| [1]刘晓阳,李广润,刘洪涛,等.硫酸钙人工骨/骨髓间充质干细胞构建组织工程化骨诱导脊柱融合[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(21):3281-3286.
[2]王居勇,沈惠良,折井久彌,等.种植骨髓干细胞的多孔人工骨在猴脊柱后外侧融合术中的应用[J].中国康复理论与实践,2010,16(5):432-435.
[3]徐卫袁.构建骨髓间充质干细胞/牛骨形态发生蛋白/丝素蛋白组织工程骨的试验研究[D].苏州:苏州大学, 2005.
[4]郑召民,邝冠明,陈辉,等.人骨形成蛋白4基因修饰的组织工程化骨促进脊柱融合的研究[J].中华外科杂志, 2009, 47(3):197-201.
[5]杨军.多孔微球包埋rhBMP-2及复合骨髓基质干细胞应用于鼠脊柱融合的试验研究[D].上海:第二军医大学,2009.
[6]林春阳.组织工程人工骨成骨活性因子(BMP9, OPG)相关研究[D].重庆:重庆医科大学,2011.
[7]王斌,吕浩然,王伟雄,等.异体皮质人工骨复合物治疗骨折不愈合及骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013,17(51): 8821-8826.
[8]Davis R, Auerbach JD, Bae H, et al. Can low-grade spondylolisthesis be effectively treated by either coflex interlaminar stabilization or laminectomy and posterior spinal fusion Two-year clinical and radiographic results from the randomized, prospective, multicenter US investigational device exemption trial: clinical article. J Neurosurg Spine. 2013;19(2):174-184.
[9]Wu P, Luo C, Pang X, et al. Surgical treatment of thoracic spinal tuberculosis with adjacent segments lesion via one-stage transpedicular debridement, posterior instrumentation and combined interbody and posterior fusion, a clinical study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013;133(10):1341-1350.
[10]朱海燕,邹浩,甘一波,等.生物工程骨在山羊脊柱横突间植骨融合的试验研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2014, 29(9): 916-918.
[11]丁金勇,靳安民,张梅霞,等.骨髓间充质干细胞分化为成骨细胞优化生物活性玻璃的试验研究[J].中国医师杂志, 2006,8(4):444-447.
[12]陈海峰,王健.富集骨髓干细胞复合人工骨在椎体后路融合中的临床应用[J].临床骨科杂志, 2009,12(3): 259-261.
[13]Park JH, Ahn Y, Choi BS, et al. Antithrombotic effects of aspirin on 1-or 2-level lumbar spinal fusion surgery: a comparison between 2 groups discontinuing aspirin use before and after 7 days prior to surgery. Spine. 2013;38(18):1561-1565.
[14]Oestergaard LG, Maribo T, Bünger CE, et al. The Canadian Occupational Performance Measure's semistructured interview: its applicability to lumbar spinal fusion patients. A prospective randomized clinical study. Eur Spine J. 2012;21(1):115-121.
[15]张才龙,夏长所,叶发刚,等.磷酸钙人工骨复合骨髓基质干细胞移植修复骨缺损的试验[J].中国临床康复, 2005, 9(46):140-142.
[16]潘玮敏,胡蕴玉,陈俊伟,等.两种接种密度骨髓基质干细胞复合β-TCP对兔腰椎横突间融合的效果[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2009,17(14):1087-1089.
[17]Rohl K, Rohrich F. Artificial disc versus spinal fusion in the treatment of cervical spine degenerations in tetraplegics: a comparison of clinical results. Spinal cord. 2009;47(9):705-708.
[18]Wigfield C, Gill S, Nelson R, et al. Influence of an artificial cervical joint compared with fusion on adjacent-level motion in the treatment of degenerative cervical disc disease.J Neurosurg. 2002;96(1 Suppl): 17-21.
[19]Wu SH, Li Y, Zhang YQ, et al. Porous titanium-6 aluminum-4 vanadium cage has better osseointegration and less micromotion than a poly-ether-ether-ketone cage in sheep vertebral fusion. Artif Organs. 2013;37(12):E191-E201.
[20]Koo KH, Lee JM, Ahn JM, et al. Controlled delivery of low-dose bone morphogenetic protein-2 using heparin-conjugated fibrin in the posterolateral lumbar fusion of rabbits. Artif Organs. 2013;37(5):487-494.
[21]马兴,胡蕴玉,熊卓,等.新型仿生活性人工骨诱导兔腰椎横突间脊柱融合研究[J].中华试验外科杂志, 2005,22(11): 1387-1389.
[22]Venkatesan J, Kim SK. Nano-hydroxyapatite composite biomaterials for bone tissue engineering--a review. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2014;10(10):3124-3140..
[23]Tsai CH, Hsu HC, Chen YJ, et al. Using the growth factors-enriched platelet glue in spinal fusion and its efficiency. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2009;22(4):246-250.
[24]Tanaka N, Nakanishi K, Fujimoto Y, et al. Expansive laminoplasty for cervical myelopathy with interconnected porous calcium hydroxyapatite ceramic spacers: comparison with autogenous bone spacers. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2008;21(8):547-552.
[25]Koo KH, Yeo DH, Ahn JM, et al. Lumbar posterolateral fusion using heparin-conjugated fibrin for sustained delivery of bone morphogenic protein-2 in a rabbit model. Artif Organs. 2012;36(7):629-634.
