中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (48): 7163-7168.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.48.003
• 人工假体 artificial prosthesis • 上一篇 下一篇
保护股方肌及修复后方软组织对后外侧入路全髋关节置换早期脱位的影响
史思峰,卢文海,周 冰,陈向阳,赵凤朝,郭开今
- 徐州医科大学附属医院骨科,江苏省徐州市 221002
Protection of quadratus femoris and posterior soft tissue repair for the prevention of early dislocation in total hip arthroplasty through posterolateral approach
Shi Si-feng, Lu Wen-hai, Zhou Bing, Chen Xiang-yang, Zhao Feng-chao, Guo Kai-jin
- Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221002, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
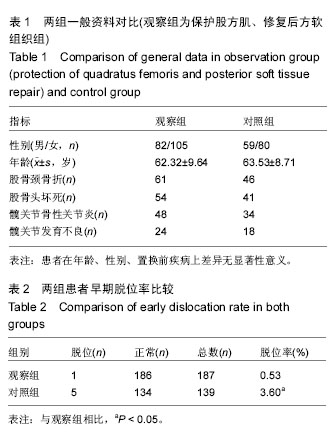
在后外侧入路进行初次全髋关节置换过程中保护股方肌、修复后方软组织:可能较部分切开股方肌、不进行后方软组织修复置换后的早期脱位率更低,保护股方肌在维持髋关节后方软组织平衡起到一定作用。
人工髋关节脱位:是由于假体位置不良、髋关节活动角度过大、局部软组织张力差等原因导致的人工股骨头从人工髋臼中脱出,从而引起患者疼痛、肢体畸形活动障碍等一系列临床表现。
摘要
背景:髋关节脱位是全髋关节置换后主要并发症之一。后外侧入路是髋关节置换的常用手术入路。后方软组织是否进行修复,现在学术界存在争议,而对于股方肌的保护,以往文献未给予充分的关注。
目的:探讨在应用后外侧入路进行全髋关节置换时,修复后方软组织、保护股方肌对置换后早期脱位的影响。
方法:回顾性分析2013年1月至2015年8月在徐州医科大学附属医院骨科进行的后外侧入路的初次全髋关节置换患者326例的资料。根据术中情况分为观察组和对照组,观察组187例为修复后方软组织、保护股方肌组,对照组139例为不修复后方软组织,部分切开股方肌组。将置换后3个月发生的脱位定义为早期脱位。比较两种方法对置换后早期脱位率的影响。
结果与结论:观察组早期脱位1例(1/187,脱位率0.5%),对照组早期脱位5例(5/139,脱位率3.6%)。对照组患者髋关节早期脱位率显著高于观察组(P < 0.05)。结果说明,在后外侧入路进行的初次全髋关节置换过程中,采用保护股方肌、修复后方软组织较不修复后方软组织、部分切开股方肌的方式早期脱位率更低。保护股方肌及修复后方软组织对维持髋关节软组织的平衡有一定意义。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-3236-9860(史思峰)
中图分类号:
.jpg)