| [1]Setzen G, Williams EF 3rd. Tissue response to suture materials implanted subcutaneously in a rabbit model. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1997;100(7):1788-1795.[2]Altman GH, Diaz F, Jakuba C, et al. Silk-based biomaterials. Biomaterials. 2003;24(3):401-416.[3]Wang Y, Kim HJ, Vunjak-Novakovic G, et al. Stem cell-based tissue engineering with silk biomaterials. Biomaterials. 2006;27(36):6064-6082.[4]Kundu B, Rajkhowa R, Kundu SC, et al. Silk fibroin biomaterials for tissue regenerations. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013;65(4):457-470.[5]Bray LJ, George KA, Ainscough SL,et al. Human corneal epithelial equivalents constructed on Bombyx mori silk fibroin membranes. Biomaterials. 2011;32(22): 5086-5091.[6]薛豪杰,胡丹丹.低溶胀壳聚糖/丝素蛋白复合膜的制备及性能测试[J].蚕业科学, 2011,37(6): 1073-1078.[7]Mottaghitalab F, Hosseinkhani H, Shokrgozar MA, et al. Silk as a potential candidate for bone tissue engineering. J Control Release. 2015;215:112-128.[8]Teimouri A,Azadi M,Emadi R,et al. Preparation, characterization, degradation and biocompatibility of different silk fibroin based composite scaffolds prepared by freeze-drying method for tissue engineering application. Polymer Degradation & Stability. 2015; 121:18-29.[9]Wenk E, Merkle HP, Meinel L. Silk fibroin as a vehicle for drug delivery applications. J Control Release. 2011; 150(2):128-141.[10]孙春光,张芃.纳米丝素颗粒药物缓释剂的研制及在治疗小鼠溃疡性结肠炎中的药物控制释放作用[J].蚕业科学, 2011,37(4):706-712.[11]Wang X, Wenk E, Zhang X, et al. Growth factor gradients via microsphere delivery in biopolymer scaffolds for osteochondral tissue engineering. J Control Release. 2009;134(2):81-90.[12]Hyun CK, Kim IY, Frost SC. Soluble fibroin enhances insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Nutr. 2004;134(12):3257-3263.[13]Park JH, Nam Y, Park SY, et al. Silk fibroin has a protective effect against high glucose induced apoptosis in HIT-T15 cells. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2011;25(4):238-243.[14]黄国平,陈克平.家蚕丝素水解物治疗糖尿病的研究进展[J].安徽农业科学,2010, 38(25): 13577-13579.[15]Byun EB, Sung NY, Kwon SK, et al. In vitro and in vivo studies on the cytotoxicity of irradiated silk fibroin against mouse melanoma tumor cell. Radiation Physics & Chemistry.2009; 78(7-8):429-431.[16]Cheema SK, Gobin AS, Rhea R, et al. Silk fibroin mediated delivery of liposomal emodin to breast cancer cells. Int J Pharm. 2007;341(1-2):221-229.[17]Gupta V, Mun GH, Choi B, et al. Repair and reconstruction of a resected tumor defect using a composite of tissue flap-nanotherapeutic-silk fibroin and chitosan scaffold. Ann Biomed Eng. 2011;39(9): 2374-2387.[18]Inouye K, Kurokawa M, Nishikawa S, et al. Use of Bombyx mori silk fibroin as a substratum for cultivation of animal cells. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1998; 37(3):159-164.[19]Altman GH, Horan RL, Lu HH, et al. Silk matrix for tissue engineered anterior cruciate ligaments. Biomaterials. 2002;23(20):4131-4141.[20]吴海涛,钟翠平,顾云娣. 蚕丝在软骨细胞立体培养中的应用[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2000,14(5): 301-304.[21]Gu Y, Chen L, Yang HL, et al. Evaluation of an injectable silk fibroin enhanced calcium phosphate cement loaded with human recombinant bone morphogenetic protein-2 in ovine lumbar interbody fusion. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2011;97(2):177-185.