| [1] Matas AJ, Smith JM, Skeans MA, et al. OPTN/SRTR 2011 annual data report: kidney. Am J Transplant. 2013;13:11-46.
[2] Nankivell BJ, Kuypers DR.Diagnosis and prevention of chronic kidney allograft loss. Lancet.2011;378:1428-1437.
[3] Jardine AG, Gaston RS, Fellstrom BC, et al. Prevention of cardiovascular disease in adult recipients of kidney transplants. Lancet.2011;378:1419-1427.
[4] Farrugia D, Mahboob S, Cheshire J, et al. Malignancy- related mortality following kidney transplantation is common. Kidney Int.2014;85:1395-1403.
[5] Saint-Marcoux F, Woillard JB, Monchaud C, et al. How to handle missed or delayed doses of tacrolimus in renal transplant recipients? A pharmacokinetic investigation. Pharmacol Res.2015;100:281-287.
[6] Saitman A, Metushi IG, Mason DS,et al. Evaluation of the Waters MassTrak LC-MS/MS Assay for Tacrolimus and a Comparison to the Abbott Architect Immunoassay. Ther Drug Monit. Ther Drug Monit. 2016;38(3):300-304.
[7] Ansermot N, Fathi M, Veuthey JL, et al. Quantification of cyclosporine and tacrolimus in whole blood. Comparison of liquid chromatography-electrospray mass spectrometry with the enzyme multiplied immunoassay technique. Clin Biochem.2008;41(10-11): 910-913.
[8] Vanhove T, Annaert P, Kuypers DR,et al.Clinical determinants of calcineurin inhibitor disposition: a mechanistic review. Drug Metab Rev. 2016;48(1):88-112.
[9] Bekersky I, Dressler D, Mekki QA. Effect of low- and high-fat meals on tacrolimus absorption following 5 mg single oral doses to healthy human subjects.J Clin Pharmacol 2001;41:176-182.
[10] Bekersky I, Dressler D, Mekki Q. Effect of time ofmeal consumption on bioavailability of a single oral 5 mg tacrolimus dose. J Clin Pharmacol. 2001;41:289–297.
[11] Hanley MJ, Cancalon P, Widmer WW, et al. Program in Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Tufts University School of Medicine,Boston, Massachusetts 02111, United States of America. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol, 2011; 7(3): 267-286.
[12] Uno T, Yasui-Furukori N. Effect of grapefruit juice in relation to human pharmacokinetic study. Curr Clin Pharmacol.2006;1:157-161.
[13] Egashira K,SasakiH, HiguchiH,Ieiri I. Food–drug interaction of tacrolimuswith pomelo, ginger, and turmeric juice in rats. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2012;27:242-247.
[14] Zhang W,Lim LY.Effects of spice constituents on P-glycoprotein-mediated transport and CYP3A4-mediated metabolism in vitro. Drug Metab Dispos. 2008;36:1283-1290.
[15] Maes BD, Lemahieu W, Kuypers D, et al. Differential effect of diarrhea on FK506 versus cyclosporine A trough levels and resultant prevention of allograft rejection in renal transplant recipients. Am J Transplant. 2002;2:989-992.
[16] Kawauchi S, Nakamura T, Yasui H, et al. Intestinal and hepatic expression of cytochrome P450s and mdr1a in rats with indomethacin-induced small intestinal ulcers. Int J Med Sci.2014;11(12):1208-1217.
[17] Thorn M, Finnstrom N, Lundgren S,et al. Cytochromes P450 and MDR1 mRNA expression along the human gastrointestinal tract. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2005;60: 54-60.
[18] van Boekel GA, Aarnoutse RE, van der Heijden JJ,et al. Effect of mild diarrhea on tacrolimus exposure. Transplantation.2012;94:763–767.
[19] Pallet N, Etienne I, Buchler M, et al. Long-term clinical impact of adaptation of initial tacrolimus dosing to CYP3A5 genotype. Am J Transplant. 2016 Mar 17. doi: 10.1111/ajt.13788.
[20] vanMaarseveen EM, Rogers CC, Trofe-Clark J,et al. Drug-drug interactions between antiretroviral and immunosuppressive agents in HIV-infected patients after solid organ transplantation: a review. AIDS Patient Care STDS.2012;26: 568-581.
[21] vanMaarseveen EM, Crommelin HA, Mudrikova T,et al. Pretransplantation pharmacokinetic curves of tacrolimus in HIV-infected patients on ritonavir-containing cART: a pilot study. Transplantation 2013;95:397-402.
