| [1] Gemmell E, Marshall RI, Seymour GJ. Cytokines and prostaglandins in immune homeostasis andtissue destruction in periodontal disease. Periodontol. 1997; 14:112-143. [2] Trowbridge HO, Emling RC. Inflammation. A review of the process. Implant Dent. 1997;6(3):238.[3] Soares GMS, Figueiredo LC, Faveri M, et al. Mechanisms of action of systemic antibiotics used in periodontal treatment and mechanisms of bacterial resistance to these drugs. J Appl Oral Sci. 2012; 20(3):295-309. [4] Chen FM, Sun HH, Lu H, et al. Stem cell-delivery therapeutics for periodontal tissue regeneration. Biomaterials. 2012;33(27):6320-6344.[5] Górska R, Gregorek H, Kowalski J, et al. Relationship between clinical parameters and cytokine profiles in inflamed gingival tissue and serum samples from patients with chronic periodontitis. J Clin Periodontol. 2003;30(12):1046-1052. [6] Havemose-Poulsen A, Sørensen LK, Stoltze K, et al. Cytokine profiles in peripheral blood and whole blood cell cultures associated with aggressive periodontitis, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, and rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Periodontol. 2005;76(12):2276-2285. [7] 孟焕新.牙周病学[M].3版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2000. [8] Graves DT, Cochran D. The contribution of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor to periodontal tissue destruction. J Periodontol. 2003;74(3):391-401. [9] Rimondi E, Zweyer M, Ricci E, et al. Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand (RANKL) modulates the expression of genes involved in apoptosis and cell cycle in human osteoclasts. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2007;290(7):838-845.[10] Schett G, Middleton S, Bolon B, et al. Additive bone-protective effects of anabolic treatment when used in conjunction with RANKL and tumor necrosis factor inhibition in two rat arthritis models. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52(5):1604-1611. [11] Yasuda H, Shima N, Nakagawa N, et al. Osteoclast differentiation factor is a ligand for osteoprotegerin/osteoclastogenesis-inhibitory factor and is identical to TRANCE/RANKL. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95(7):3597-3602.[12] 刘琪,Bartold M.慢性牙周炎中核因子κB受体活化子,护骨素和肿瘤坏死因子-α的蛋白表达[J].口腔医学,2004, 24(6):347-349.[13] Liang L, Yu J, Wang Y, et al. Estrogen regulates expression of osteoprotegerin and RANKL in human periodontal ligament cells through estrogen receptor beta. J Periodontol. 2008;79(9):1745-1751.[14] Nick JA, Young SK, Arndt PG, et al. Selective suppression of neutrophil accumulation in ongoing pulmonary inflammation by systemic inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Immunol. 2002; 169(9):5260-5269.[15] Kim EK, Choi EJ. Compromised MAPK signaling in human diseases: an update. Arch Toxicol. 2015;89(6): 867-882. [16] Arthur JSC, Ley SC. Mitogen-activated protein kinases in innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2013;13(9): 679-692.[17] Li Z, Jiang Y, Ulevitch R J, et al. The primary structure of p38γ: a new member of p38 group of MAP kinases. Biochemical and biophysical research communications. 