中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (52): 7803-7808.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.52.007
• 纳米生物材料 nanobiomaterials • 上一篇 下一篇
玻璃酸钠壳聚糖纳米粒对烧伤角膜新生血管生长的影响
鲁 静1,武士科2,陈 光1,赵 越1,李 丹1
- 河北大学附属医院,1眼科;2骨科,河北省保定市 071000
Effect of sodium hyaluronate/chitosan nanoparticles on the neovascularization in burned cornea
Lu Jing1, Wu Shi-ke2, Chen Guang1, Zhao Yue1, Li Dan1
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, 2Department of Orthopaedics, Affiliated Hospital of Hebei University, Baoding 071000, Hebei Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
玻璃酸钠:又名透明质酸钠,是由N-乙酰葡萄糖醛酸反复交替而形成的一种高分子多糖体生物材料。玻璃酸钠为关节滑液的主要成分,是软骨基质的成分之一,在关节腔内起润滑作用,可覆盖和保护关节软骨,改善关节挛缩,抑制软骨变性变化表面,改善病理性关节液,增加滴滑功能。
玻璃酸钠壳聚糖纳米粒:将玻璃酸钠制作成由壳聚糖纳米粒包裹而成的药物,对体内外环境都有较强抵抗能力,纳米粒外层的聚电解质系统,能够延长蛋白质药物在外环境的保存期限,能够明显地提高治疗效果,并能降低药物带来的一定不良反应。
背景:将玻璃酸钠制作成由壳聚糖纳米粒包裹而成的药物,可以使药物更好地作用于烧伤角膜。
目的:验证玻璃酸钠壳聚糖纳米粒对烧伤角膜新生血管生长的影响。
方法:将30只SD大鼠随机分为3组,模型组、实验组制备碱烧伤角膜模型,正常对照组不造模,实验组在造模后2周后滴注玻璃酸钠壳聚糖纳米粒悬液治疗,1次/d,10 μL/次,正常对照组与模型组给予等量生理盐水,持续4周。4周后,裂隙灯观察眼角膜新生血管动态生长情况;ELISA法测定白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α含量;苏木精-伊红染色观察角膜病理学变化;聚合酶链式反应实时荧光定量PCR检测检测血管内皮因子和环氧化酶2 mRNA表达量。
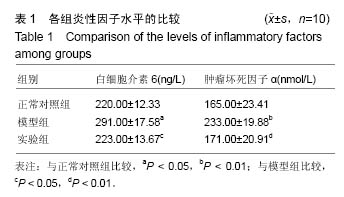
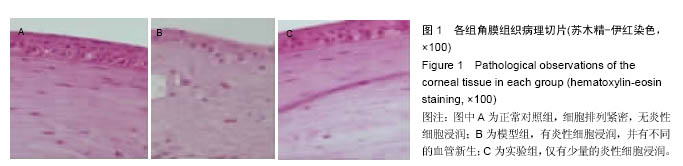
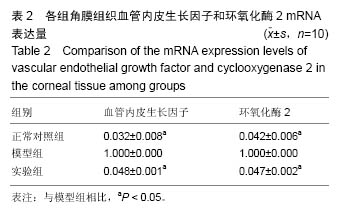
结果与结论:①与正常对照组比较,模型组角膜新生血管面积、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α、血管内皮生长因子、环氧化酶2水平显著升高(P < 0.05,P < 0.01);与模型组比较,实验组角膜新生血管面积、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α、血管内皮生长因子、环氧化酶2水平显著降低(P < 0.05);②模型组眼角组织有大量炎性细胞及新生血管产生,实验组仅有少量炎性细胞存在;③结果表明,玻璃酸钠壳聚糖纳米粒可抑制烧伤角膜新生血管的生长。
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)