[22] Jackson A, D'Avolio A, Moyle G,et al. Pharmacokinetics of the co-administration of boceprevir and St John's wort to male and female healthy volunteers.J Antimicrob Chemother.2014;69(7):1911-1915.
[23] Mai I, Stormer E, Bauer S, et al. Impact of St John's wort treatment on the pharmacokinetics of tacrolimus and mycophenolic acid in renal transplant patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant.2003;18:819-822.
[24] Hesselink DA, Bouamar R, Elens L,et al. The role of pharmacogenetics in the disposition of and response to tacrolimus in solid organ transplantation. Clin Pharmacokinet.2014;53:123-139.
[25] van Gelder T, van Schaik RH, Hesselink DA. Pharmacogenetics and immunosuppressive drugs in solid organ transplantation.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2014; 10:725-731.
[26] Elens L, Bouamar R, Hesselink DA, et al. A new functional CYP3A4 intron 6 polymorphism significantly affects tacrolimus pharmacokinetics in kidney transplant recipients. Clin Chem.2011;57:1574-1583.
[27] Ro H, Min SI, Yang J, et al. Impact of tacrolimus intraindividual variability and CYP3A5 genetic polymorphism on acute rejection in kidney transplantation. Ther Drug Monit.2012;34:680-685.
[28] Borra LC, Roodnat JI, Kal JA,et al. Highwithin- patientvariability in the clearance of tacrolimus is a risk factor for poor long-term outcome after kidney transplantation. Nephrol DialTransplant. 2010;25: 2757-2763.
[29] van Gelder T, Gabardi S. Methods, strengths, weaknesses, and limitations of bioequivalence tests with special regard to immunosuppressive drugs. Transpl Int.2013;26:771-777.
[30] van Gelder T,ESOT Advisory Committee on Generic Substitution.European Society for Organ Transplantation Advisory Committee recommendations on generic substitution of immunosuppressive drugs. Transpl Int.2011;24:1135-1141.
[31] Kahan BD, Welsh M, Schoenberg L, et al. Variable oral absorption of cyclosporine. A biopharmaceutical risk factor for chronic renal allograft rejection. Transplantation.1996;62:599-606.
[32] Stoves J, Newstead CG. Variability of cyclosporine exposure and its relevance to chronic allograft nephropathy: a case–control study. Transplantation. 2002;74:1794-1797.
[33] van Gelder T. Within-patient variability in immunosuppressive drug exposure as a predictor for poor outcome after transplantation. Kidney Int. 2014; 85:1267-1268.
[34] Sapir-Pichhadze R, Wang Y, Famure O, et al. Time-dependent variability in tacrolimus trough blood levels is a risk factor for late kidney transplant failure. Kidney Int.2014;85:1404-1411.
[35] Pollock-Barziv SM, Finkelstein Y,Manlhiot C, et al. Variability in tacrolimus blood levels increases the risk of late rejection and graft loss after solid organ transplantation in older children. Pediatr Transplant 2010;14:968-975.
[36] Hsiau M, Fernandez HE, Gjertson D,et al.Monitoring nonadherence and acute rejection with variation in blood immunosuppressant levels in pediatric renal transplantation. Transplantation.2011;92:918–922.
[37] Prytula AA, Bouts AH, Mathot RA, et al. Intra-patient variability in tacrolimus trough concentrations and renal function decline in pediatric renal transplant recipients. Pediatr Transplant.2012;16:613-618.