[26]胡文,黄旗凯,苏佳灿,等.骨形态发生蛋白2纳米人工骨在成人特发性脊柱畸形矫正融合中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(29):5497-5500.
[27]Chung J, Kim SM, Yi BJ, et al. Cadaver study for spinal fusion surgery using an image-guided surgical robot system. Int J Control Automation Systems. 2010;8(3): 564-573.
[28]Davis RJ, Errico TJ, Bae H, et al. Decompression and coflex interlaminar stabilization compared with decompression and instrumented spinal fusion for spinal stenosis and low-grade degenerative spondylolisthesis: two-year results from the prospective, randomized, multicenter, food and drug administration investigational device exemption trial. Spine. 2013;38(18):1529-1539.
[29]蔡志刚,芮钢.纤维蛋白胶复合自体骨髓与人工骨促进脊柱融合的现状与展望[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(16):2933-2936.
[30]Yamada T, Yoshii T, Sotome S, et al. Hybrid grafting using bone marrow aspirate combined with porous β-tricalcium phosphate and trephine bone for lumbar posterolateral spinal fusion: a prospective, comparative study versus local bone grafting. Spine. 2012;37(3):E174-E179.
[31]Iwai C, Taneichi H, Inami S, et al. Clinical outcomes of combined anterior and posterior spinal fusion for dystrophic thoracolumbar spinal deformities of neurofibromatosis-1: fate of nonvascularized anterior fibular strut grafts. Spine. 2013;38(1):44-50.
[32]Godil SS, Parker SL, O'Neill KR, et al. Comparative effectiveness and cost-benefit analysis of local application of vancomycin powder in posterior spinal fusion for spine trauma Presented at the 2013 Joint Spine Section Meeting Clinical article. J Neurosurg Spine. 2013;19(3):331-335.
[33]马兴,胡蕴玉,熊卓,等.仿生活性人工骨诱导兔椎板间多节段脊柱融合的研究[J].中华创伤杂志, 2005,21(7): 491-495.
[34]Winn SR,Hollinger JO.An osteogenic cell culture system to evaluate the cytocompatibility of Osteoset, a calcium sulfate bone void filler. Biomaterials. 2000;21 (23):2413-2425.
[35]Crandall DG, Revella J, Patterson J, et al. Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with rhBMP-2 in spinal deformity, spondylolisthesis, and degenerative disease-part 1: large series diagnosis related outcomes and complications with 2- to 9-year follow-up. Spine. 2013;38(13):1128-1136.
[36]Zou X, Zou L, Foldager C, et al. Different mechanisms of spinal fusion using equine bone protein extract, rhBMP-2 and autograft during the process of anterior lumbar interbody fusion. Biomaterials. 2009;30(6): 991-1004.
[37]Dodds RA, York Ely AM, Zhukauskas R, et al. Biomechanical and radiographic comparison of demineralized bone matrix, and a coralline hydroxyapatite in a rabbit spinal fusion model. J Biomater Appl. 2010;25(3):195-215.
[38]Elowitz EH,Yanni DS, Chwajol M, et al. Evaluation of indirect decompression of the lumbar spinal canal following minimally invasive lateral transpsoas interbody fusion: Radiographic and outcome analysis. Minim Invasive Neurosurg. 2011;54(5/6):201-206.
[39]李智钢,李明,侯铁胜,等.原位自体骨与磷酸钙人工骨混合植骨在脊柱侧凸畸形矫正融合术中的应用[J].临床骨科杂志,2006,9(1):20-21.
[40]马兴,胡蕴玉,吴小明,等.结构型PLGA/TCP/Col/ ADSCs-OB仿生活性人工骨的体外构建及其在兔腰椎横突间脊柱融合的试验研究[J].生物医学工程研究, 2008, 27(2):84-92. |
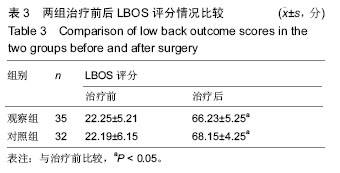
.jpg)
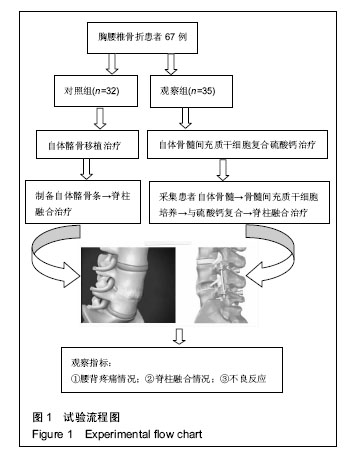

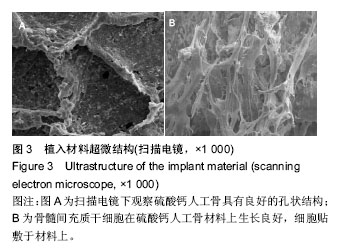
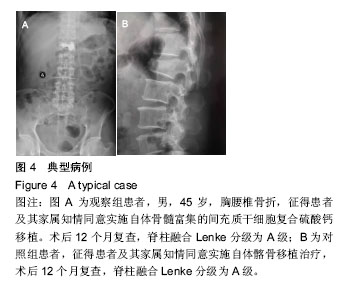
.jpg)