[22]Zhang W, Wang X, Wang S, et al. The use of injectable sonication-induced silk hydrogel for VEGF(165) and BMP-2 delivery for elevation of the maxillary sinus floor. Biomaterials. 2011;32(35):9415-9424.[23]Mirahmadi F, Tafazzoli-Shadpour M, Shokrgozar MA, et al. Enhanced mechanical properties of thermosensitive chitosan hydrogel by silk fibers for cartilage tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2013;33(8):4786-4794.[24]Song JY, Kim SG, Lee JW, et al. Accelerated healing with the use of a silk fibroin membrane for the guided bone regeneration technique. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2011;112(6):e26-33.[25]Yang L, Yaseen M, Zhao X, et al. Gelatin modified ultrathin silk fibroin films for enhanced proliferation of cells. Biomed Mater. 2015;10(2):025003.[26]Rodríguez-Lozano FJ, García-Bernal D, Aznar-Cervantes S, et al. Effects of composite films of silk fibroin and graphene oxide on the proliferation, cell viability and mesenchymal phenotype of periodontal ligament stem cells. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2014; 25(12):2731-2741.[27]Dhyani V, Singh N. Controlling the cell adhesion property of silk films by graft polymerization. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014;6(7):5005-5011.[28]Meechaisue C, Wutticharoenmongkol P, Waraput R, et al. Preparation of electrospun silk fibroin fiber mats as bone scaffolds: a preliminary study. Biomed Mater. 2007;2(3):181-188.[29]Li C, Vepari C, Jin HJ, et al. Electrospun silk-BMP-2 scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2006;27(16):3115-3124.[30]Zhang K, Mo X, Huang C, et al. Electrospun scaffolds from silk fibroin and their cellular compatibility. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;93(3):976-983.[31]Sofia S, McCarthy MB, Gronowicz G, et al. Functionalized silk-based biomaterials for bone formation. J Biomed Mater Res. 2001;54(1):139-148.[32]蔡鹏,朱绍兴,苏一鸣,等.全骨髓贴壁法分离培养大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞及其诱导分化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(36):7073-7077.[33]Um IC, Kweon HY, Park YH, et al. Structural characteristics and properties of the regenerated silk fibroin prepared from formic acid. Int J Biol Macromol. 2001;29(2):91-97.[34]黄雷. 酶法水解丝素蛋白工艺的优化及丝素肽抗氧化活性功能的研究[D]. 沈阳:沈阳农业大学, 2006.[35]程蕾,辛伟彪,刘祉序,等.碱脱胶法优化提取蚕丝素蛋白及其构象光谱[J].广西师范大学学报:自然科学版, 2014, 32(2): 88-94.[36]Jeong L, Lee KY, Liu JW, et al. Time-resolved structural investigation of regenerated silk fibroin nanofibers treated with solvent vapor. Int J Biol Macromol. 2006;38(2):140-144.[37]Zhou J, Cao C, Ma X. A novel three-dimensional tubular scaffold prepared from silk fibroin by electrospinning. Int J Biol Macromol. 2009;45(5):504-510.[38]Chen C, Cao C, Ma X, et al. Preparation of non-woven mats from all-aqueous silk fibroin solution with electrospinning method. Polymer. 2006; 47(18): 6322-6327.[39]Zur Nieden NI, Kempka G, Ahr HJ. In vitro differentiation of embryonic stem cells into mineralized osteoblasts. Differentiation. 2003;71(1):18-27. |
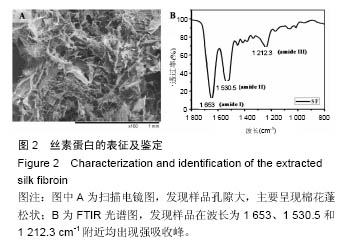
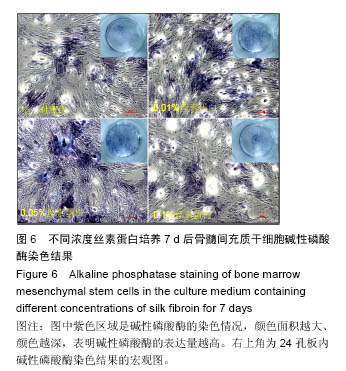
.jpg)
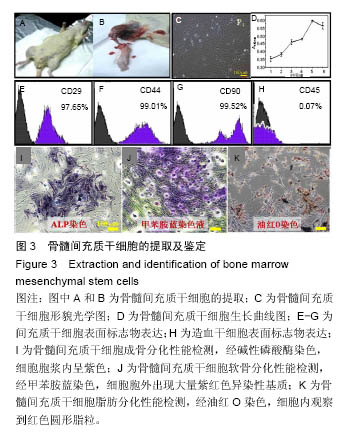
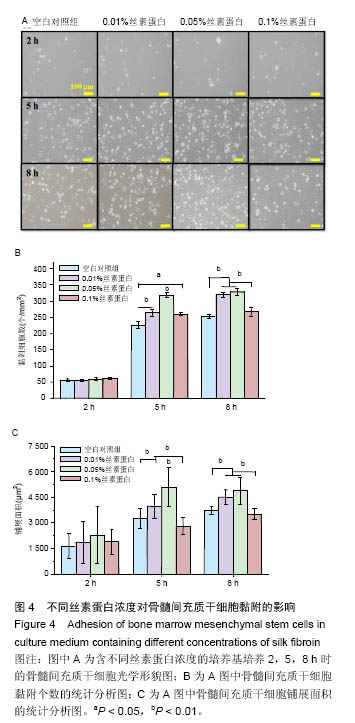
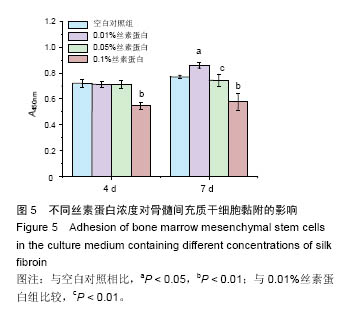
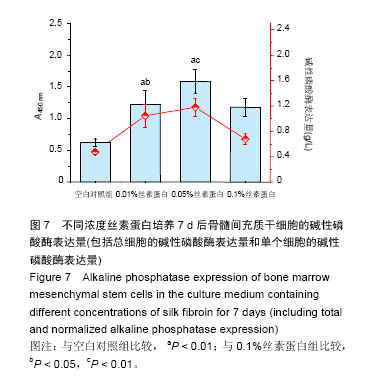
.jpg)
.jpg)