1996;228(2):334-340.[18] Jiang Y, Gram H, Zhao M, et al. Characterization of the structure and function of the fourth member of p38 group mitogen-activated protein kinases, p38δ. J Biol Chem.1997;272(48):30122-30128.[19] Wang Z, Harkins PC, Ulevitch RJ, et al. The structure of mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 at 2.1-Å resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997;94(6): 2327-2332. [20] Han J, Lee J D, Bibbs L, et al. A MAP kinase targeted by endotoxin and hyperosmolarity in mammalian cells. Science. 1994;265(5173):808-811.[21] Park EJ, Park SW, Kim HJ, et al. Dehydrocostuslactone inhibits LPS-induced inflammation by p38MAPK-dependent induction of hemeoxygenase-1 in vitro and improves survival of mice in CLP-induced sepsis in vivo. Int immunopharmacol. 2014;22(2):332-340. [22] Schieven GL. The biology of p38 kinase: a central role in inflammation. Curr Top Med Chem. 2005;5(10): 921-928.[23] Hofbauer LC, Schoppet M. Clinical implications of the osteoprotegerin/RANKL/RANK system for bone and vascular diseases. JAMA. 2004;292:490-495.[24] Matsumoto M, Sudo T, Saito T, et al. Involvement of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway in osteoclastogenesis mediated by receptor activator of NF-kappa B ligand (RANKL). J Biol Chem. 2000;275(40):31155-31161.[25] Lee HJ, Kang IK, Chung CP, et al. The subgingival microflora and gingival crevicular fluid cytokines in refractory periodontitis. J Clin Periodontol. 1995; 22(11):885-890.[26] Graves DT, Delima AJ, Assuma R, et al. Interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor antagonists inhibit the progression of inflammatory cell infiltration toward alveolar bone in experimental periodontitis. J Periodontol. 1998;69(12):1419-1425. [27] Patil C, Zhu X, Rossa C Jr, et al. p38 MAPK regulates IL-1beta induced IL-6 expression through mRNA stability in osteoblasts. Immunol Invest. 2004;33(2): 213-233. [28] Holtmann H, Winzen R, Holland P, et al. Induction of interleukin-8 synthesis integrates effects on transcription and mRNA degradation from at least three different cytokine- or stress-activated signal transduction pathways. Mol Cell Biol. 1999;19(10): 6742-6753. [29] Heidenreich O, Neininger A, Schratt G, et al. MAPKAP kinase 2 phosphorylates serum response factor in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1999;274(20):14434-14443.[30] Patil C, Rossa C Jr, Kirkwood KL, et al. Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans lipopolysaccharide induces interleukin-6 expression through multiple mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in periodontal ligament fibroblasts. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 2006;21(6):392-398. [31] Rossa C, Liu M, Patil C, et al. MKK3/6-p38 MAPK negatively regulates murine MMP-13 gene expression induced by IL-1β and TNF-α in immortalized periodontal ligament fibroblasts. Matrix Biol. 2005; 24(7): 478-488. [32] 聂嘉,张博,顾斌,等.p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶在炎症微环境作用下对牙周膜干细胞成骨分化的影响[J].