[38] Stifft F, Stolk LM, Undre N, et al. Lower variability in 24-hour exposure during once-daily compared to twice-daily tacrolimus formulation in kidney transplantation.Transplantation.2014;97(7):775-780. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
变异性:由于试验条件与试验误差的影响,使各次测定值有所不同,测定值的此种性质,称为变异性。其功能:①发生变化的属性和能力;②生物体遗传性可以改变的一种特性。在生物个体发育过程中,当环境条件不符合其遗传性的需要时,这种生物体或者死亡,或者被迫同化这种新的条件,通过新陈代谢类型的改变,形成与其亲代不同的性状,即遗传性发生了变异。
他克莫司:在分子水平,他克莫司的作用显然是利用与细胞性蛋白质(FKBP12)相结合,而在细胞内蓄积产生效用。他克莫司用量主要是根据各病患个体对于排斥及耐受性的临床评估而调整。在患者手术后的恢复期,本药的药物动力学可能会改变,因此需要调整他克莫司用药的剂量。如果疾病发生变化(例如产生排斥现象),必须考虑更换免疫抑制疗法。
文题释义:
变异性:由于试验条件与试验误差的影响,使各次测定值有所不同,测定值的此种性质,称为变异性。其功能:①发生变化的属性和能力;②生物体遗传性可以改变的一种特性。在生物个体发育过程中,当环境条件不符合其遗传性的需要时,这种生物体或者死亡,或者被迫同化这种新的条件,通过新陈代谢类型的改变,形成与其亲代不同的性状,即遗传性发生了变异。
他克莫司:在分子水平,他克莫司的作用显然是利用与细胞性蛋白质(FKBP12)相结合,而在细胞内蓄积产生效用。他克莫司用量主要是根据各病患个体对于排斥及耐受性的临床评估而调整。在患者手术后的恢复期,本药的药物动力学可能会改变,因此需要调整他克莫司用药的剂量。如果疾病发生变化(例如产生排斥现象),必须考虑更换免疫抑制疗法。.jpg) 文题释义:
变异性:由于试验条件与试验误差的影响,使各次测定值有所不同,测定值的此种性质,称为变异性。其功能:①发生变化的属性和能力;②生物体遗传性可以改变的一种特性。在生物个体发育过程中,当环境条件不符合其遗传性的需要时,这种生物体或者死亡,或者被迫同化这种新的条件,通过新陈代谢类型的改变,形成与其亲代不同的性状,即遗传性发生了变异。
他克莫司:在分子水平,他克莫司的作用显然是利用与细胞性蛋白质(FKBP12)相结合,而在细胞内蓄积产生效用。他克莫司用量主要是根据各病患个体对于排斥及耐受性的临床评估而调整。在患者手术后的恢复期,本药的药物动力学可能会改变,因此需要调整他克莫司用药的剂量。如果疾病发生变化(例如产生排斥现象),必须考虑更换免疫抑制疗法。
文题释义:
变异性:由于试验条件与试验误差的影响,使各次测定值有所不同,测定值的此种性质,称为变异性。其功能:①发生变化的属性和能力;②生物体遗传性可以改变的一种特性。在生物个体发育过程中,当环境条件不符合其遗传性的需要时,这种生物体或者死亡,或者被迫同化这种新的条件,通过新陈代谢类型的改变,形成与其亲代不同的性状,即遗传性发生了变异。
他克莫司:在分子水平,他克莫司的作用显然是利用与细胞性蛋白质(FKBP12)相结合,而在细胞内蓄积产生效用。他克莫司用量主要是根据各病患个体对于排斥及耐受性的临床评估而调整。在患者手术后的恢复期,本药的药物动力学可能会改变,因此需要调整他克莫司用药的剂量。如果疾病发生变化(例如产生排斥现象),必须考虑更换免疫抑制疗法。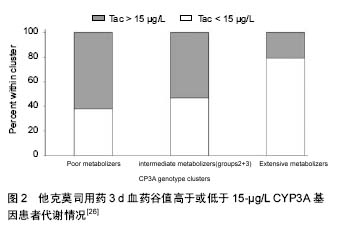
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
变异性:由于试验条件与试验误差的影响,使各次测定值有所不同,测定值的此种性质,称为变异性。其功能:①发生变化的属性和能力;②生物体遗传性可以改变的一种特性。在生物个体发育过程中,当环境条件不符合其遗传性的需要时,这种生物体或者死亡,或者被迫同化这种新的条件,通过新陈代谢类型的改变,形成与其亲代不同的性状,即遗传性发生了变异。
他克莫司:在分子水平,他克莫司的作用显然是利用与细胞性蛋白质(FKBP12)相结合,而在细胞内蓄积产生效用。他克莫司用量主要是根据各病患个体对于排斥及耐受性的临床评估而调整。在患者手术后的恢复期,本药的药物动力学可能会改变,因此需要调整他克莫司用药的剂量。如果疾病发生变化(例如产生排斥现象),必须考虑更换免疫抑制疗法。
文题释义:
变异性:由于试验条件与试验误差的影响,使各次测定值有所不同,测定值的此种性质,称为变异性。其功能:①发生变化的属性和能力;②生物体遗传性可以改变的一种特性。在生物个体发育过程中,当环境条件不符合其遗传性的需要时,这种生物体或者死亡,或者被迫同化这种新的条件,通过新陈代谢类型的改变,形成与其亲代不同的性状,即遗传性发生了变异。
他克莫司:在分子水平,他克莫司的作用显然是利用与细胞性蛋白质(FKBP12)相结合,而在细胞内蓄积产生效用。他克莫司用量主要是根据各病患个体对于排斥及耐受性的临床评估而调整。在患者手术后的恢复期,本药的药物动力学可能会改变,因此需要调整他克莫司用药的剂量。如果疾病发生变化(例如产生排斥现象),必须考虑更换免疫抑制疗法。