrocytes regulated by PTHrP treatment. Arch Oral Biol.2014;59(10):1032-1041.[22] Sassi N, Laadhar L, Allouche M, et al. Wnt signaling is involved in human articular chondrocyte de-differentiation in vitro. Biotech Histochem.2014;89(1):29-40.[23] 卢华定,蔡道章,吴刚,等.Ⅰ型胶原半月板支架负载纤维软骨细胞体外培养[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2005,13(16):1252-1255.[24] 史德海,蔡道章,周长忍,等.壳聚糖与Ⅱ型胶原复合制作组织工程软骨支架及其性能研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2005,19(4): 278-282.[25] Barberini DJ, Freitas NP, Magnoni MS, et al.Equine mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow, adipose tissue and umbilical cord: immunophenotypic characterization and differentiation potential. Stem Cell Res Ther.2014; 5(1):25.[26] Li X, Duan L, Liang Y, et al.Human Umbilical Cord Blood-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Contribute to Chondrogenesis in Coculture with Chondrocytes. Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:3827057.[27] Maurer MH.Proteomic definitions of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Int. 2011;2011:704256.[28] Revencu T, Trifan V, Nacu L, et al.Collection,isolation and characterization of the stem cells of umbilical cord blood. J Morphol Embryol. 2013;54(2):291-297.[29] Miranda JP, Filipe E, Fernandes AS, et al.The Human Umbilical Cord Tissue-Derived MSC Population UCX Promotes Early Motogenic Effects on Keratinocytes and Fibroblasts and G-CSF-Mediated Mobilization of BM-MSCs When Transplanted In Vivo. Cell Transplantation. 2015;24(5): 865-877. [30] Sekiya I, Larson BL, Vuoristo JT, et al. Comparison of effect of BMP-2,-4, and -6 on in vitro cartilage formation of human adult stem cells from bone marrow stroma. Cell Tissue Res. 2005;320(2):269-276.[31] Hennig T, Lorenz H, Thiel A, et al. Reduced chondrogenic potential of adipose tissue derived stromal cells correlates with an altered TGFbeta receptor and BMP profi le and is over- come by BMP-6. J Cell Physiol.2007;211(3):682-691.[32] Xu D, Gechtman Z, Hughes A, et al. Potential involvement of BMP receptor type IB activation in a synergistic effect of chondrogenic promotion between rhTGFbeta3 and rhGDF5 or rhBMP7 in human mesenchymal stem cells. Growth Factors. 2006;24(4):268-278.[33] Fischer J, Dickhut A, Rickert M, et al. Human articular chondrocytes secrete parathyroid hormone–related protein and inhibit hypertrophy of mesenchymal stem cells in coculture during chondrogenesis. Arthritis and Rheumatology. 2010;62(9):2696-2706.[34] 罗二梅,张家文,胡笑轲,等.共培养人脐带间充质干细胞(hUC-MSCs)和兔关节软骨细胞诱导hUC-MSCs分化成软骨细胞[J].基础医学与临床,2014,34(1):82-87.[35] Zuo Q,Cui W,Liu F,et al.Co-cultivated mesenchymal stem cells support chondrocytic differentiation of articular chondrocytes. Int Orthop.2013;37(4):747-752. |
.jpg)
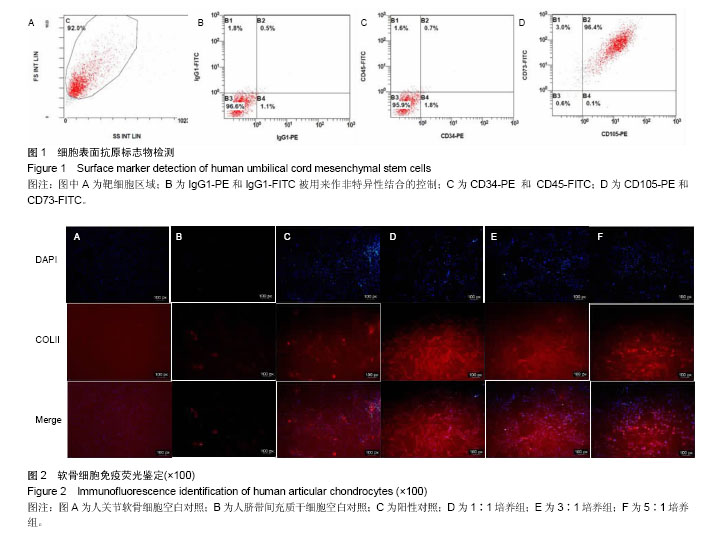
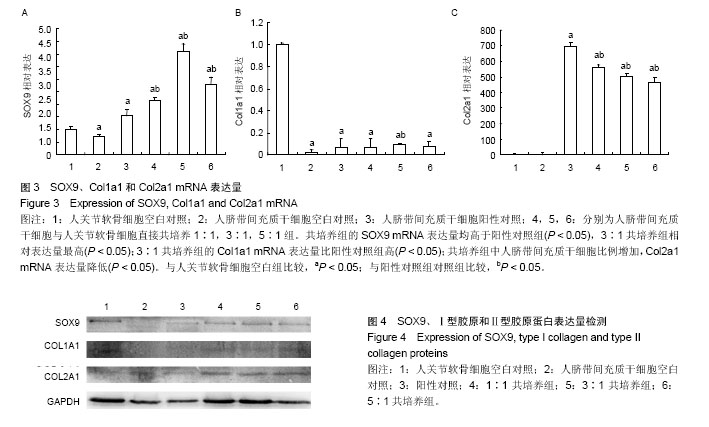
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)