中国医学科学院学报,2015,37(2):1-7.[33] Lee HJ, Cho JW, Kim SC, et al. Roles of p38 and ERK MAP kinases in IL-8 expression in TNF-α-and dexamethasone-stimulated human periodontal ligament cells. Cytokine. 2006;35(1):67-76. [34] Wu Y, Yang Y, Yang P, et al. The osteogenic differentiation of PDLSCs is mediated through MEK/ERK and p38 MAPK signalling under hypoxia. Arch Oral Biol. 2013;58(10):1357-1368. [35] Li Q, Valerio MS, Kirkwood KL. MAPK usage in periodontal disease progression. J Signal Transduct. 2012;2012:308943.[36] Rogers JE, Li F, Coatney DD, et al. A p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitor arrests active alveolar bone loss in a rat periodontitis model. J Periodontol. 2007;78(10):1992-1998 |
.jpg) 文题释义:
牙周炎:主要是由局部因素引起的牙周支持组织的慢性炎症,发病年龄以35岁以后较为多见。如龈炎未能及时治疗,炎症可由牙龈向深层扩散到牙周膜、牙槽骨和牙骨质而发展为牙周炎。由于早期多无明显自觉症状而易被忽视,待有症状时已较严重,甚至已不能保留牙齿。因而必须加强宣教预防,使患者早期就诊和及时治疗。
p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶:是一种相对分子质量为38 000的酪氨酸磷酸化蛋白激酶,属于丝裂原活化蛋白激酶家族成员。当炎症反应出现时,血液中的白细胞从血管中游出并浸润到炎症局部,此过程需要经过贴壁、黏附、游出和趋化等作用阶段,这些阶段均与p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶的激活紧密相关。
文题释义:
牙周炎:主要是由局部因素引起的牙周支持组织的慢性炎症,发病年龄以35岁以后较为多见。如龈炎未能及时治疗,炎症可由牙龈向深层扩散到牙周膜、牙槽骨和牙骨质而发展为牙周炎。由于早期多无明显自觉症状而易被忽视,待有症状时已较严重,甚至已不能保留牙齿。因而必须加强宣教预防,使患者早期就诊和及时治疗。
p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶:是一种相对分子质量为38 000的酪氨酸磷酸化蛋白激酶,属于丝裂原活化蛋白激酶家族成员。当炎症反应出现时,血液中的白细胞从血管中游出并浸润到炎症局部,此过程需要经过贴壁、黏附、游出和趋化等作用阶段,这些阶段均与p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶的激活紧密相关。.jpg) 文题释义:
牙周炎:主要是由局部因素引起的牙周支持组织的慢性炎症,发病年龄以35岁以后较为多见。如龈炎未能及时治疗,炎症可由牙龈向深层扩散到牙周膜、牙槽骨和牙骨质而发展为牙周炎。由于早期多无明显自觉症状而易被忽视,待有症状时已较严重,甚至已不能保留牙齿。因而必须加强宣教预防,使患者早期就诊和及时治疗。
p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶:是一种相对分子质量为38 000的酪氨酸磷酸化蛋白激酶,属于丝裂原活化蛋白激酶家族成员。当炎症反应出现时,血液中的白细胞从血管中游出并浸润到炎症局部,此过程需要经过贴壁、黏附、游出和趋化等作用阶段,这些阶段均与p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶的激活紧密相关。
文题释义:
牙周炎:主要是由局部因素引起的牙周支持组织的慢性炎症,发病年龄以35岁以后较为多见。如龈炎未能及时治疗,炎症可由牙龈向深层扩散到牙周膜、牙槽骨和牙骨质而发展为牙周炎。由于早期多无明显自觉症状而易被忽视,待有症状时已较严重,甚至已不能保留牙齿。因而必须加强宣教预防,使患者早期就诊和及时治疗。
p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶:是一种相对分子质量为38 000的酪氨酸磷酸化蛋白激酶,属于丝裂原活化蛋白激酶家族成员。当炎症反应出现时,血液中的白细胞从血管中游出并浸润到炎症局部,此过程需要经过贴壁、黏附、游出和趋化等作用阶段,这些阶段均与p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶的激活紧密相关。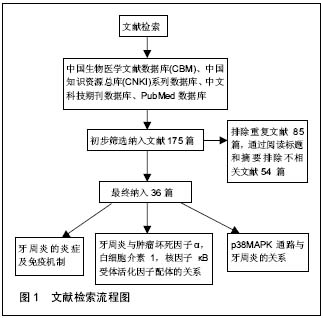
.jpg) 文题释义:
牙周炎:主要是由局部因素引起的牙周支持组织的慢性炎症,发病年龄以35岁以后较为多见。如龈炎未能及时治疗,炎症可由牙龈向深层扩散到牙周膜、牙槽骨和牙骨质而发展为牙周炎。由于早期多无明显自觉症状而易被忽视,待有症状时已较严重,甚至已不能保留牙齿。因而必须加强宣教预防,使患者早期就诊和及时治疗。
p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶:是一种相对分子质量为38 000的酪氨酸磷酸化蛋白激酶,属于丝裂原活化蛋白激酶家族成员。当炎症反应出现时,血液中的白细胞从血管中游出并浸润到炎症局部,此过程需要经过贴壁、黏附、游出和趋化等作用阶段,这些阶段均与p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶的激活紧密相关。
文题释义:
牙周炎:主要是由局部因素引起的牙周支持组织的慢性炎症,发病年龄以35岁以后较为多见。如龈炎未能及时治疗,炎症可由牙龈向深层扩散到牙周膜、牙槽骨和牙骨质而发展为牙周炎。由于早期多无明显自觉症状而易被忽视,待有症状时已较严重,甚至已不能保留牙齿。因而必须加强宣教预防,使患者早期就诊和及时治疗。
p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶:是一种相对分子质量为38 000的酪氨酸磷酸化蛋白激酶,属于丝裂原活化蛋白激酶家族成员。当炎症反应出现时,血液中的白细胞从血管中游出并浸润到炎症局部,此过程需要经过贴壁、黏附、游出和趋化等作用阶段,这些阶段均与p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶的激活紧密相关。